 PDF(758 KB)
PDF(758 KB)


山西省东南部地区鼠传病原体流行状况研究
于娟, 边香, 谢冰, 赵永波, 毕格越, 杜夏延, 毕丽芳, 栗冬梅, 饶华祥
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2) : 211-215.
 PDF(758 KB)
PDF(758 KB)
 PDF(758 KB)
PDF(758 KB)
山西省东南部地区鼠传病原体流行状况研究
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Prevalence of rodent-borne pathogens in the southeast of Shanxi province, China
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}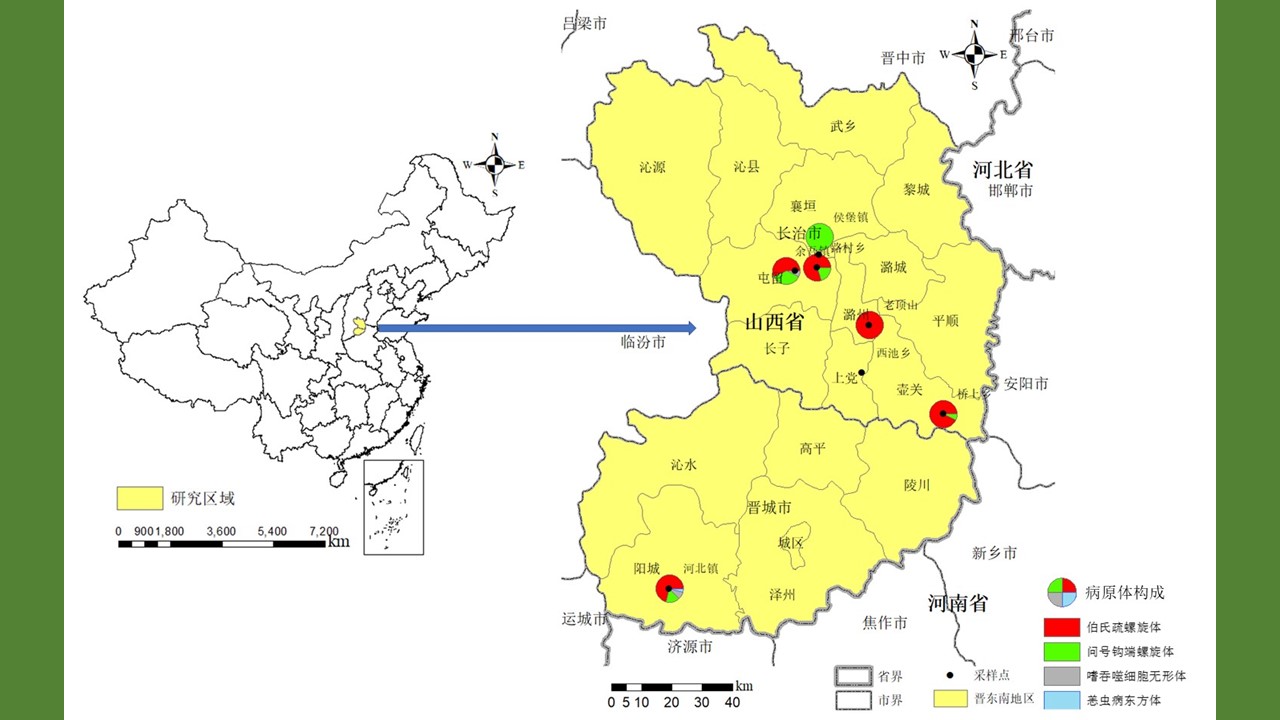
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |