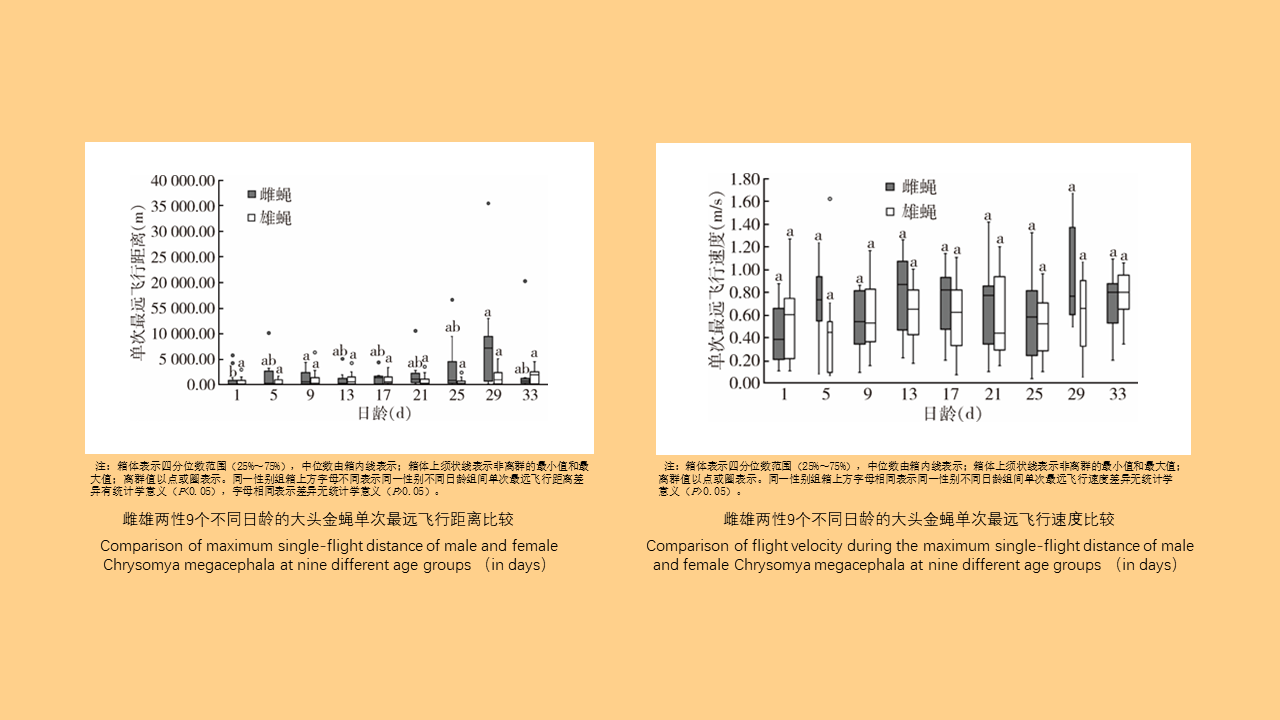
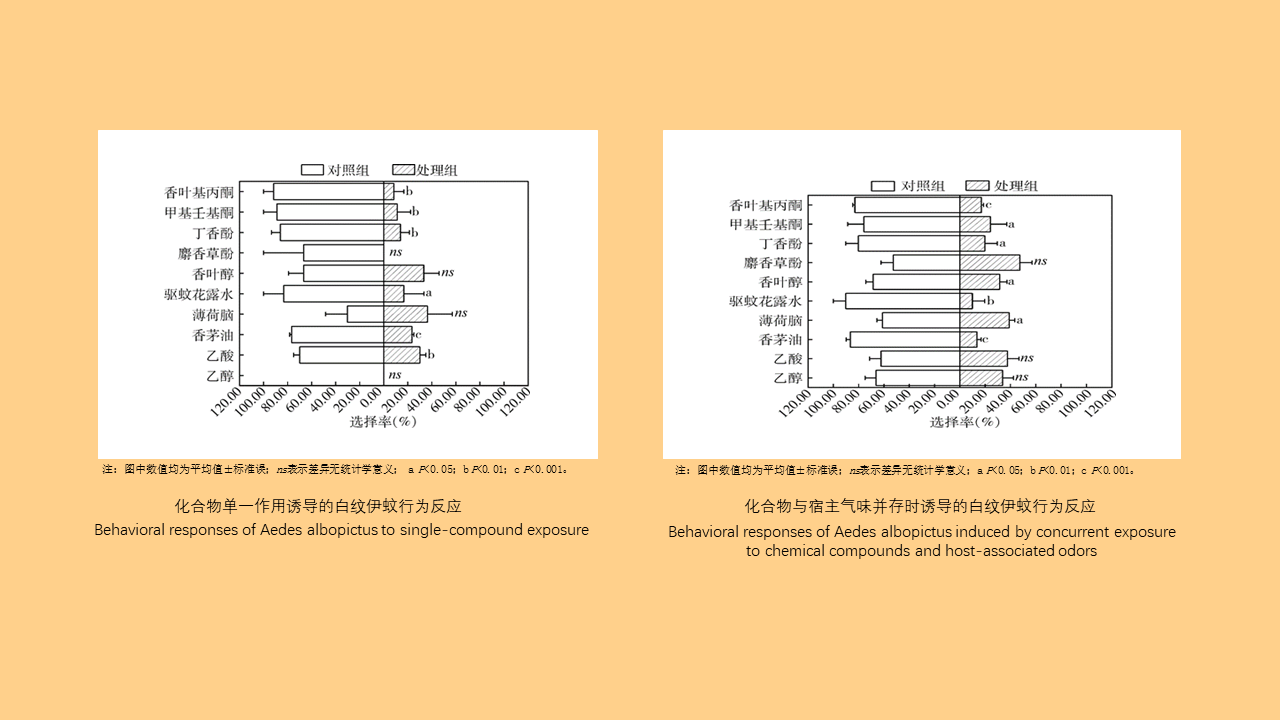
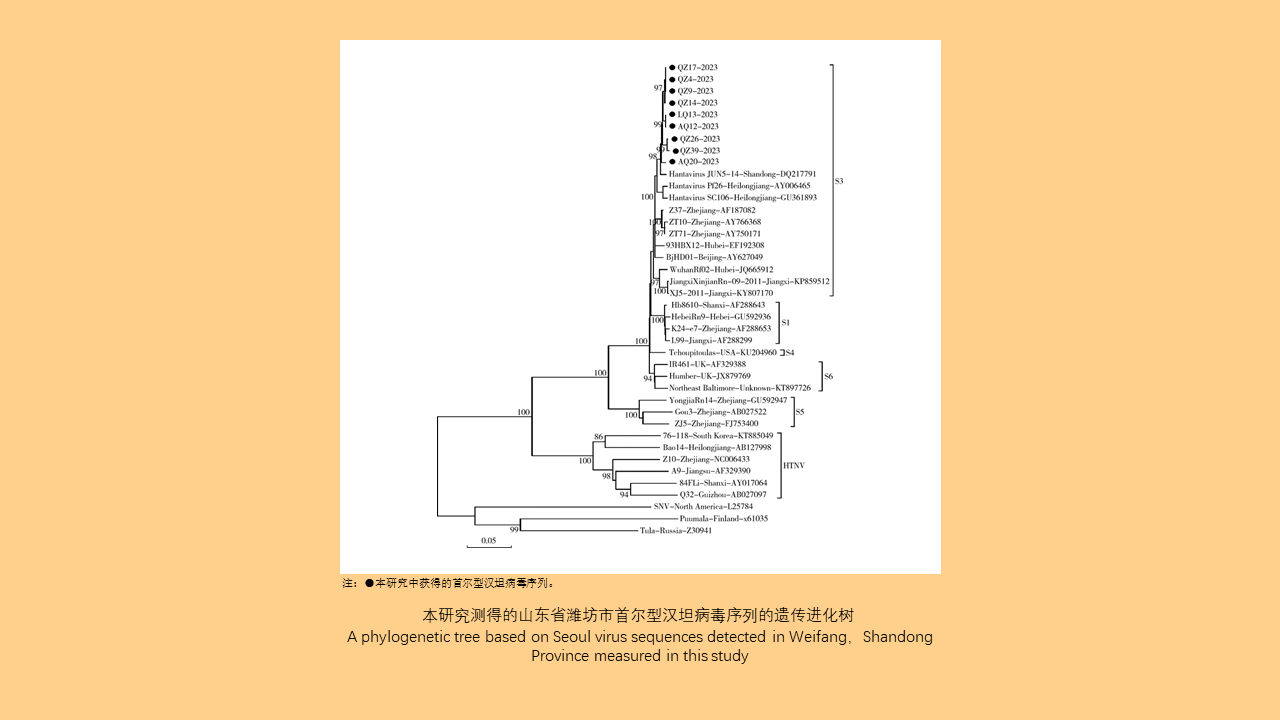
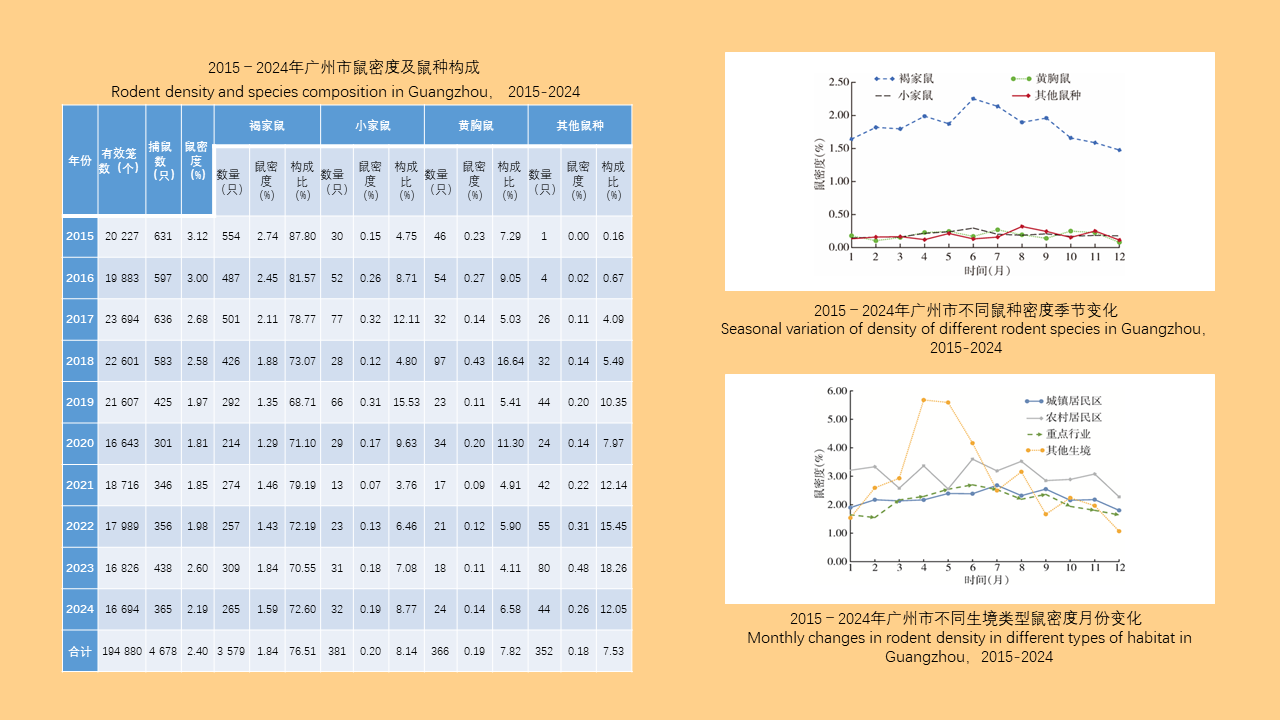
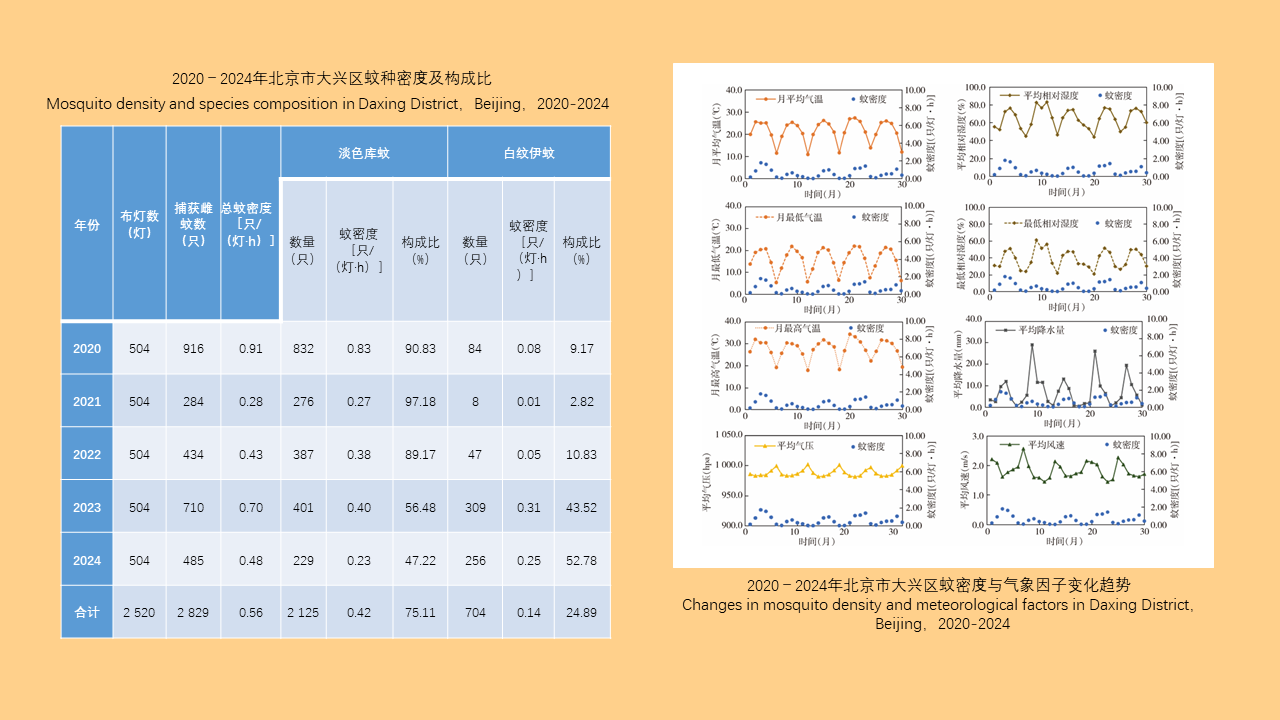
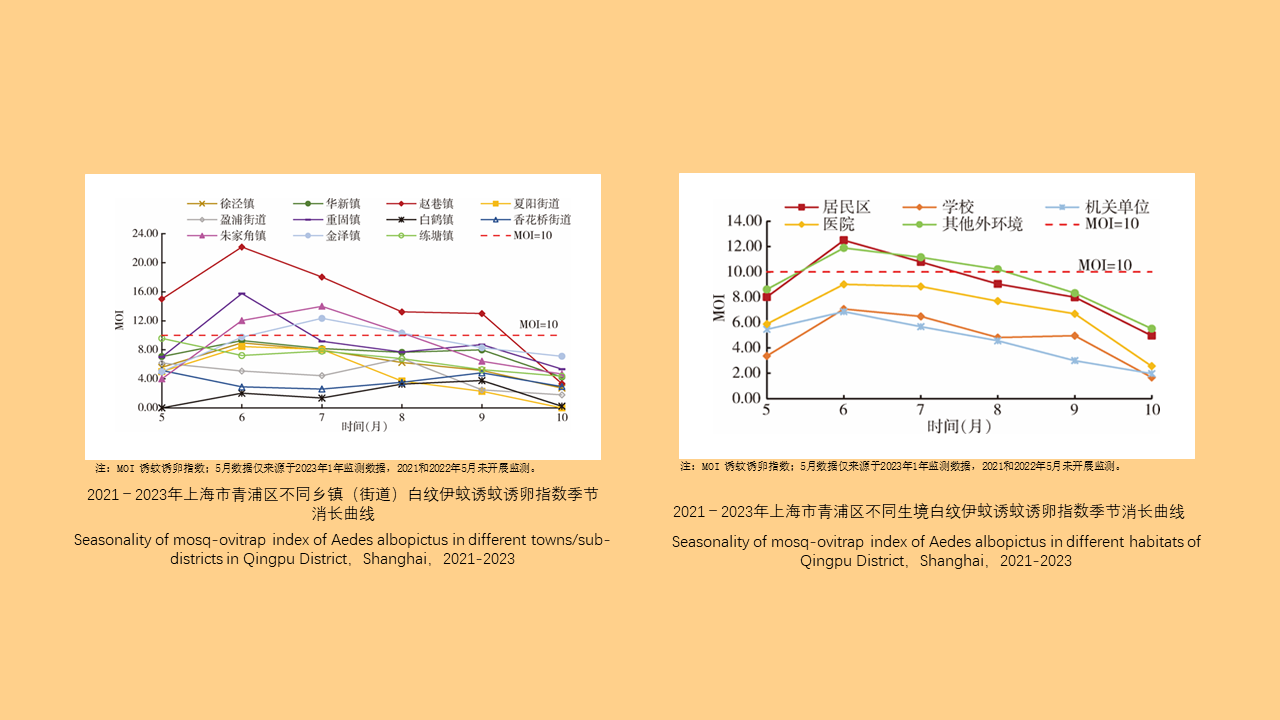
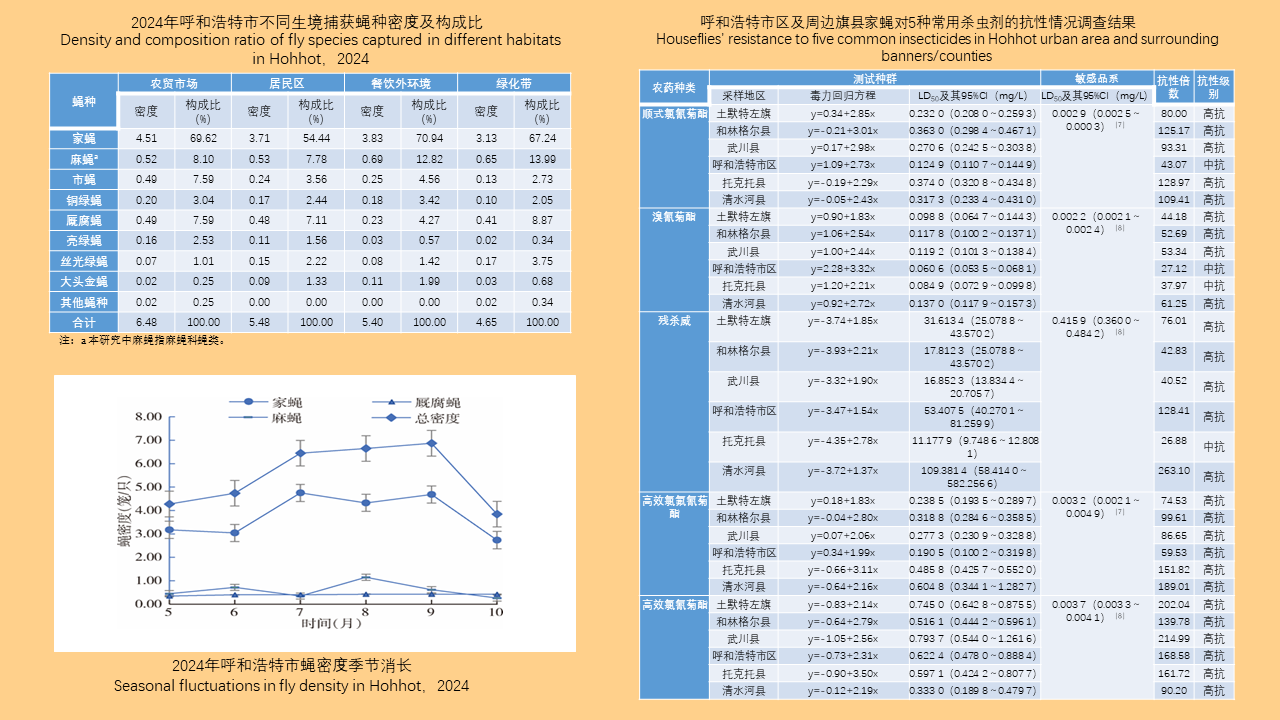
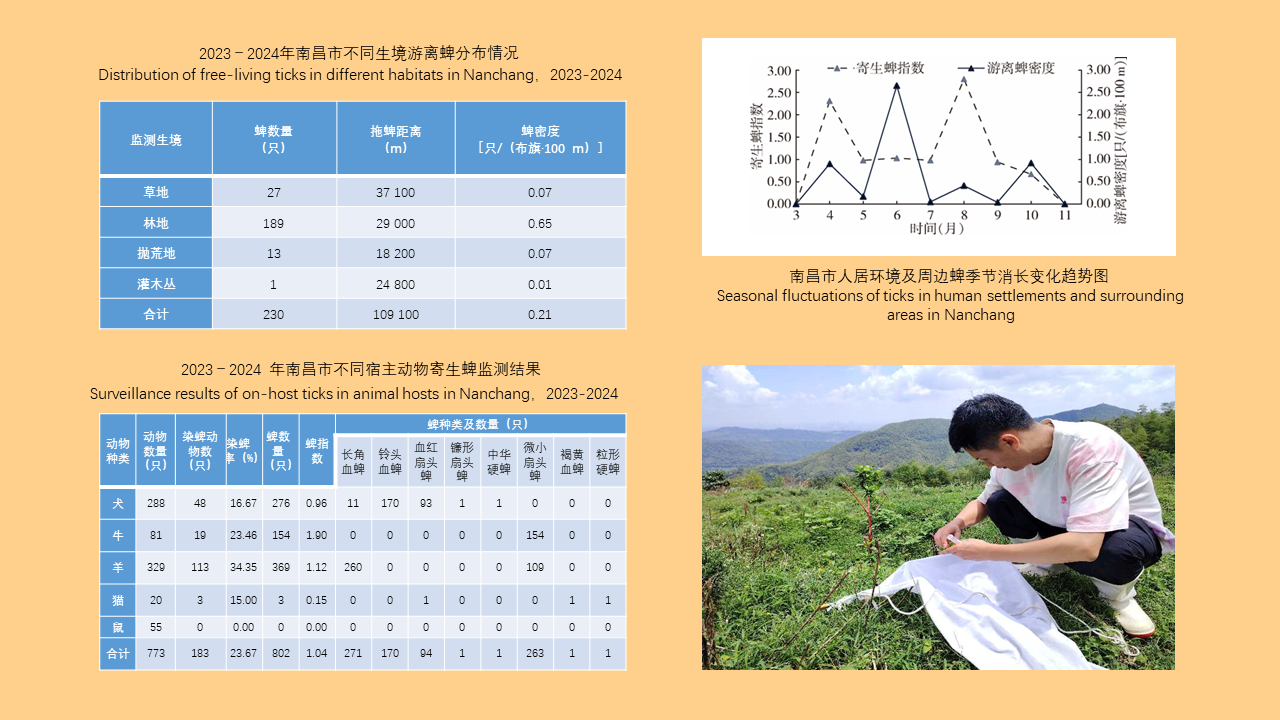
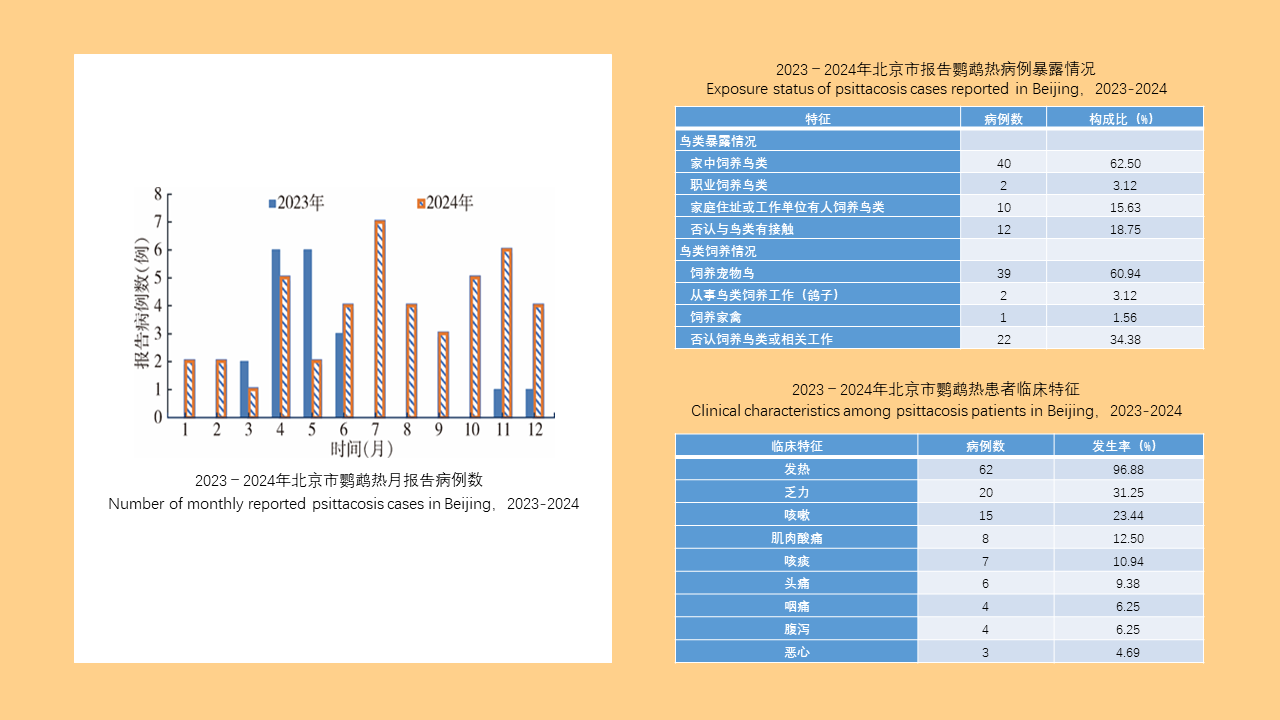
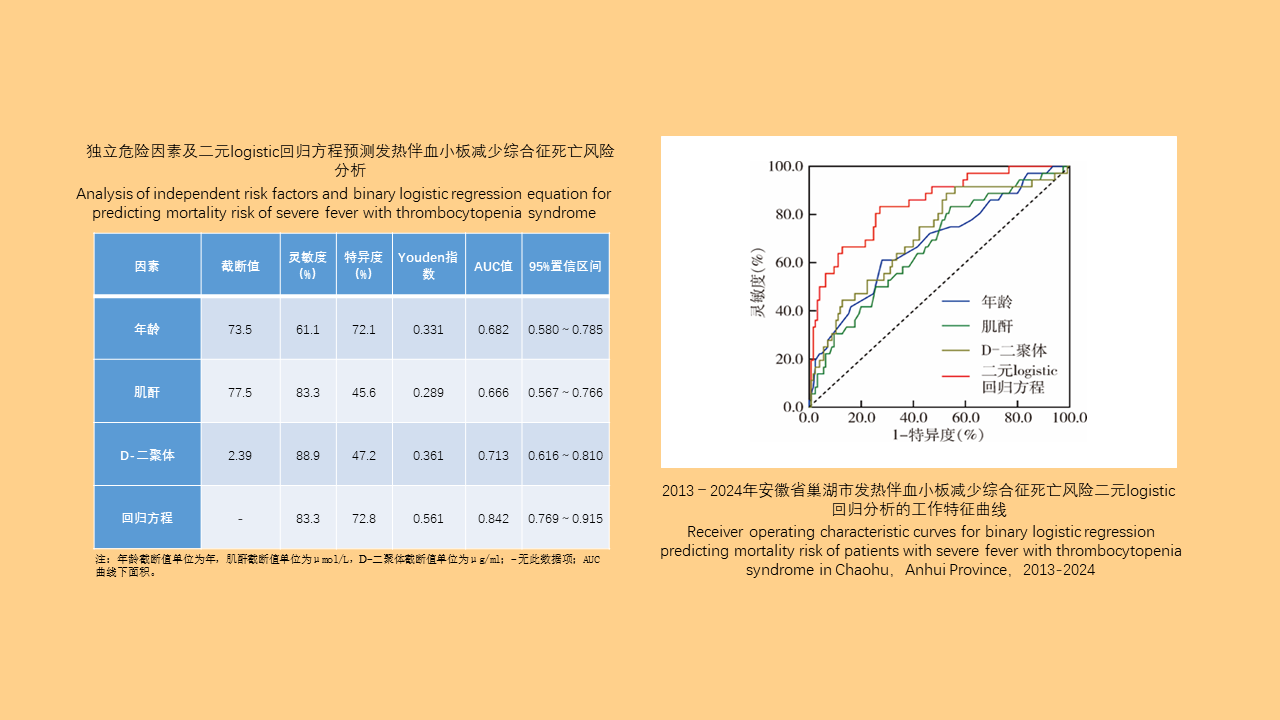
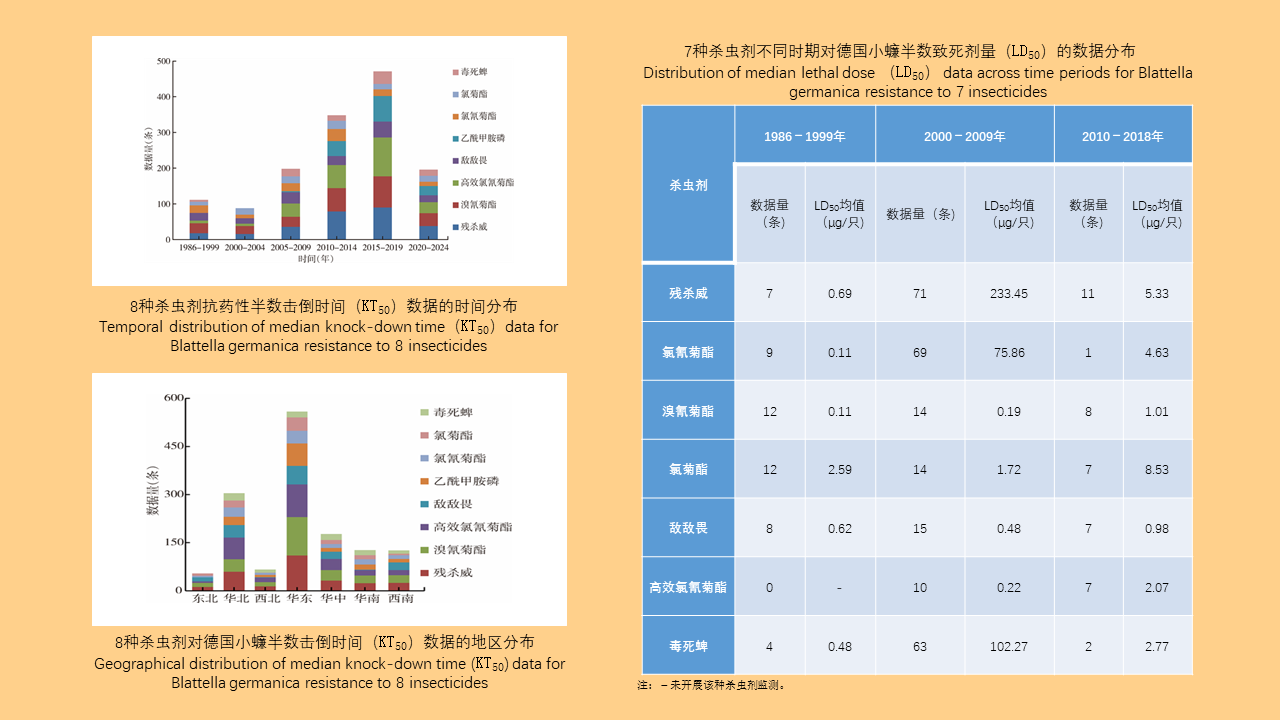
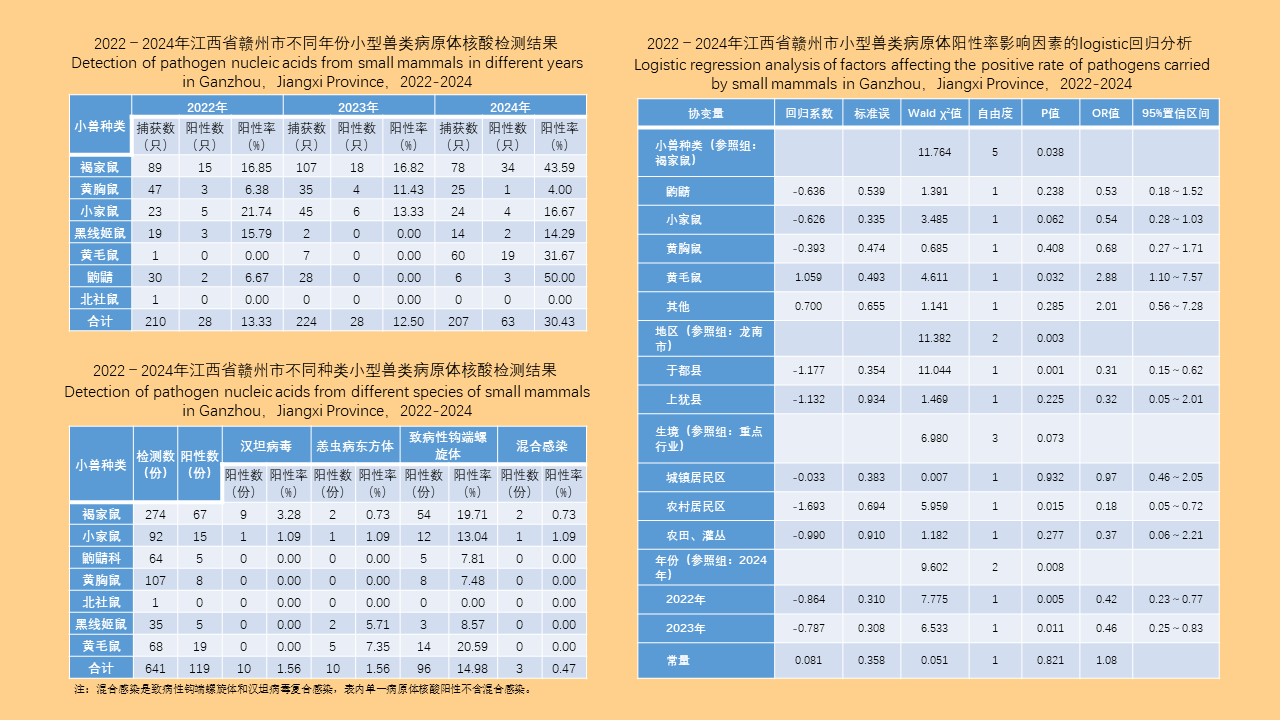
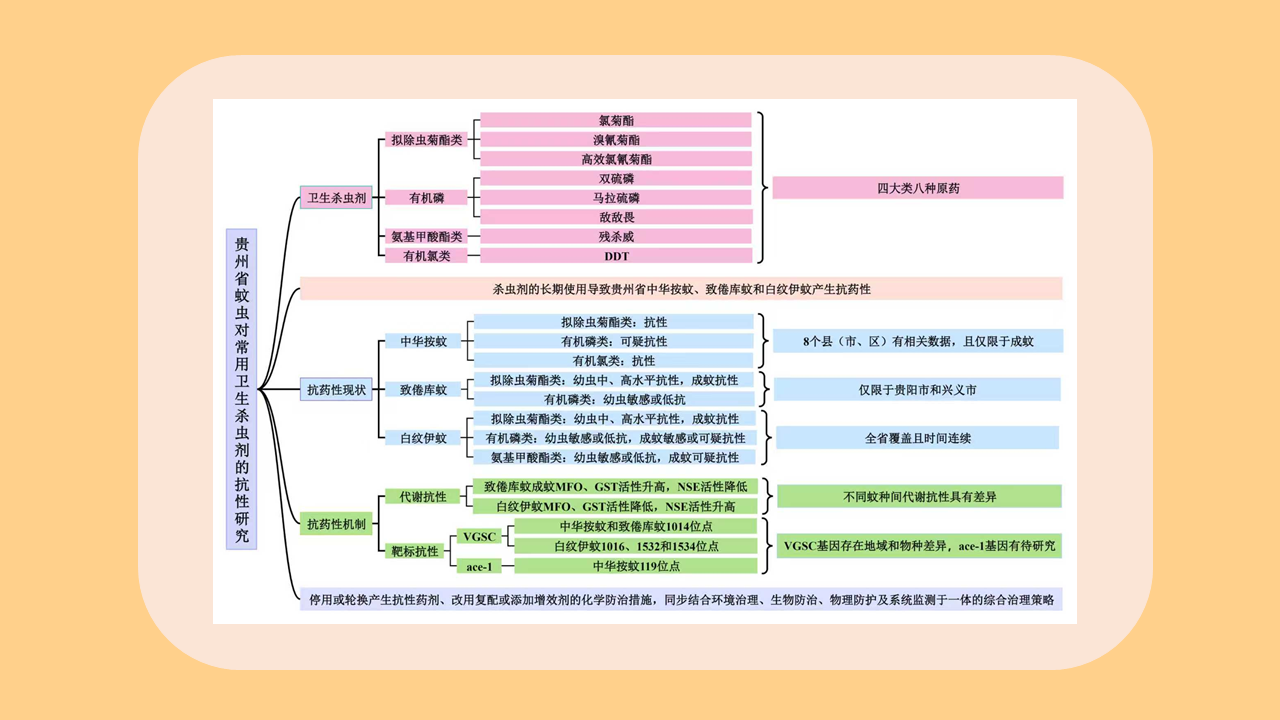
