 PDF(915 KB)
PDF(915 KB)


浙江省衢州市农村地区2020-2021年小兽分布及其病原体携带情况调查
钟建跃, 王金娜, 杨辉, 曹国平, 吴瑜燕, 陈韦华, 余樟有, 方春福
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6) : 805-808.
 PDF(915 KB)
PDF(915 KB)
 PDF(915 KB)
PDF(915 KB)
浙江省衢州市农村地区2020-2021年小兽分布及其病原体携带情况调查
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}An investigation of small mammal distribution and their infection with pathogens in rural areas of Quzhou, Zhejiang province, China
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}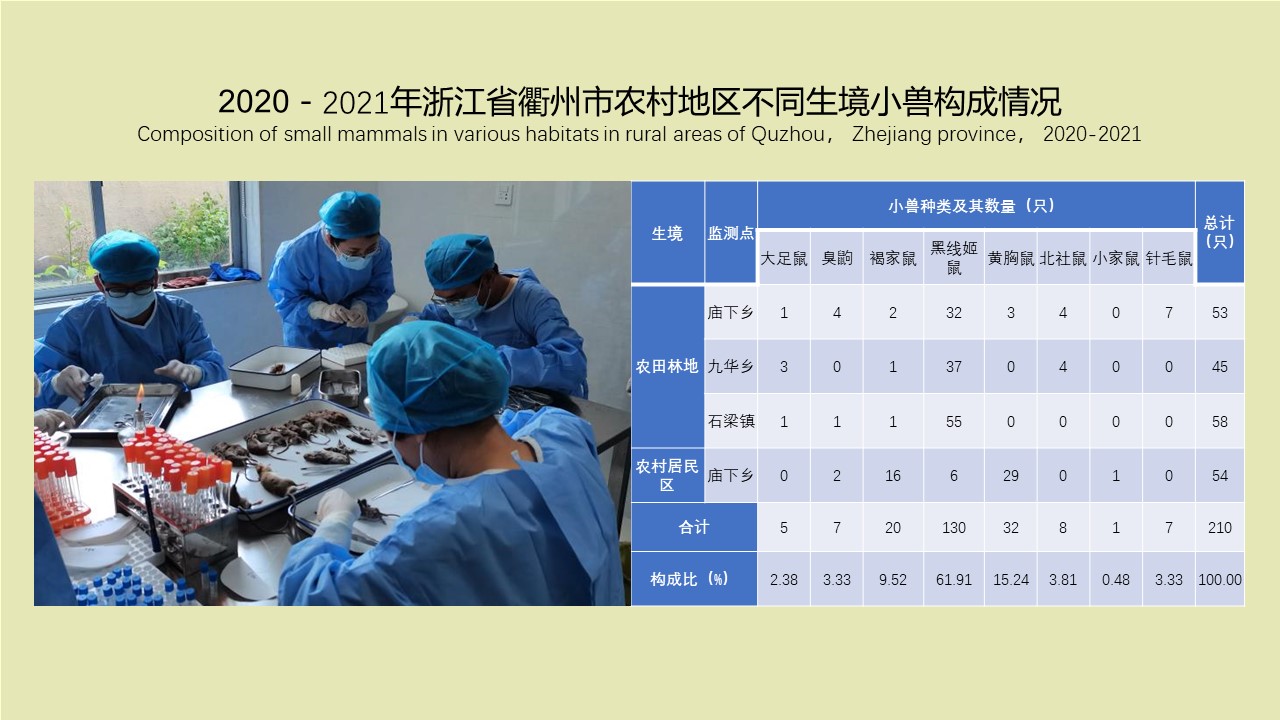
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |