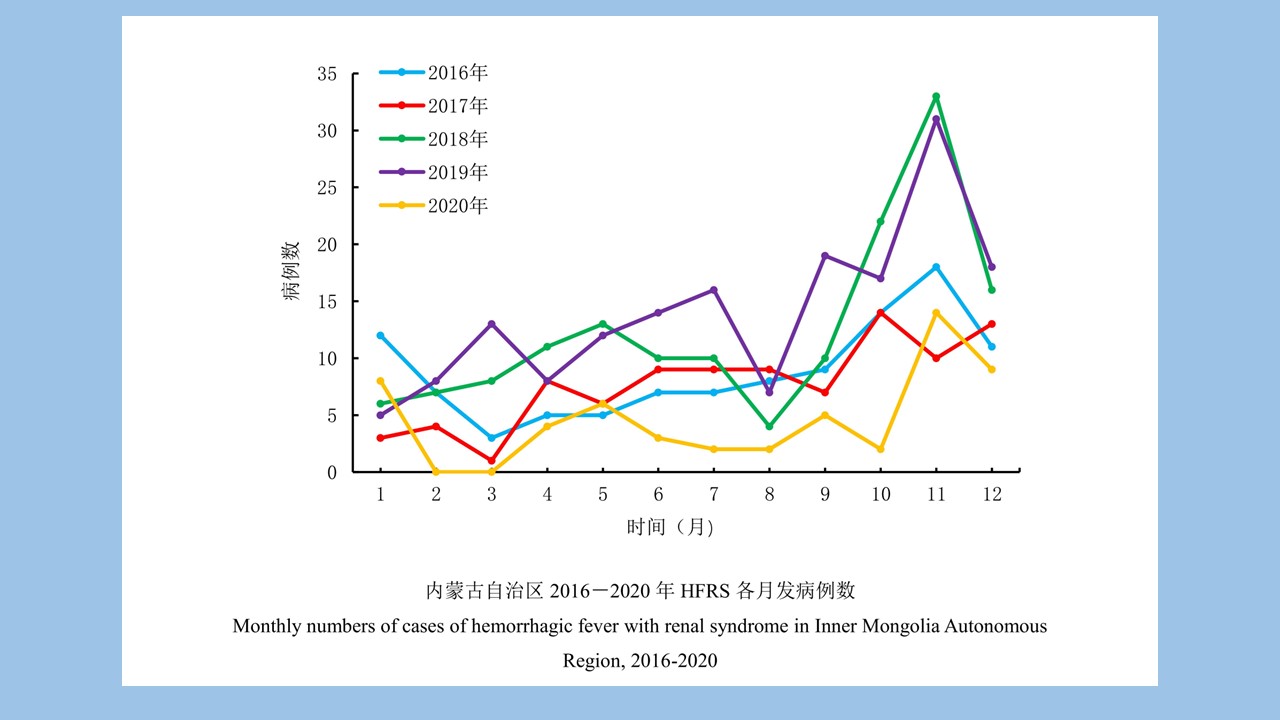
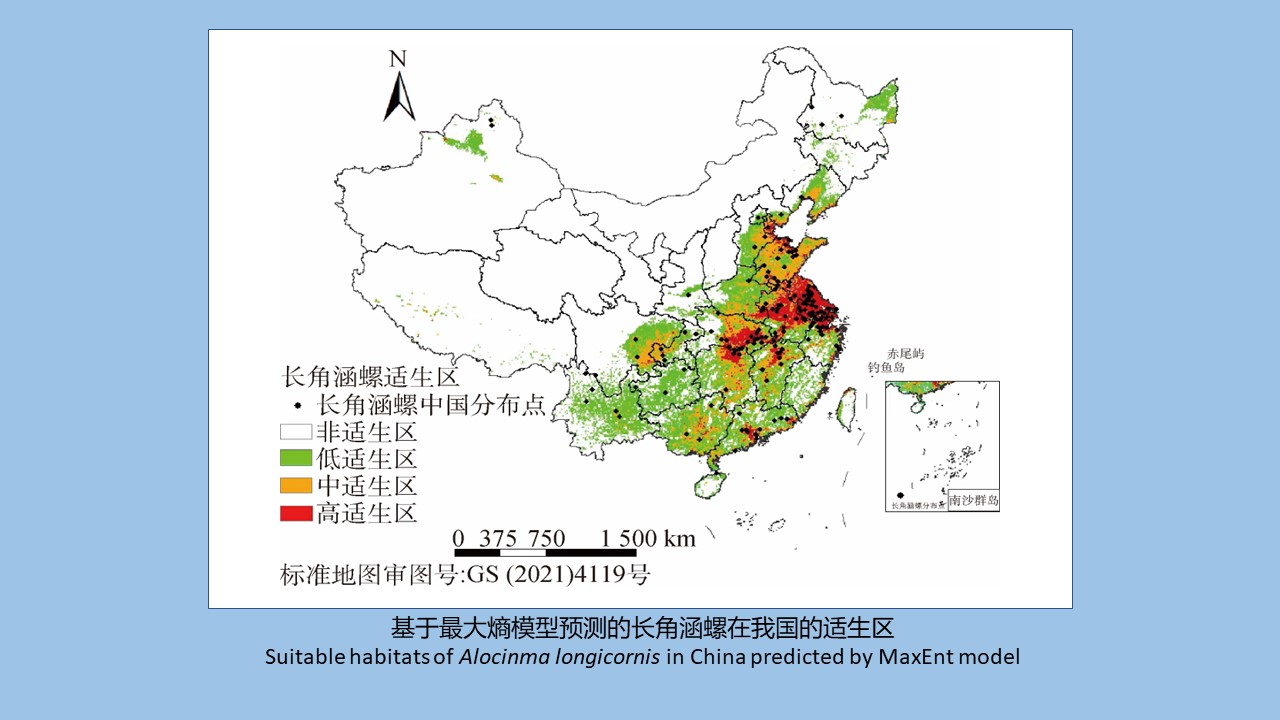
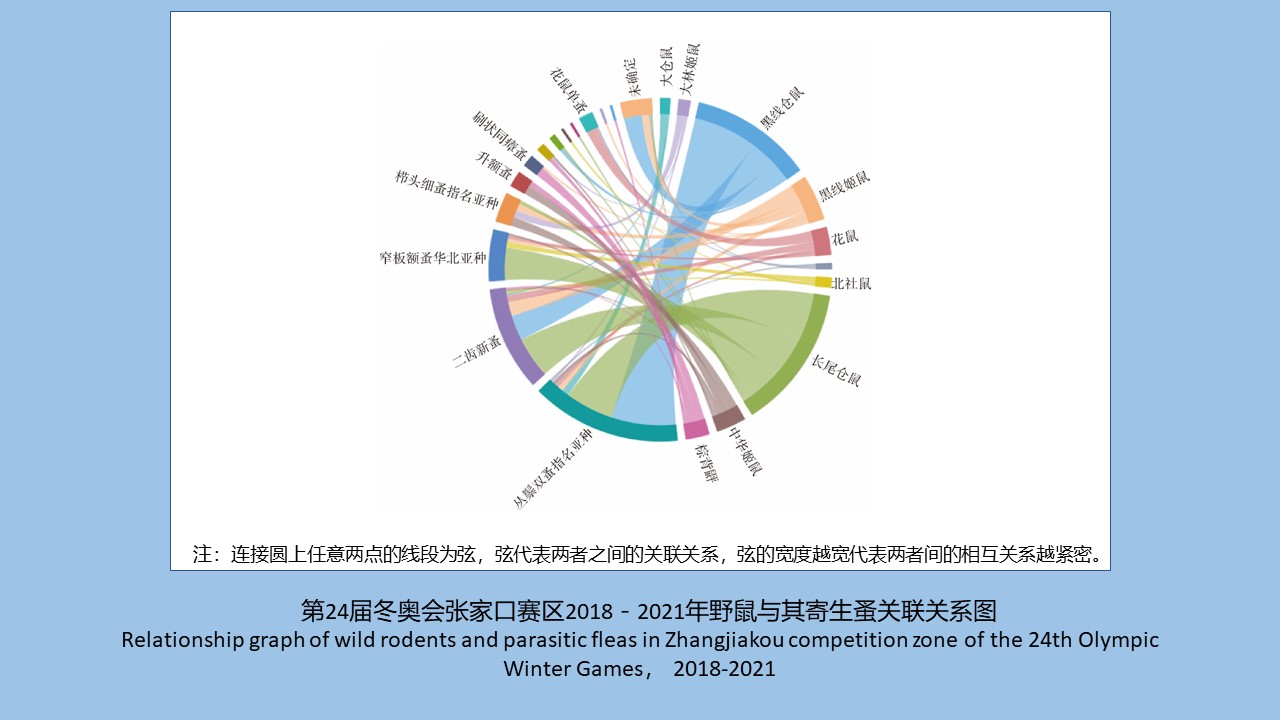
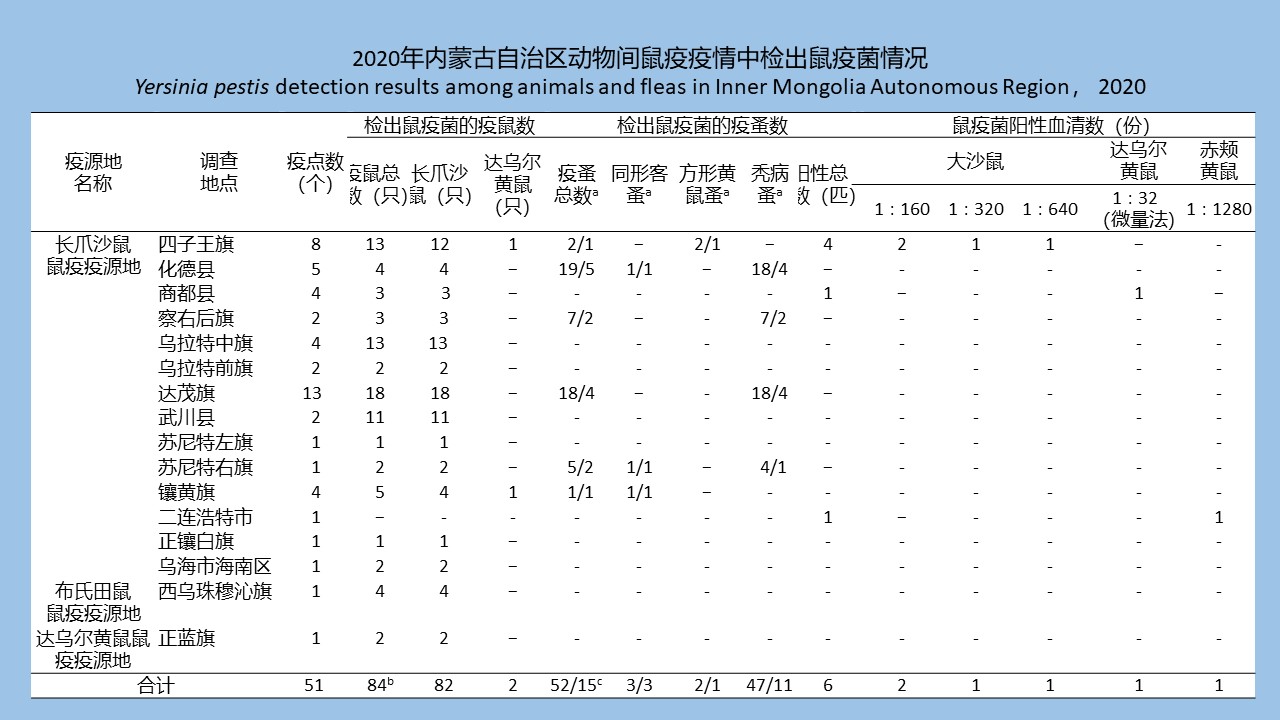
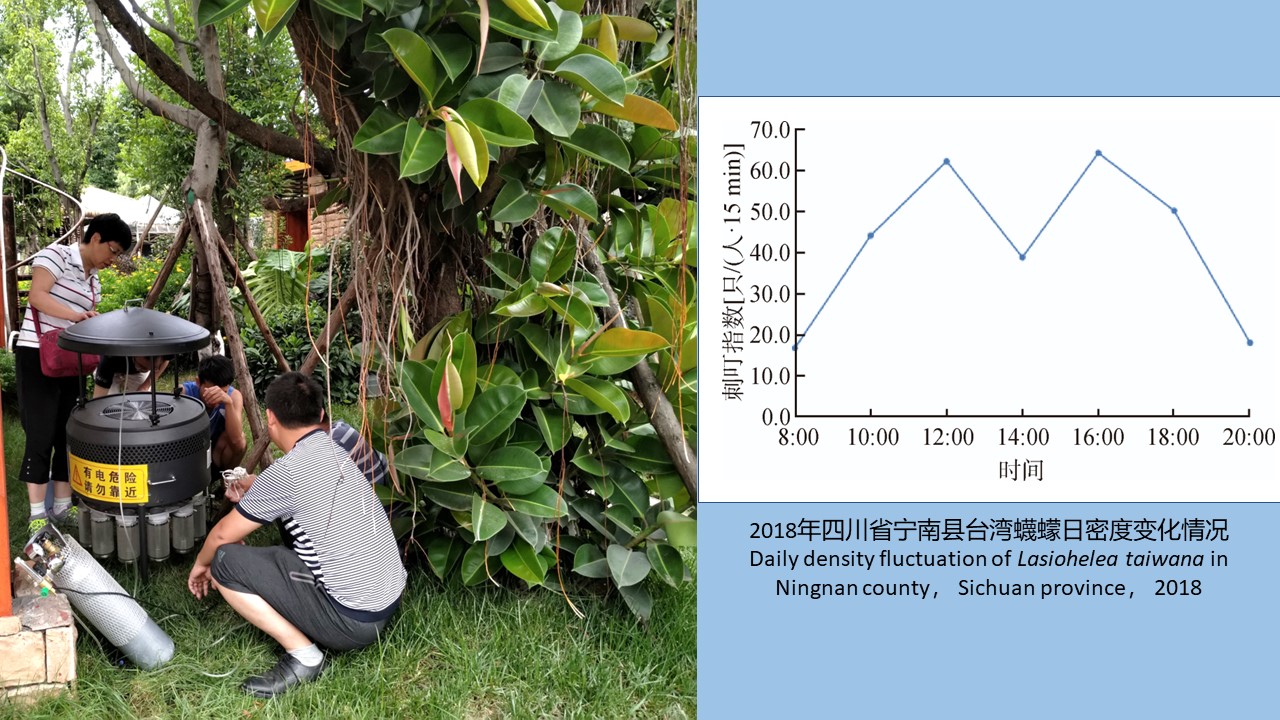
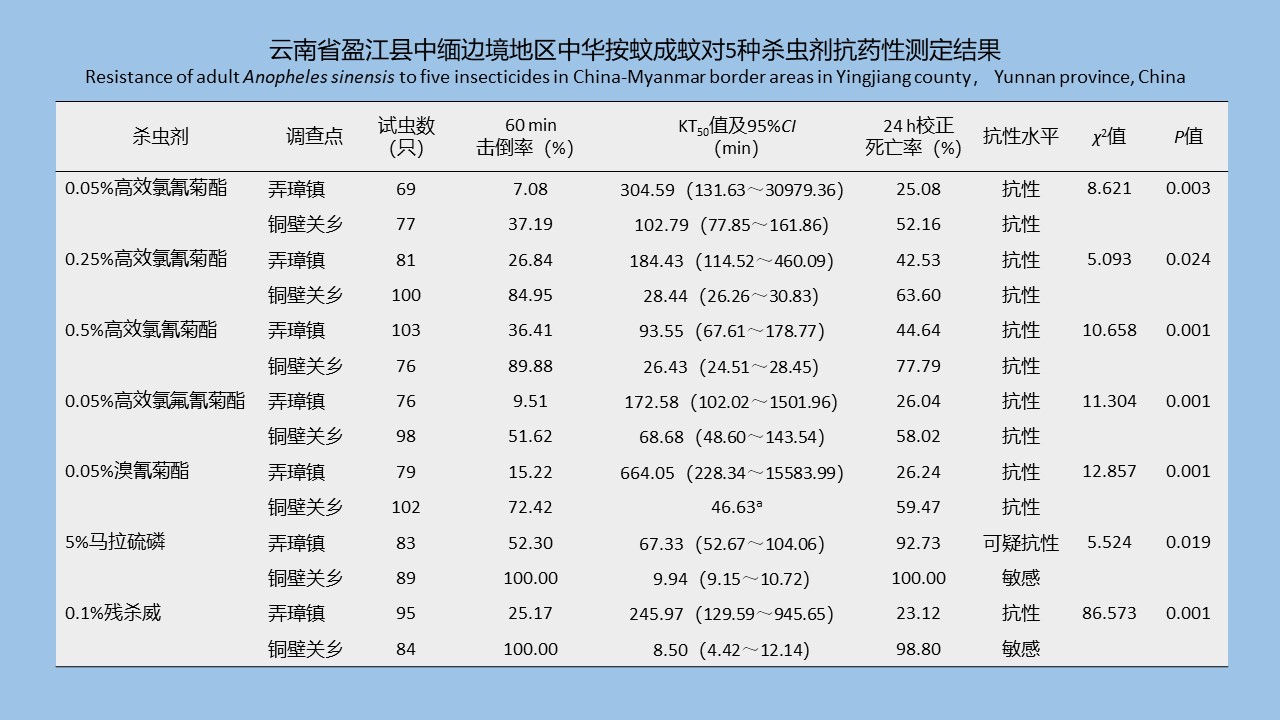
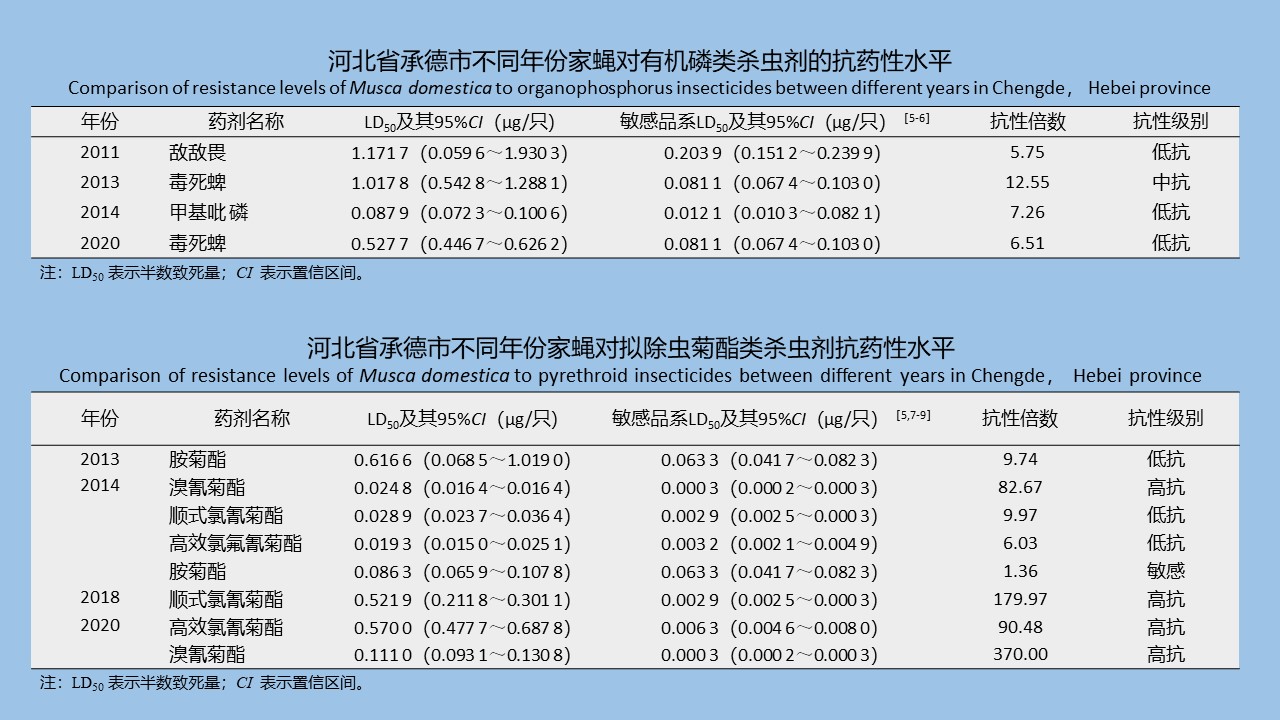
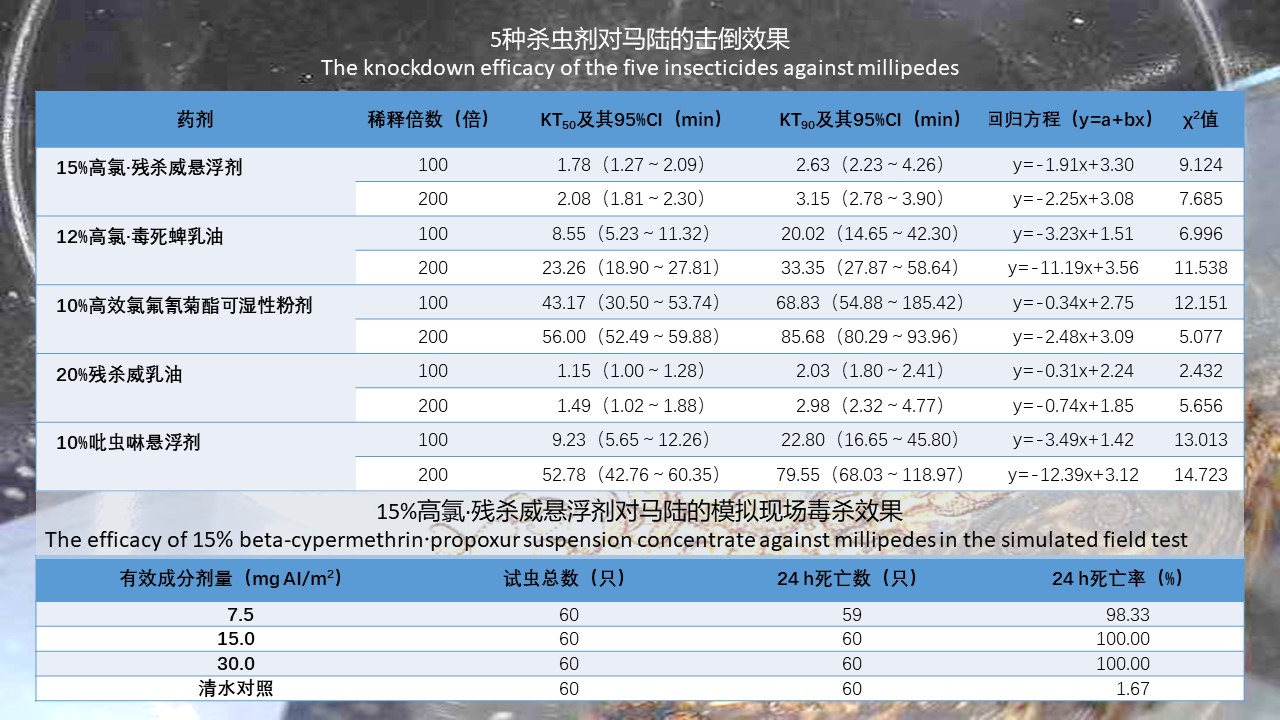
SHI Meng-ting, HE Shan, LI Wei-yi, XIAO Qiu-qiu, CHENG Jin-zhi, WU Jia-hong
Objective To investigate the effects of different diets on the density of Wolbachia in the ovary, fat body, and the other tissues in female Aedes aegypti of the WB strain. Methods After eclosion, Ae. aegypti mosquitoes of the WB strain were divided into glucose group (fed with glucose), white sugar group (fed with white sugar), and blood group (fed with blood for 2 hours on the 3rd day). Mosquitoes in each group were collected on days 4, 4.5, 5, and 6 to harvest the ovary, fat body, and the other tissues. DNA was extracted to determine the density of Wolbachia in all tissues using quantitative real-time PCR. SPSS 20.0 software was used for data analysis. The Kruskal-Wallis H test was used to compare the density of Wolbachia under different diets and at different days of age.Results On day 4.5, Wolbachia densities in the ovary in the glucose, white sugar, and blood groups were 2.149, 2.773, and 0.761, respectively, with a statistically lower density in the blood group (H=40.754, P<0.001); Wolbachia densities in the fat body in the three groups were 0.859, 1.189, 1.298, respectively, and the differences were not statistically significant (H=1.631, P=0.442). Wolbachia densities in the other tissues were 0.505, 0.405, 1.012, respectively, and the differences were not statistically significant (H=6.306, P=0.043). Under different diets but at the same days of age, Wolbachia densities in the ovary were lowest in the blood group on days 4, 5, and 6, and highest in the white sugar group on days 4 and 6 (H=14.335, P=0.001; H=22.049, P<0.001; H=4.266, P=0.084); for the fat body on days 4 and 6 and the other tissues on days 4, 5, and 6, Wolbachia densities were highest in the blood group, followed by the white sugar group, and lowest in the glucose group (H=7.186, P=0.028; H=10.504, P=0.005; H=16.338, P<0.001; H=14.083, P=0.001; H=4.266, P=0.118). At different days of age but under the same diets, Wolbachia densities in the ovary, fat body, and the other tissues in the glucose group had no statistical differences between different days of age (H=4.683, P=0.096; H=2.451, P=0.294; H=0.293, P=0.864); under the white sugar diet, Wolbachia densities in the ovary and fat body were no statistically increased with days of age (H=4.731, P=0.094; H=0.390, P=0.823); under the blood diet, Wolbachia densities in the ovary and fat body were first decreased and then increased with days of age (H=20.572, P<0.001; H=9.675, P=0.008). Conclusion Feeding blood reduces the density of Wolbachia in the reproductive tissue but increases its density in the non-reproductive tissues of Ae. aegypti mosquitoes of the WB strain. Under laboratory conditions, the mosquitoes can be fed with white sugar to increase the density of Wolbachia in the body.