Objective: Analyze the bioassay data on insecticide resistance in Blattella germanica in China to understand the distribution of insecticide types, temporal trends, and geographical patterns, with the aim of providing data support for the chemical control of B. germanica. Methods: The search terms "Blattella germanica" "insecticide resistance" "residual film method" or "topical application method" were used to retrieve all relevant articles from the databases of China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI, 1994-2024), Wanfang Data Knowledge Service Platform (Wanfang, 1998-2024), VIP Chinese Journal Service Platform (VIP, 1989-2024), and the PubMed (1966-2024). Excel 2013 software was used to organize the data, and SPSS 19.0 software was employed for analysis of variance or t-test. Results: A total of 103 articles were retrieved from CNKI, 93 from Wanfang, 23 from VIP, and 4 from PubMed. A total of 150 publications employed the residual film method for insecticide resistance testing on B. germanica, generating 1 515 data points on median knockdown time (KT50) derived from 24 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) in China. A total of 25 insecticides in 5 categories were tested, with pyrethroids being the most represented (14 insecticides). Among the 25 insecticides, propoxur yielded the largest KT50 dataset (277 data points), followed by deltamethrin (266 data points). The data from eight insecticides, including propoxur, deltamethrin, beta-cypermethrin, dichlorvos, acephate, cypermethrin, permethrin, and chlorpyrifos, accounted for 93.20% of the total KT50 data. Temporal analysis (1986-1999, 2000-2004, 2005-2009, 2010-2014, 2015-2019, 2020-2024) revealed statistically significant differences in KT50 values for propoxur, deltamethrin, beta-cypermethrin, dichlorvos, acephate, permethrin, and chlorpyrifos (all P < 0.05). The regional