 PDF(1251 KB)
PDF(1251 KB)


云南省2020年肾综合征出血热病例分析和部分地区宿主动物调查
杨卫红, 杨晓龙, 杨丽芬, 邝国鹏, 李华昌, 潘虹, 王娟, 韩茜, 冯云
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3) : 394-399.
 PDF(1251 KB)
PDF(1251 KB)
 PDF(1251 KB)
PDF(1251 KB)
云南省2020年肾综合征出血热病例分析和部分地区宿主动物调查
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Case analysis of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and investigation of host animals in Yunnan province in 2020
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}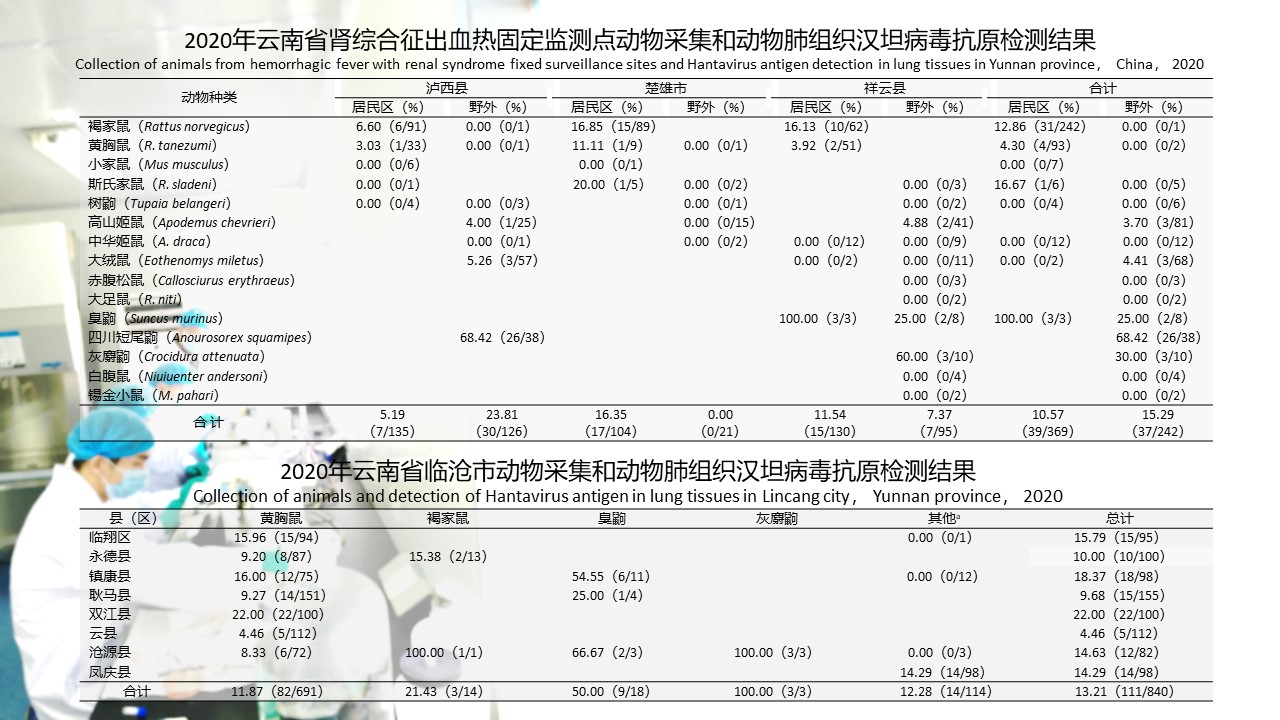
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |