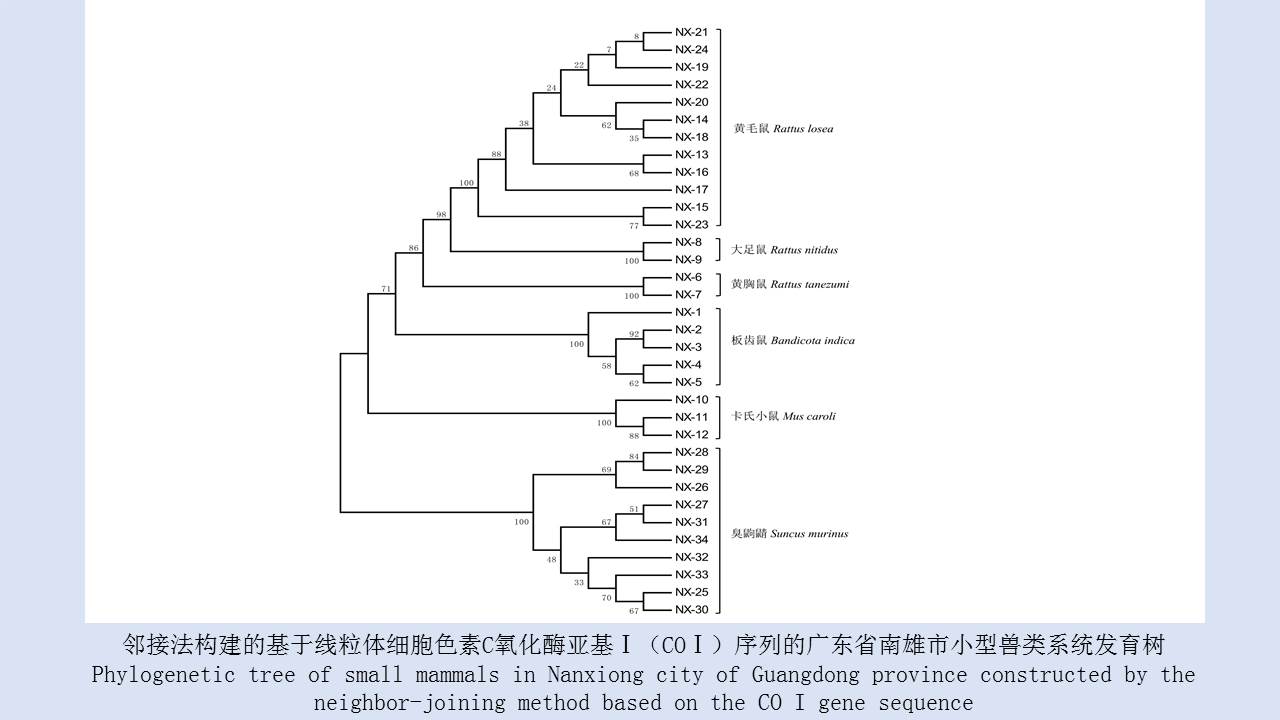
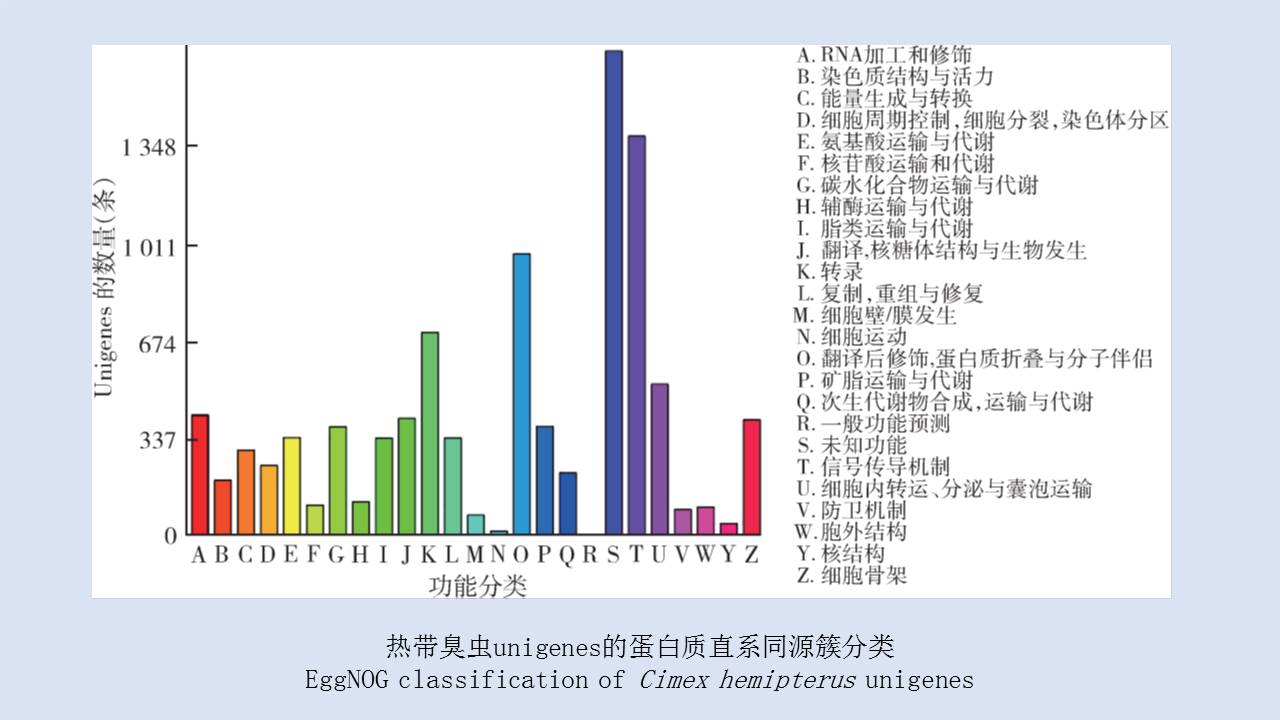
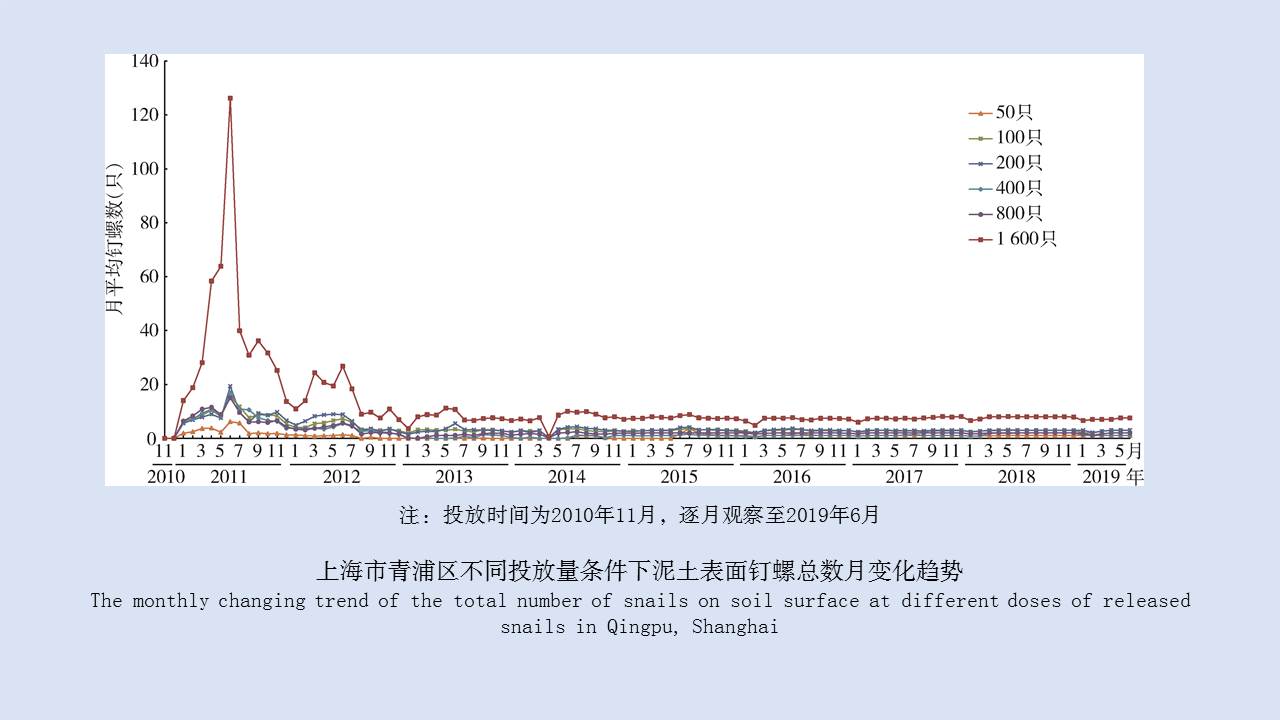
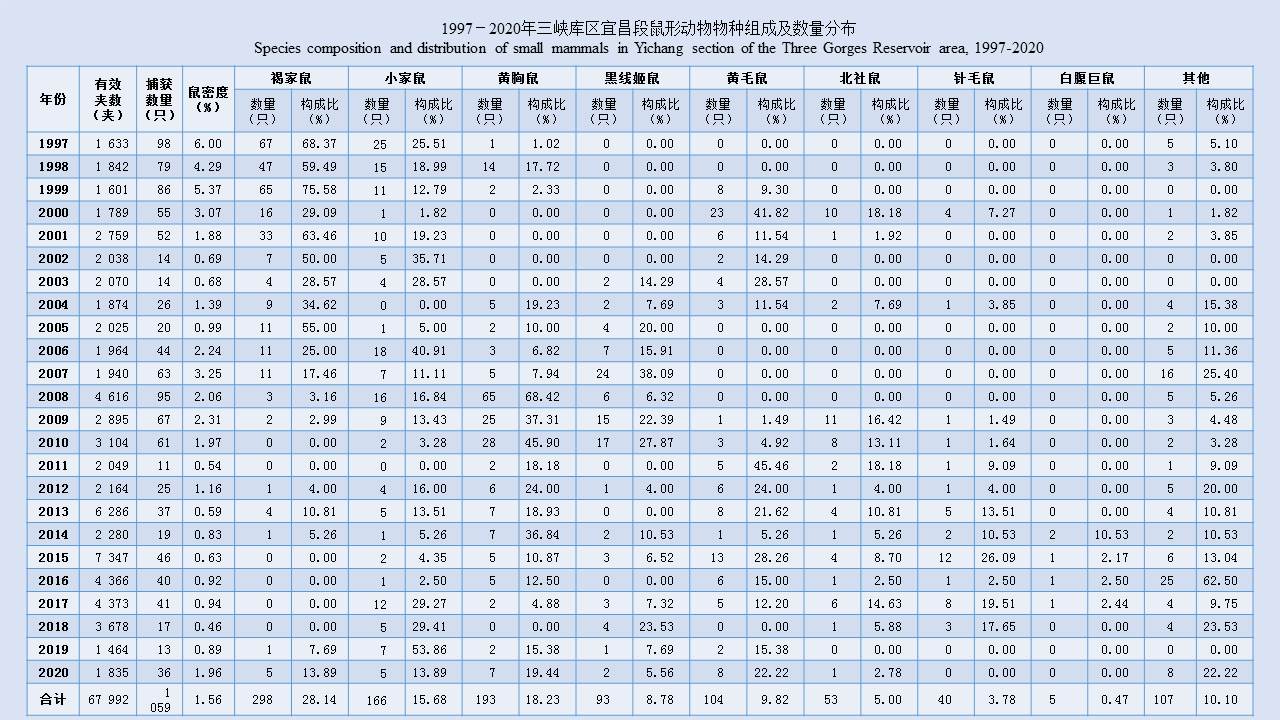
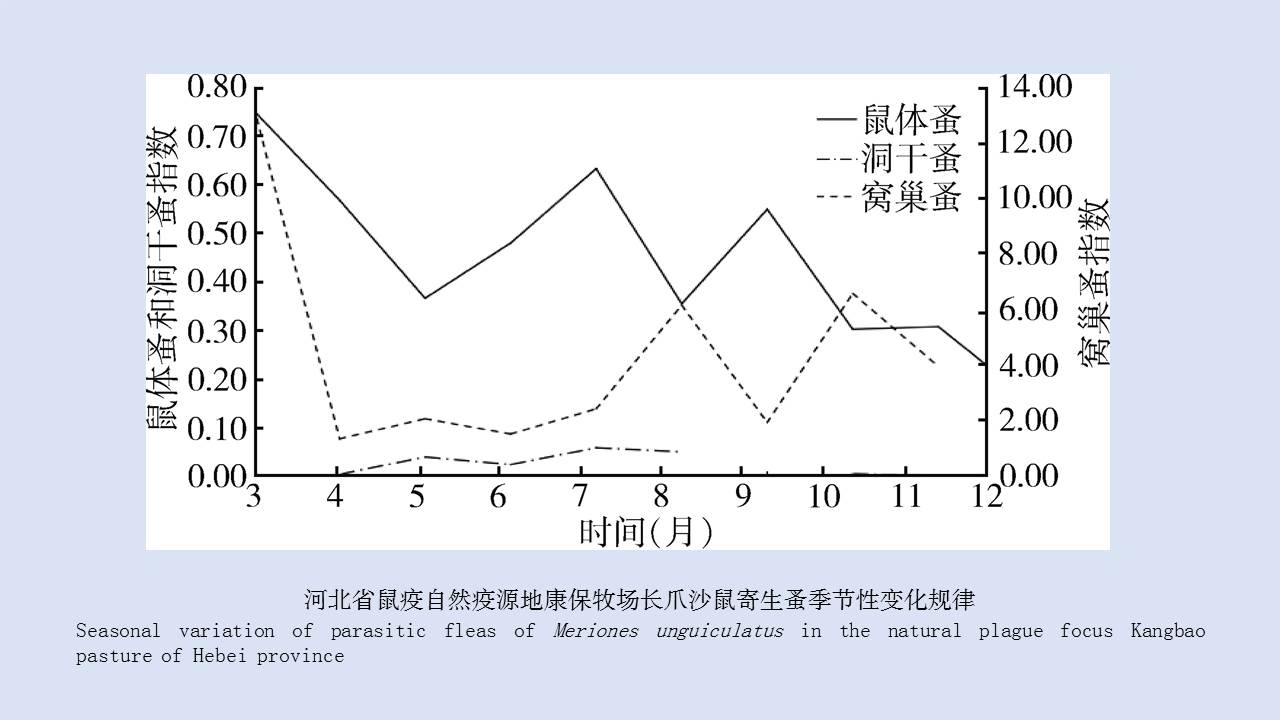
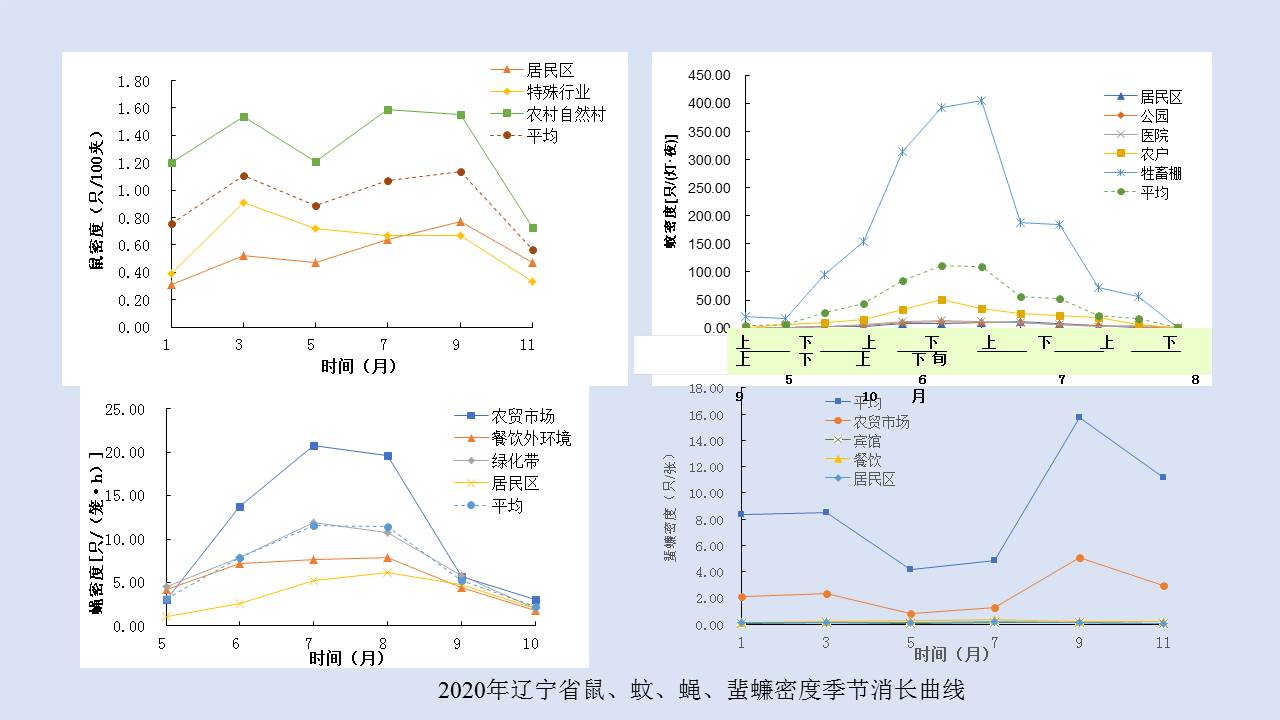
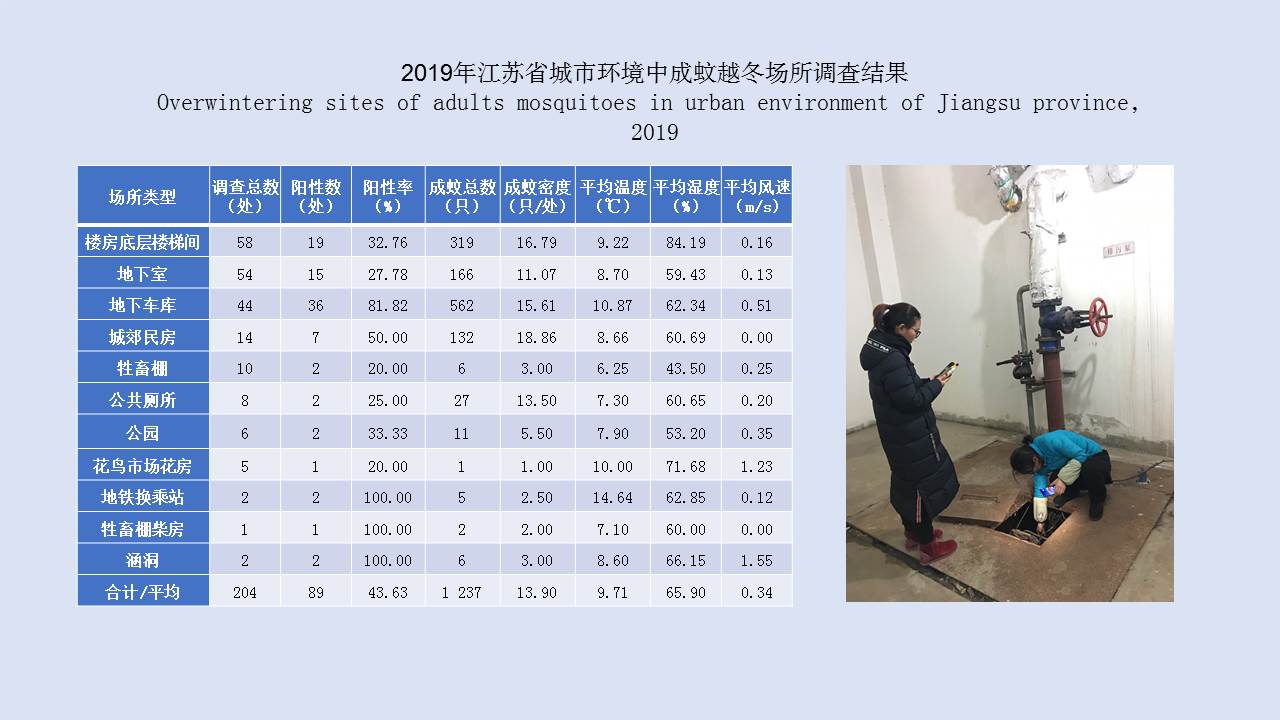
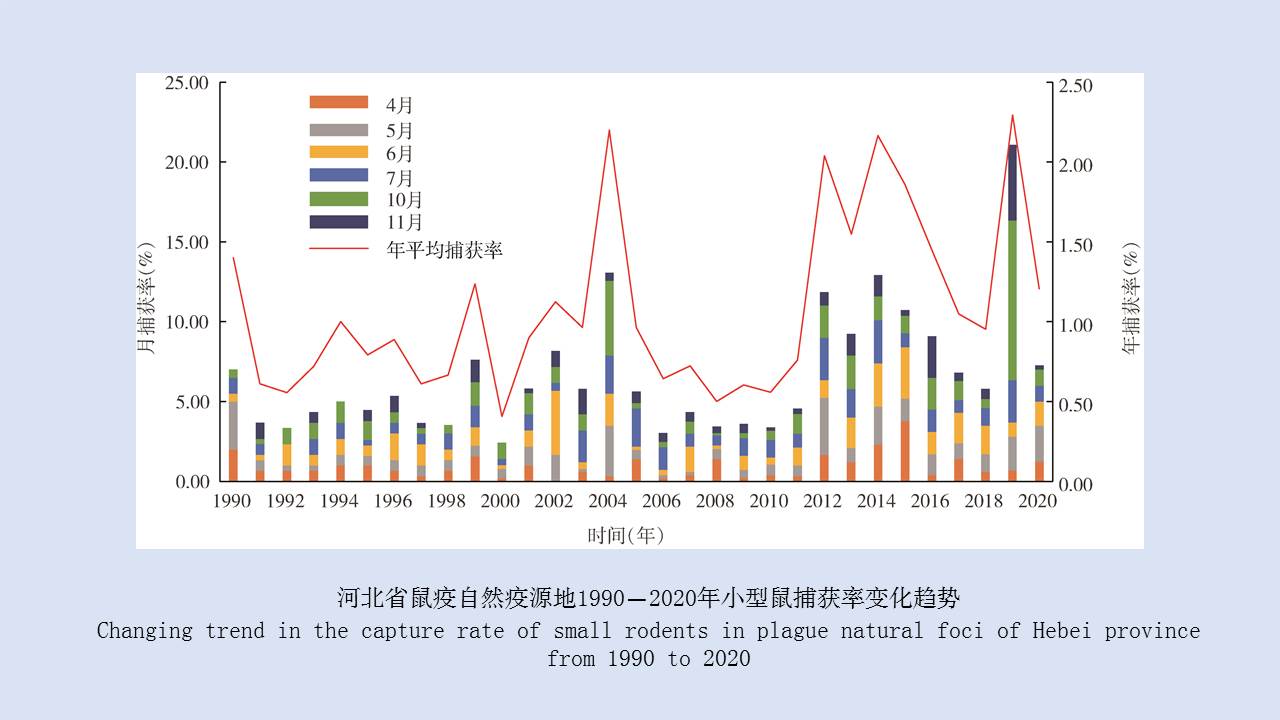
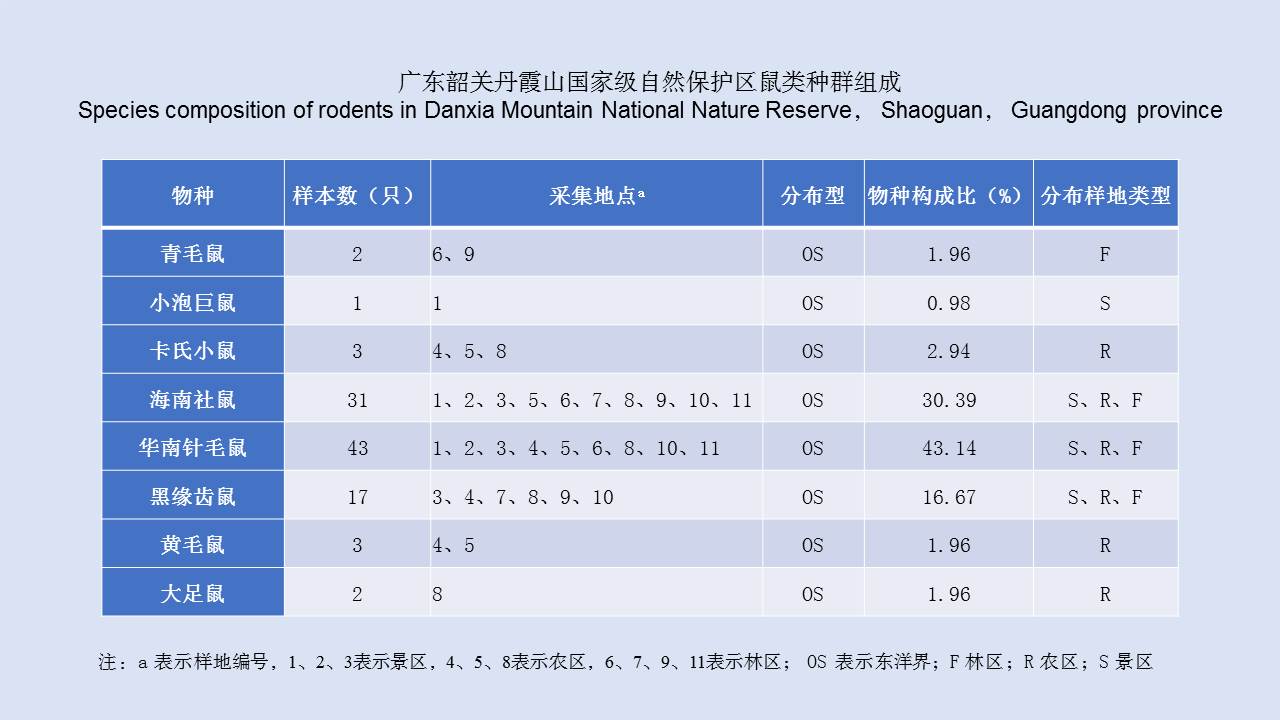
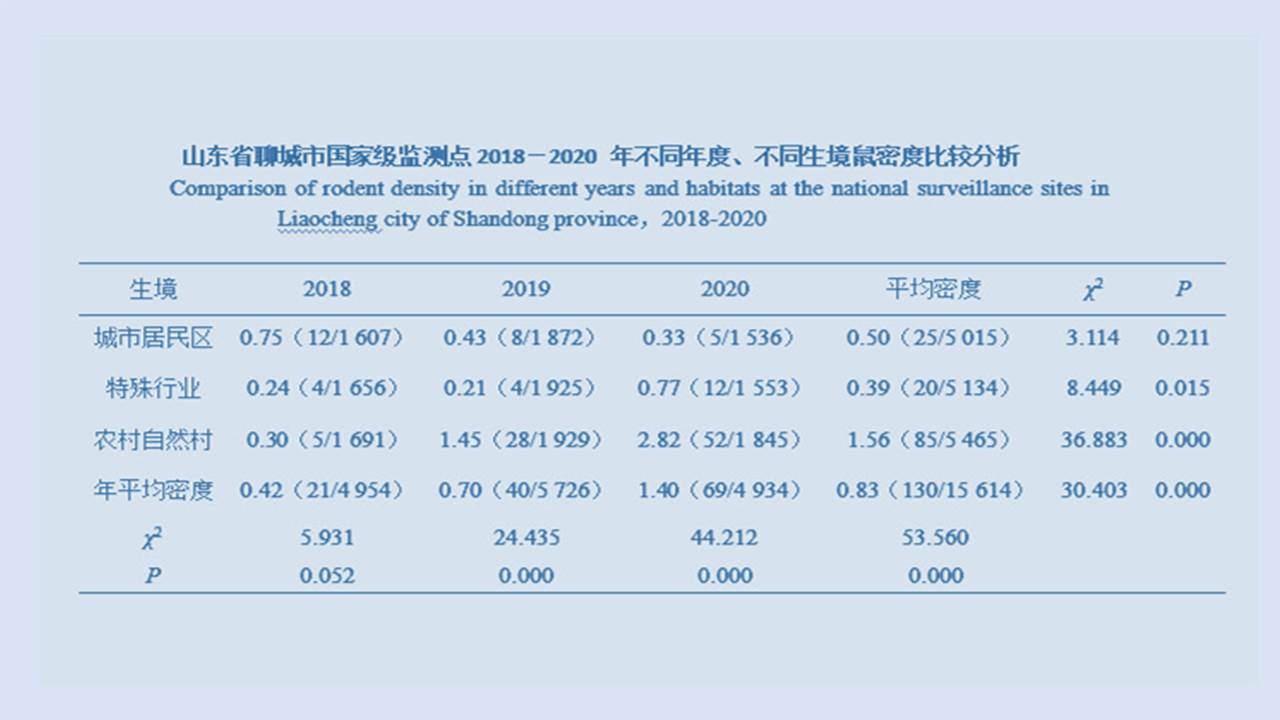
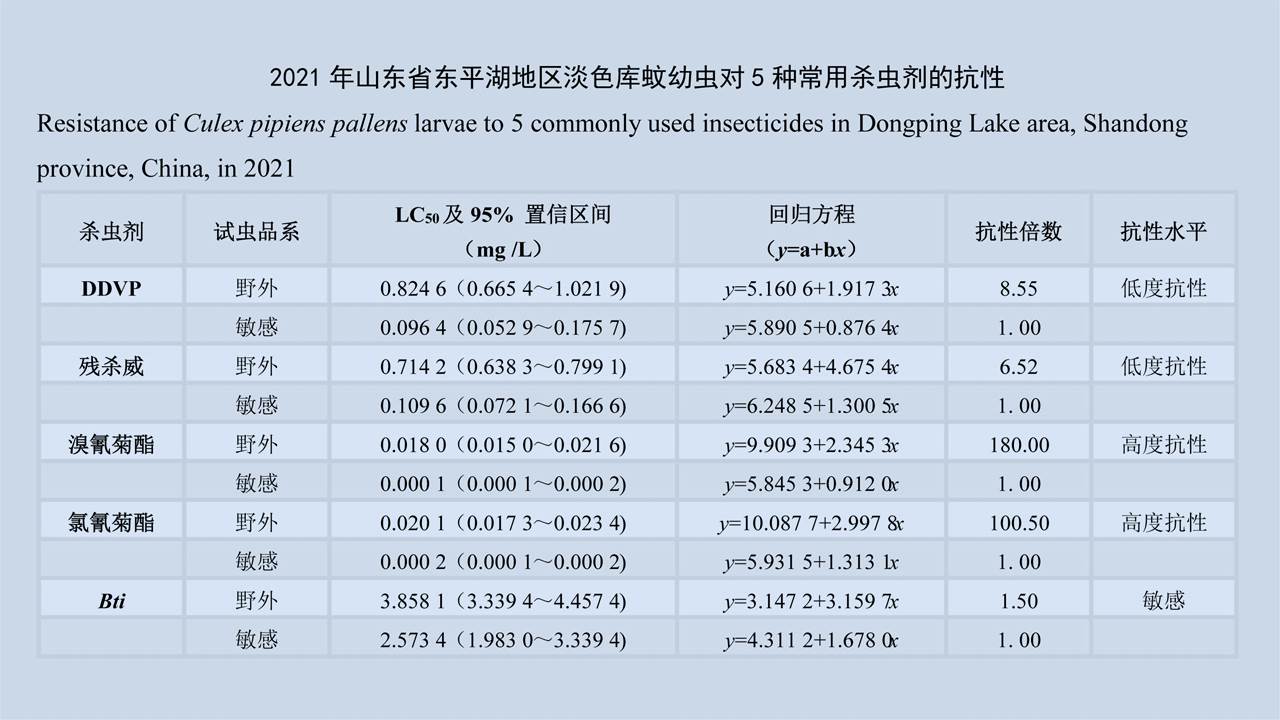
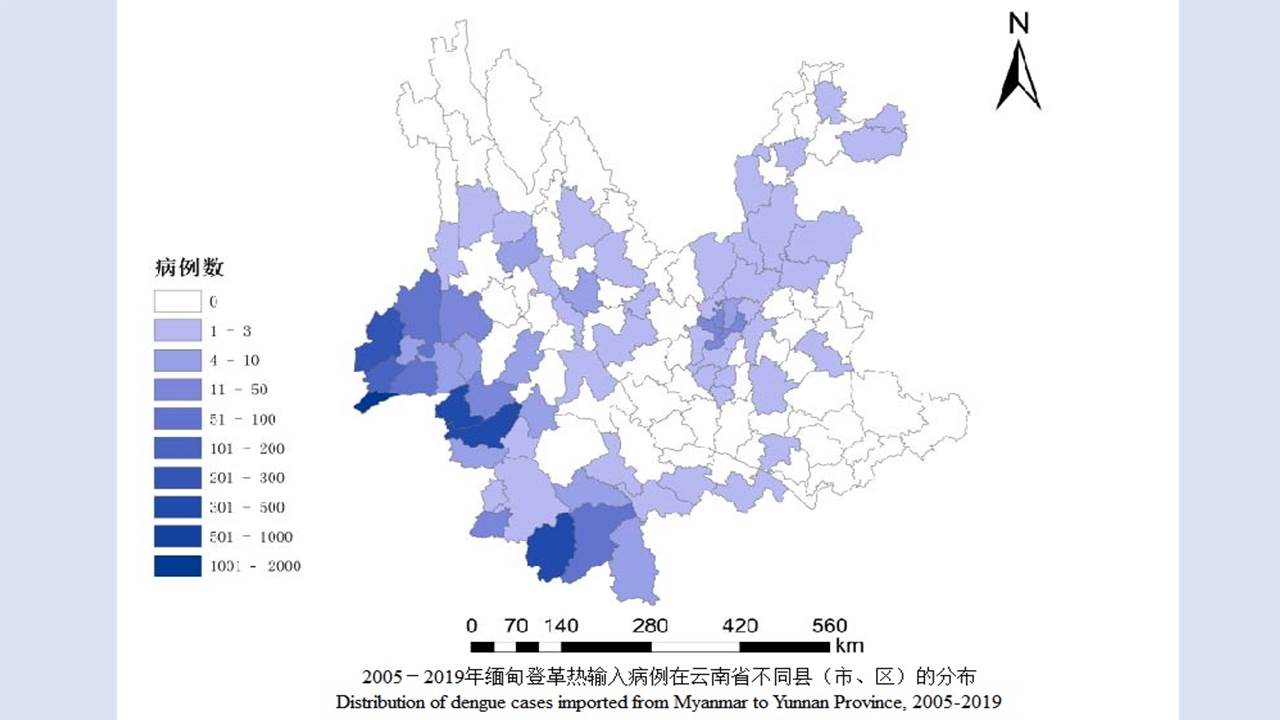
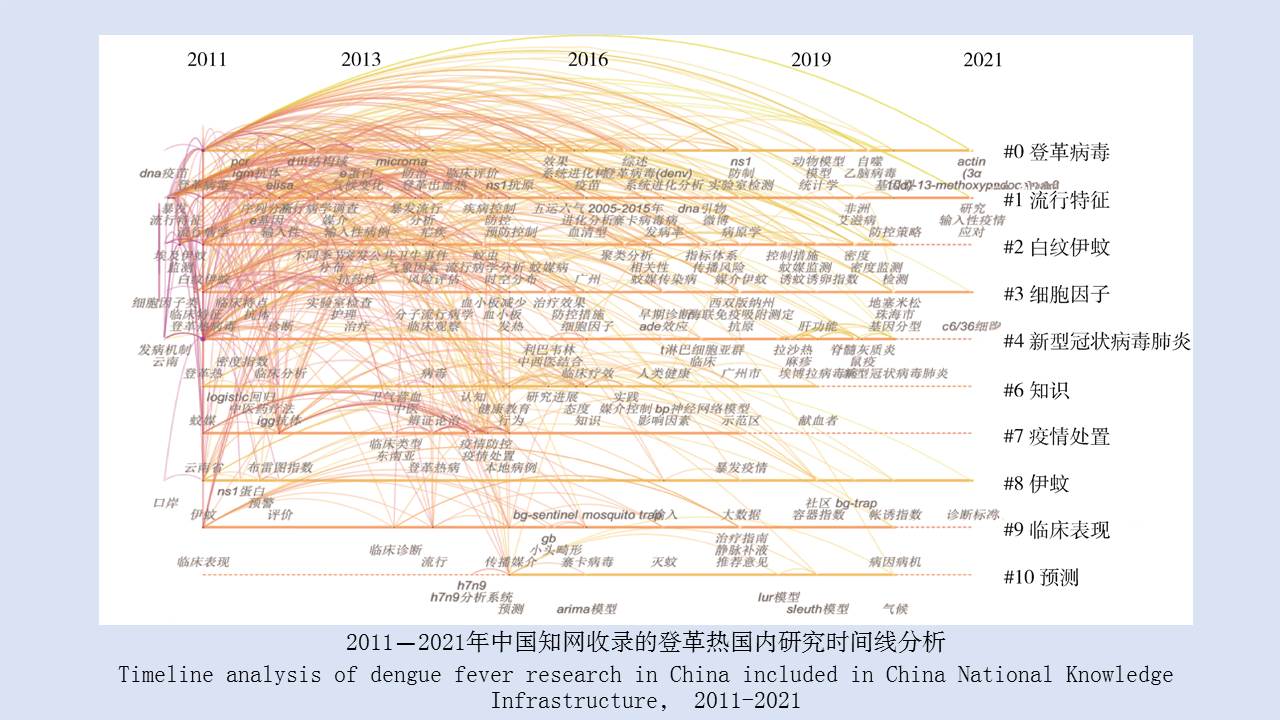
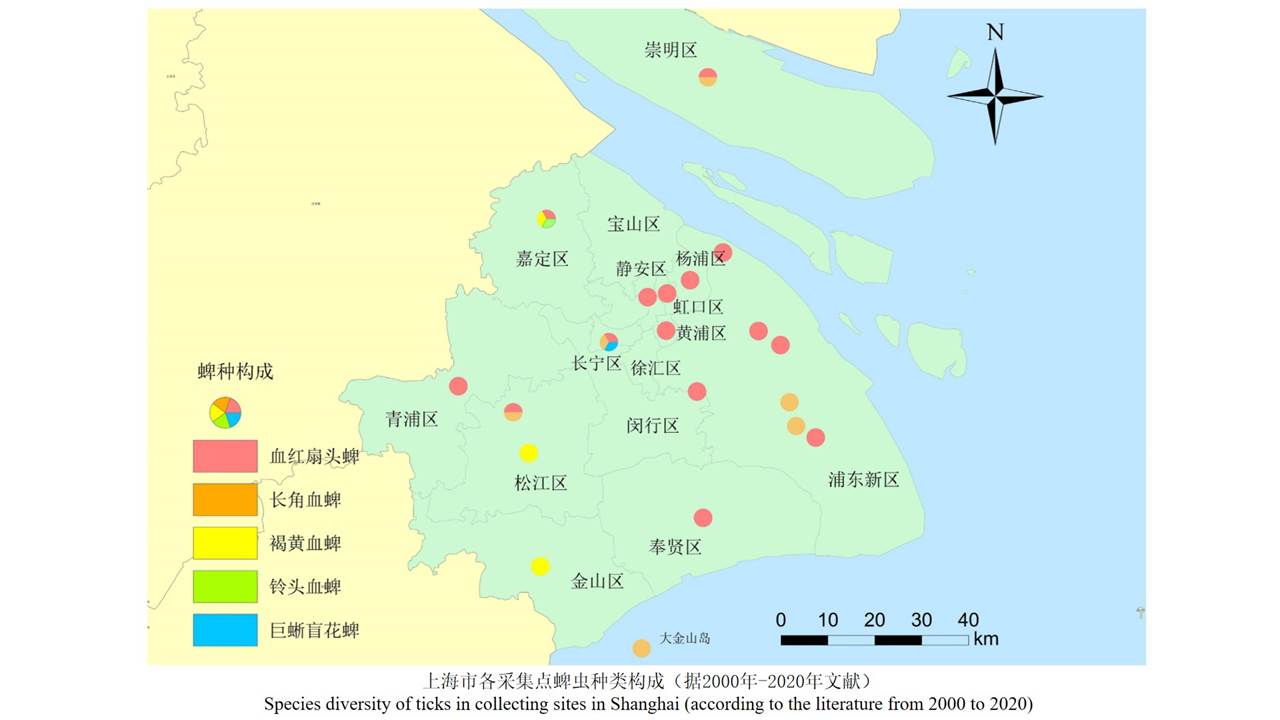
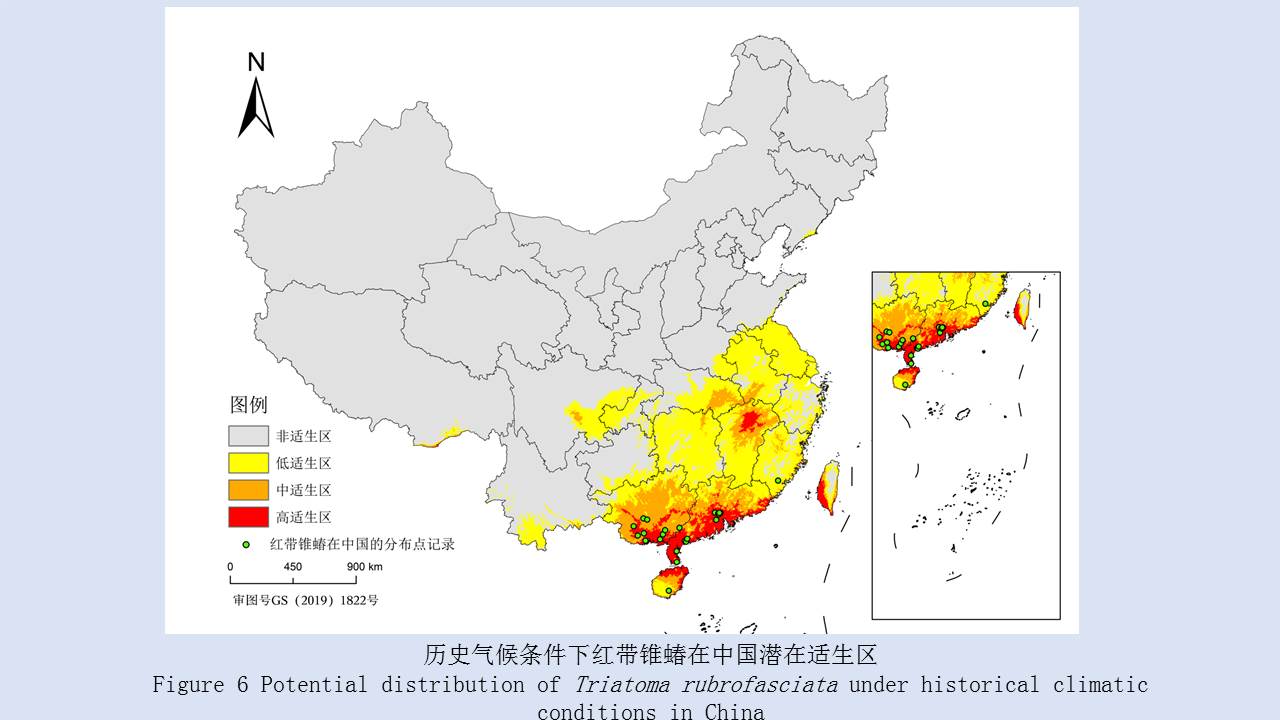
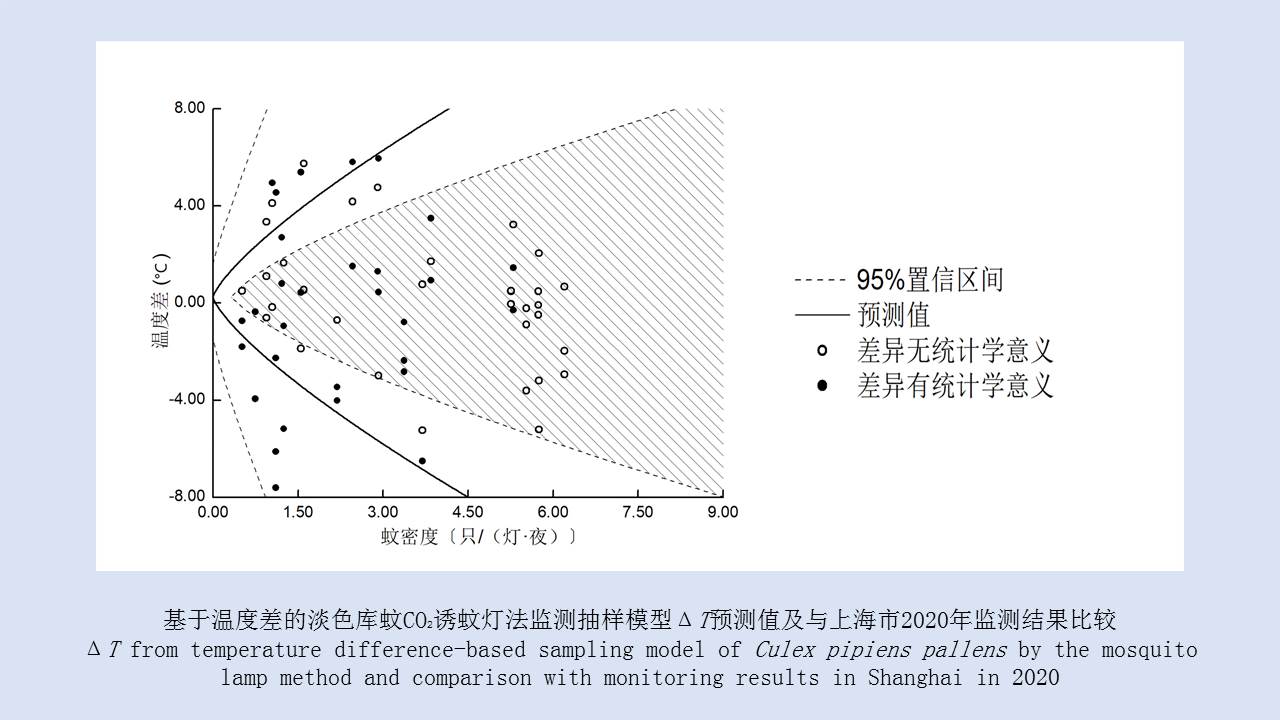
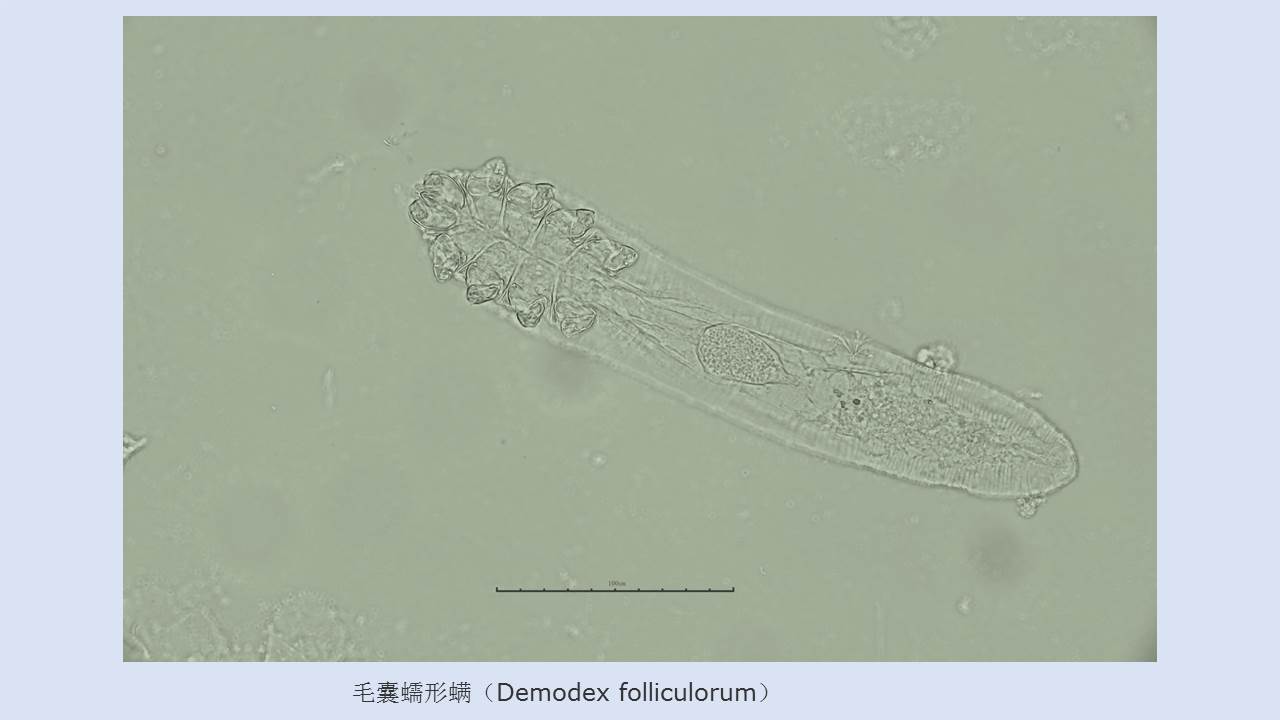
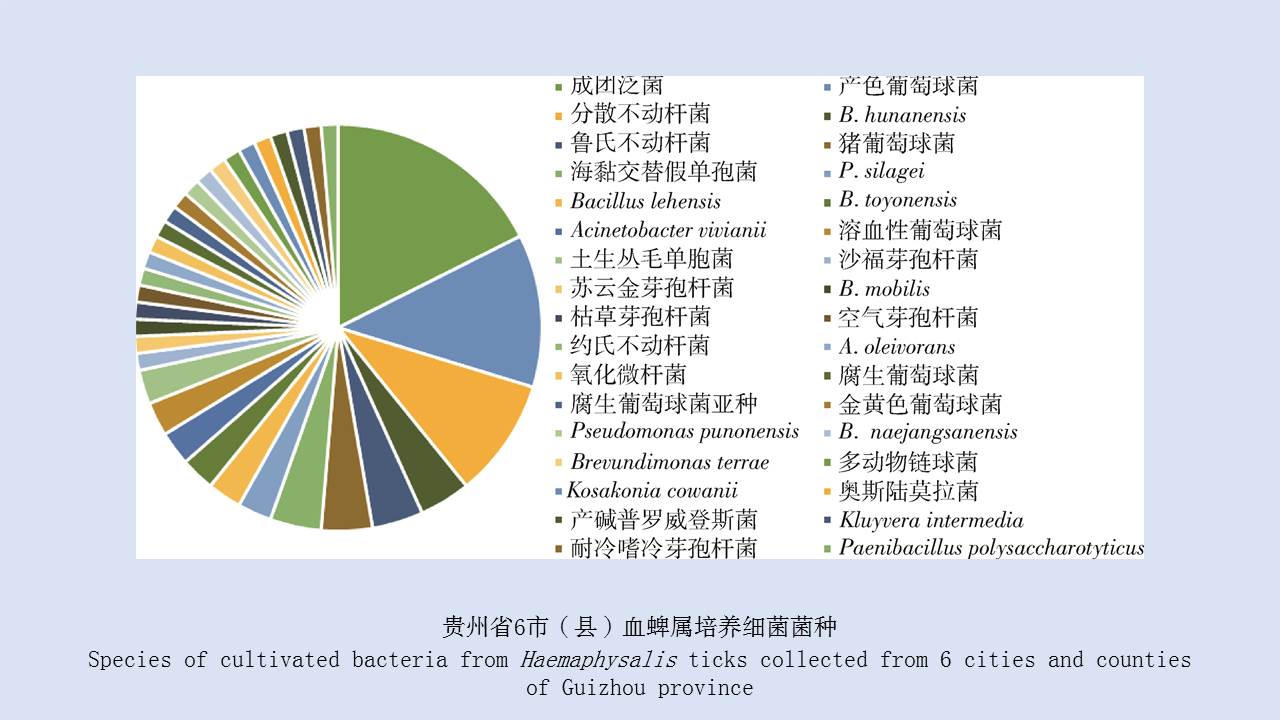
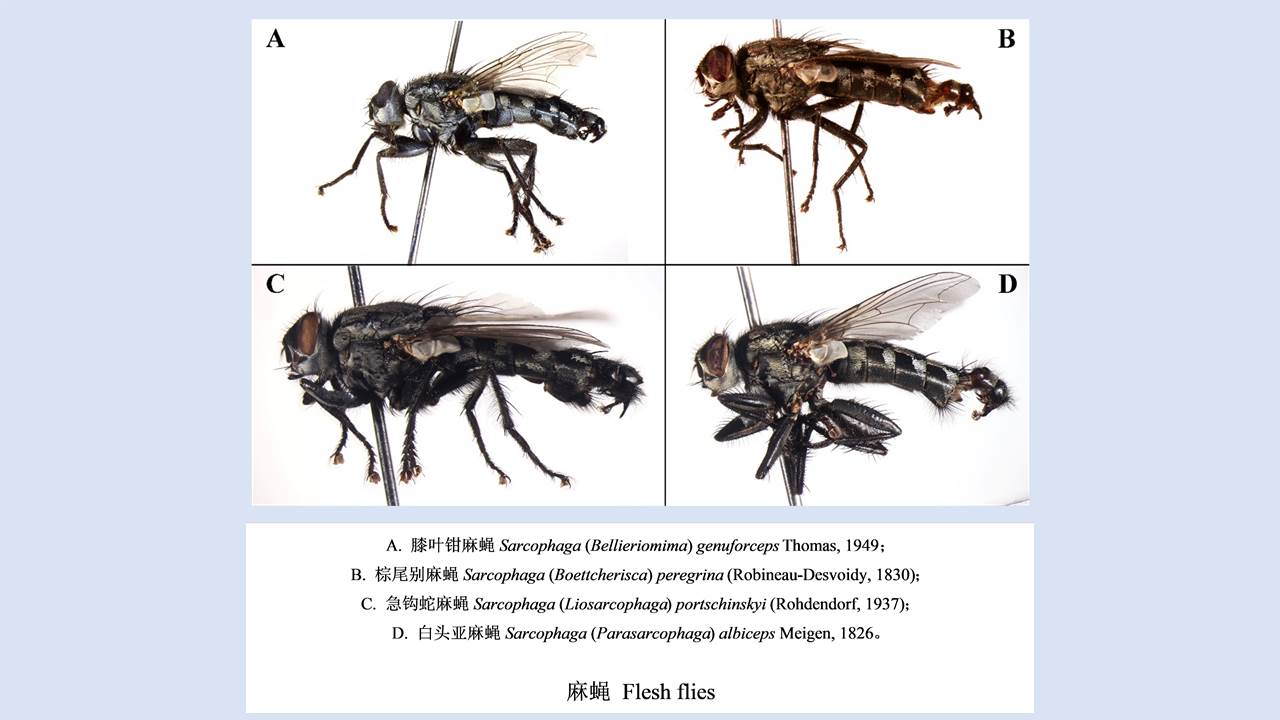
LIU Xiao-bo, YUE Yu-juan, JIA Qing-chen, ZHAO Ning, GUO Yu-hong, ZHAO Chun-chun, LIANG Ying, WANG Jun, WU Hai-xia, LIU Qi-yong
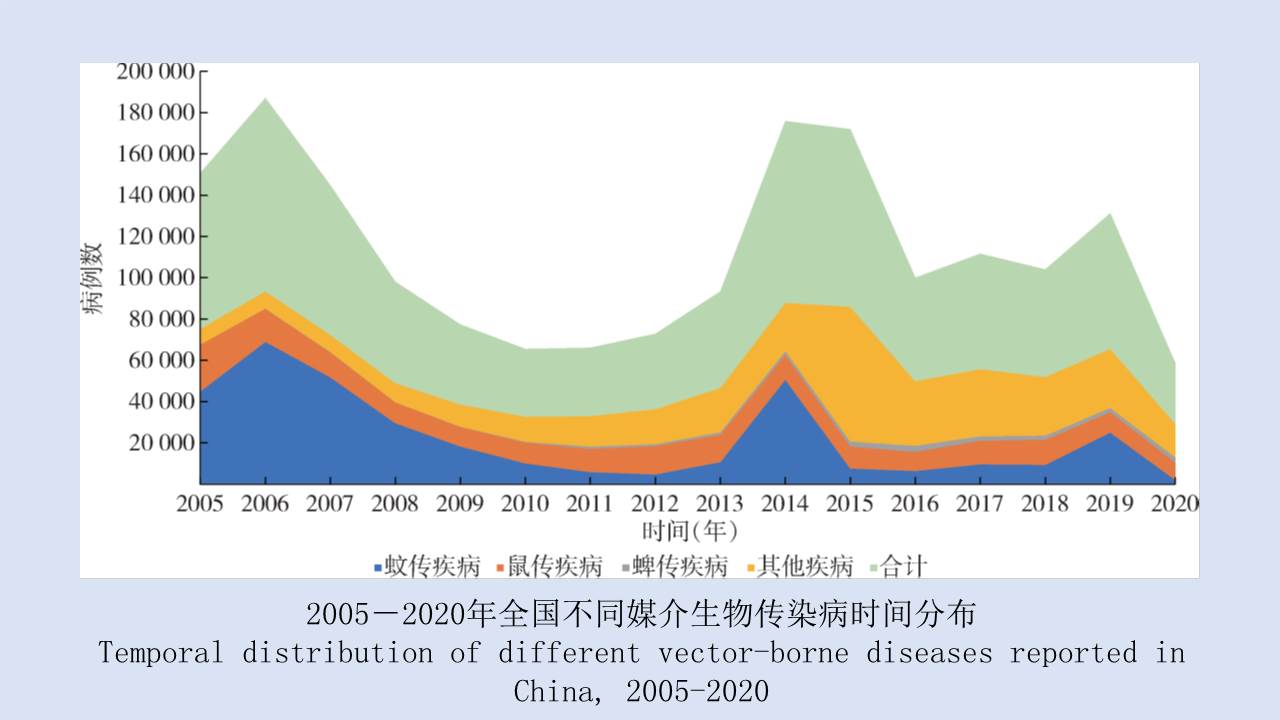
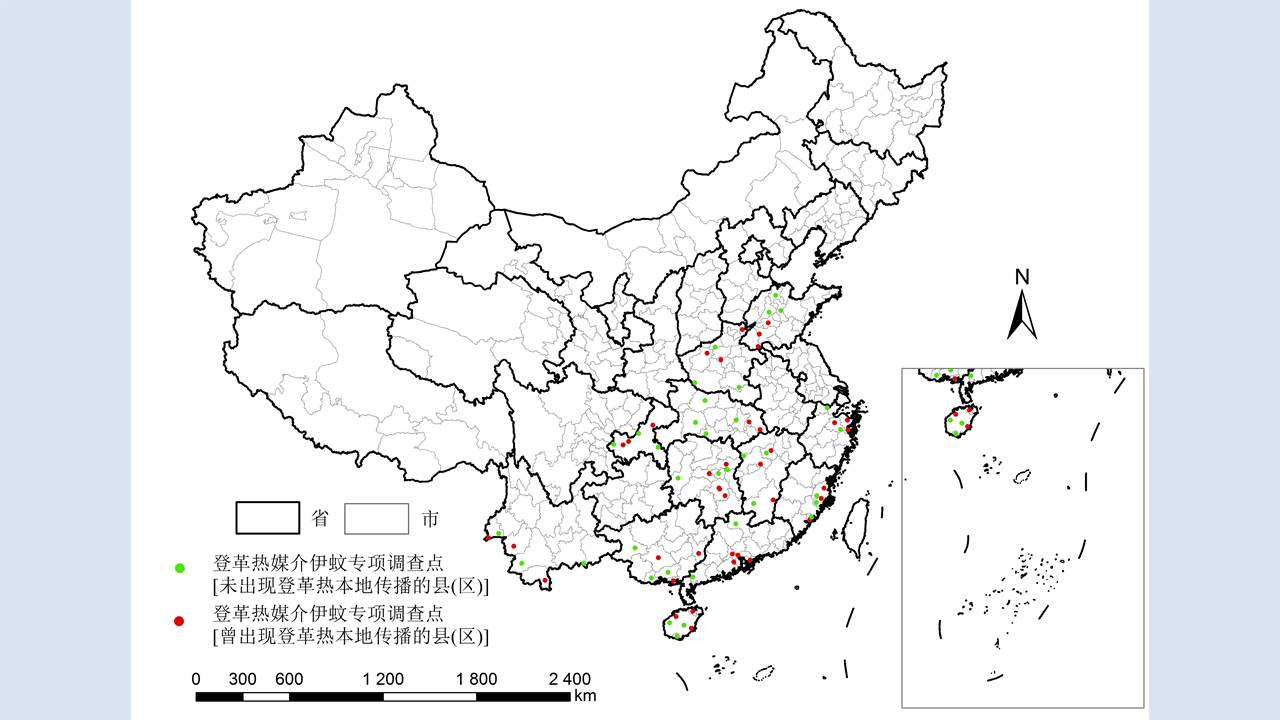