distribution of KT50 data for insecticides varies, with more comprehensive data available in north China and east China, and relatively less in northeast China and northwest China. From 2010 to 2014, there were statistically significant differences in the KT50 values of propoxur and beta-cypermethrin between north and east China regions (t=3.000, P=0.006; t=1.668, P=0.203); Additionally, From 2015 to 2019, there were statistically significant differences in the KT50 values of propoxur and beta-cypermethrin among the north China, east China, central China, and southwest China (F=2.885, P=0.042; F=4.170, P=0.008). Twenty-seven studies employed the topical application method to determine the median lethal dose (LD50) for B. germanica, from 14 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities). These studies involved 18 insecticides from 5 categories, with pyrethroids being the most represented. The data from six insecticides such as propoxur, cypermethrin, chlorpyrifos, deltamethrin, permethrin and dichlorvos accounted for 88.59% of the 377 LD50 data collected. Significant differences in LD50 values for propoxur, cypermethrin, permethrin, and chlorpyrifos were observed across 1986-1999, 2000-2009, and 2010-2018 for B. germanica (all P < 0.05). For transport vehicles (passenger trains, ships, and aircraft), 19 studies using the residual film method provided 148 KT50 data points for B. germanica. The studies covered 19 insecticides from 5 categories, with pyrethroids being the most represented. Data on KT50 values of B. germanica from vehicles for five insecticides, including deltamethrin, propoxur, beta-cypermethrin, acephate and cyhalothrin accounted for 73.65% of the total dataset. There were no statistically significant differences in KT50 values for deltamethrin, propoxur, and beta-cypermethrin against B. germanica collected from passenger trains and ships (all P > 0.05). Conclusions: The bioassay data for insecticide resistance in B. germanica exhibit temporal and regional variations. Data on resistance obtained through the residual film method are more extensive than those from the topical application method. Considering both simplicity of operation and scientific accuracy, it is recommended to adopt harmonized surveillance methods and evaluation indicators for B. germanica resistance, along with commonly used insecticides, in order to obtain more effective and reliable data support.