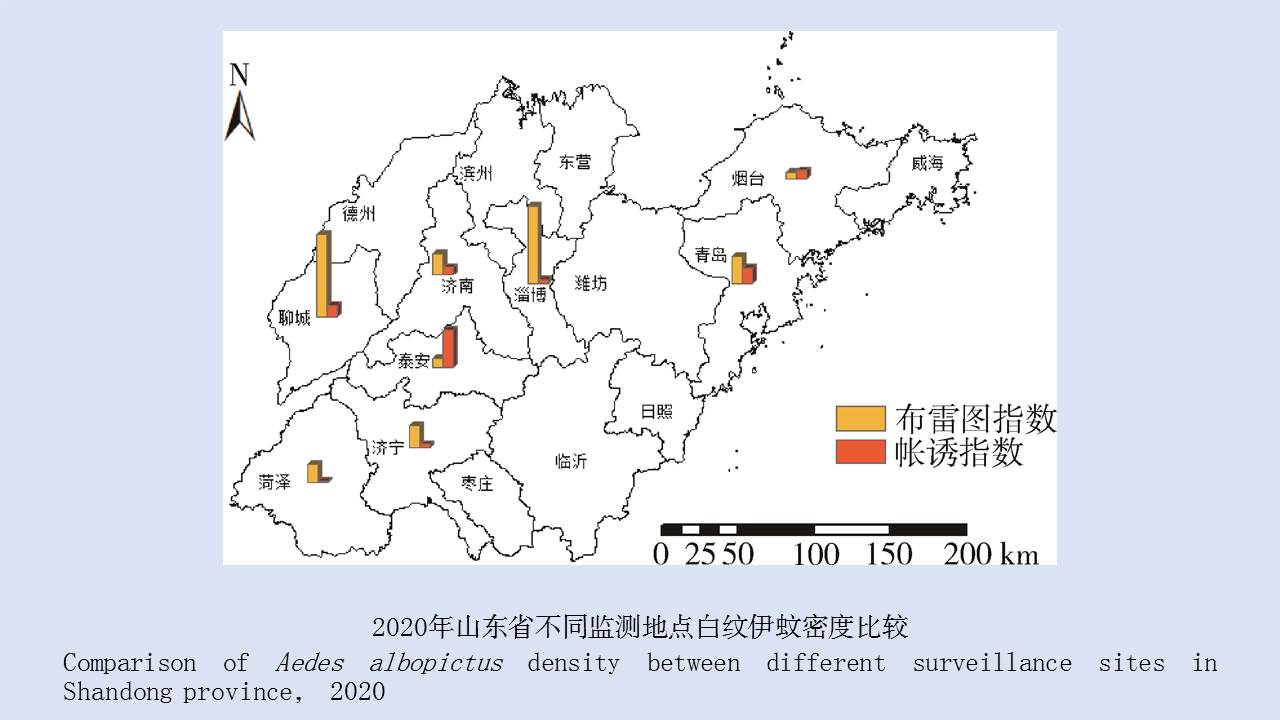
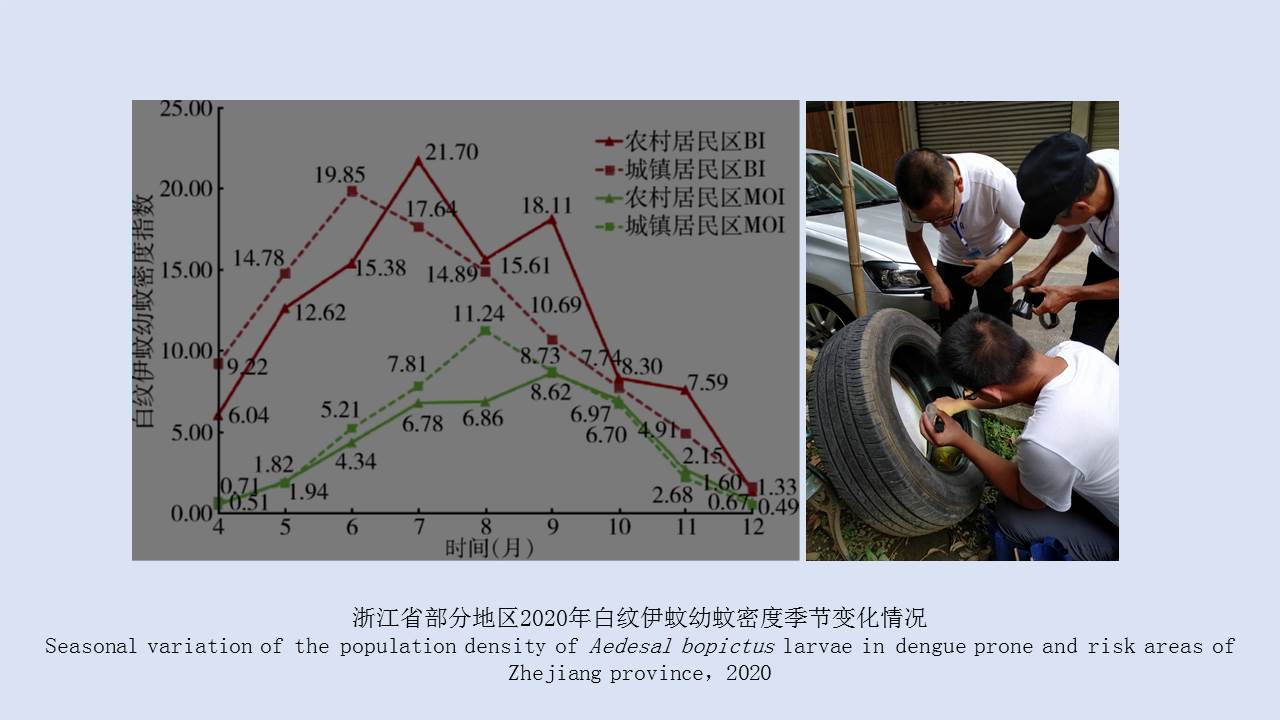
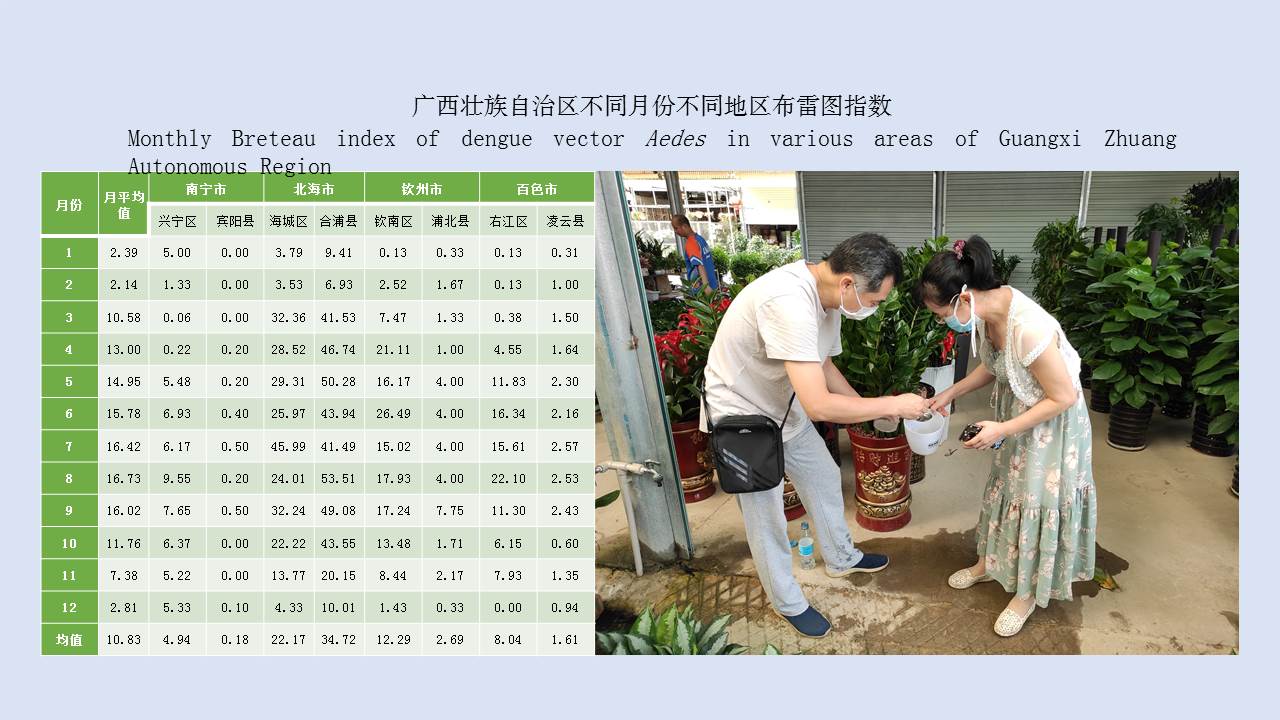
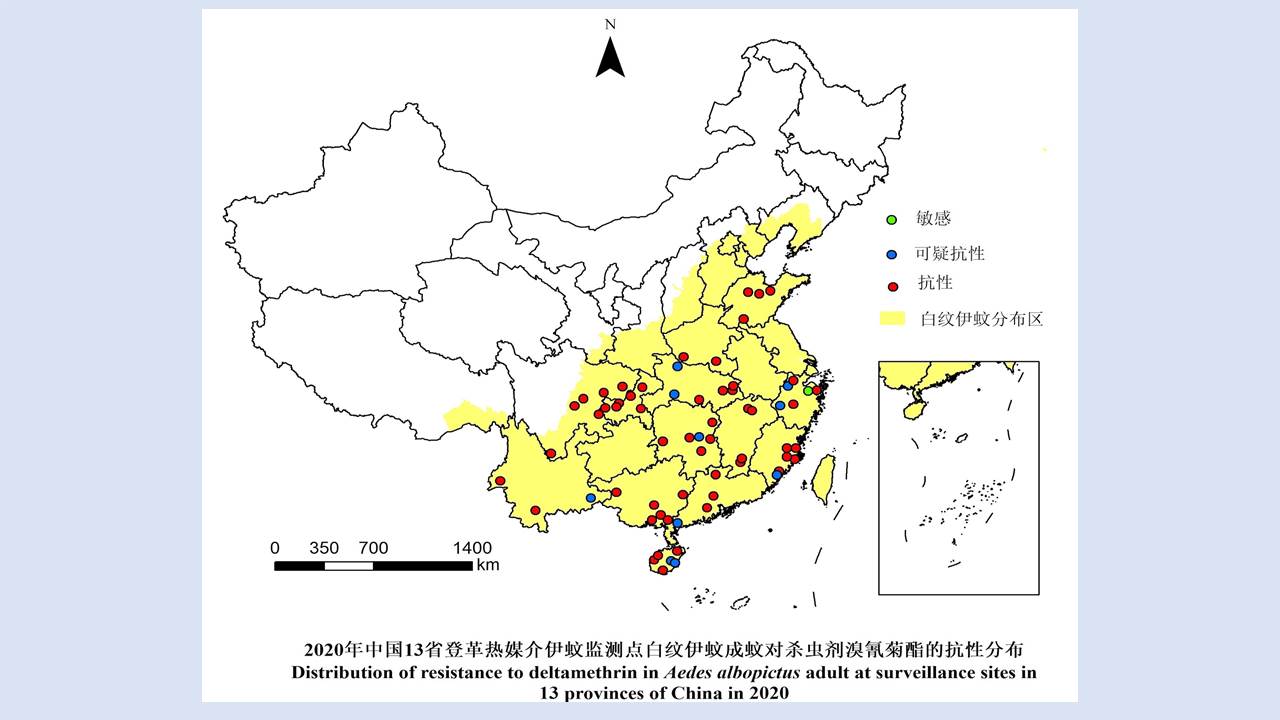
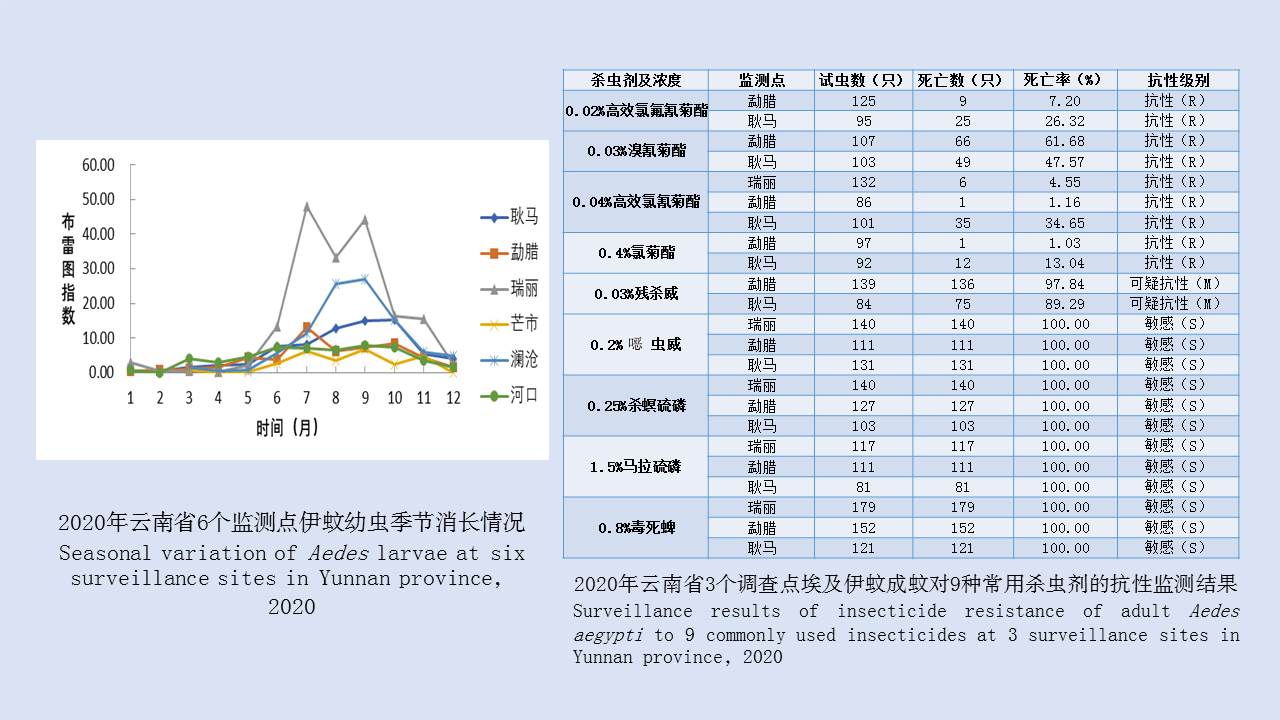
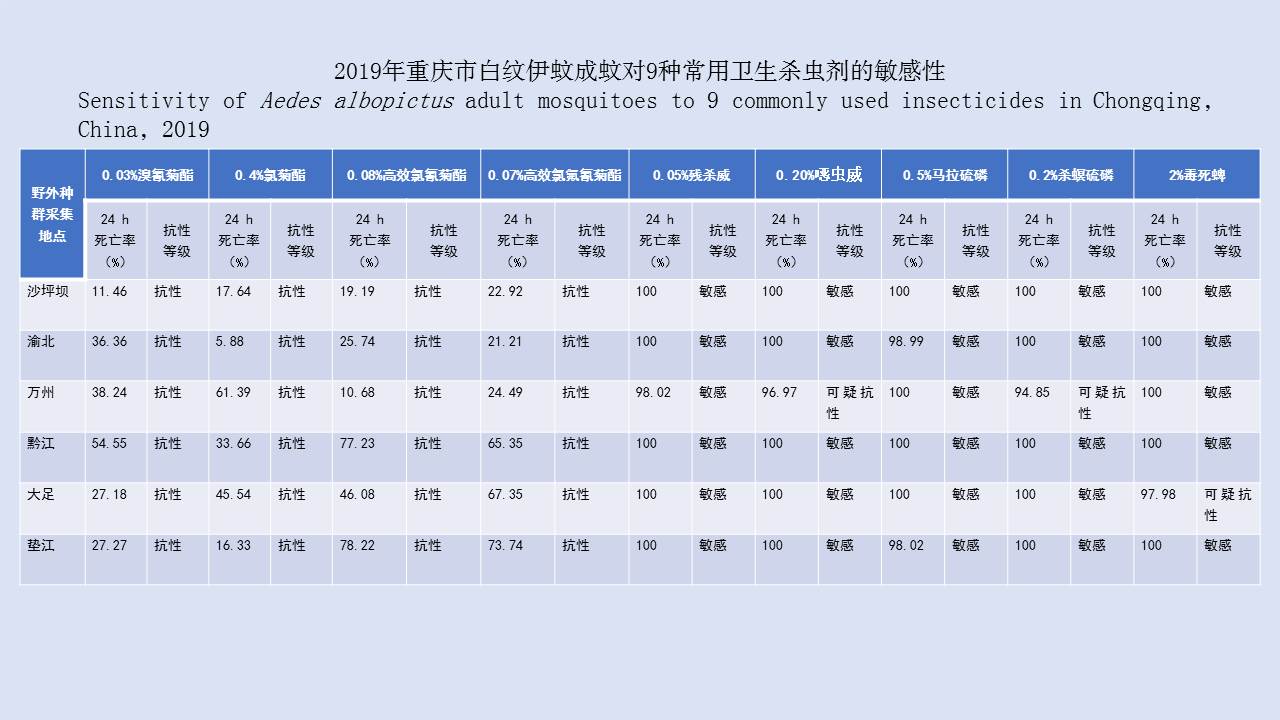
Objective To analyze the ecological surveillance results of Aedes vector in 12 provinces (autonomous regions or municipalities) in China in 2020-2021, and to provide a scientific basis for risk assessment, prediction, early warning, and control of Aedes-borne diseases. Methods The surveillance data of larval and adult Aedes densities at the special investigation sites of Aedes vector in 12 provinces (autonomous regions or municipalities) in China were collected and statistically analyzed by SPSS 18.0 software. Results In 2020-2021, the mean Breteau index (BI) was >10.00 in Hainan, Zhejiang, and Hunan provinces and >5.00 in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (Guangxi) and Yunnan, Henan, and Shandong provinces. The mean mosq-ovitrap index (MOI) was >5.00 in Guangxi, Guangdong, Hainan, and Shandong. The mean net trap index was ≥2.00 mosquitoes/net·hour in Henan, Hubei, and Shandong and >1.00 mosquito/net·hour in Guangxi, Guangdong, Hainan, Yunnan, Fujian, and Hunan. There were no statistical differences in BI, MOI, and net trap index between class I provinces (Guangdong, Hainan, Guangxi, Fujian, Yunnan, and Zhejiang) and other classes of provinces (t=0.766, 1.030, and -0.745, all P>0.05). The mean BI in 2020-2021 was higher than that in 2017-2019 in Guangdong, Guangxi, Yunnan, and Shandong, but lower than that in the three years in other provinces. The Aedes vector was found to be active throughout the year at the investigation sites in Guangdong, Hainan, Guangxi and Yunnan, from March to December in Fujian, Zhejiang, and Hubei, and from April to November in Chongqing municipality, Shandong and Henan, and from April to December in Jiangxi. The results of BI and MOI were inconsistent in Yunnan, Guangxi, and Hubei. During the study period, the BI of Aedes vector was >5.00 in areas where dengue outbreaks and local cases occurred, and >10.00 in Ruili city in Yunnan, Cenxi city of Wuzhou in Guangxi, and Sanjiao town of Zhongshan in Guangdong; the net trap index in Cenxi city of Guangxi was >2.00 mosquitoes/net·hour. Conclusion In 2020-2021, the mean Aedes density in the provinces with local cases of dengue fever in China was high, with spatio-temporal heterogeneity among different regions. It is suggested that in the local transmission areas of dengue in China, it is necessary to adjust moderately annual surveillance periods, to continuously strengthen Aedes vector surveillance and risk assessment, and to systematically sort out the ecological investigation results of Aedes vector, so as to provide a scientific basis for the revision and improvement of Aedes vector surveillance scheme and the outbreak control of Aedes-borne diseases in China.