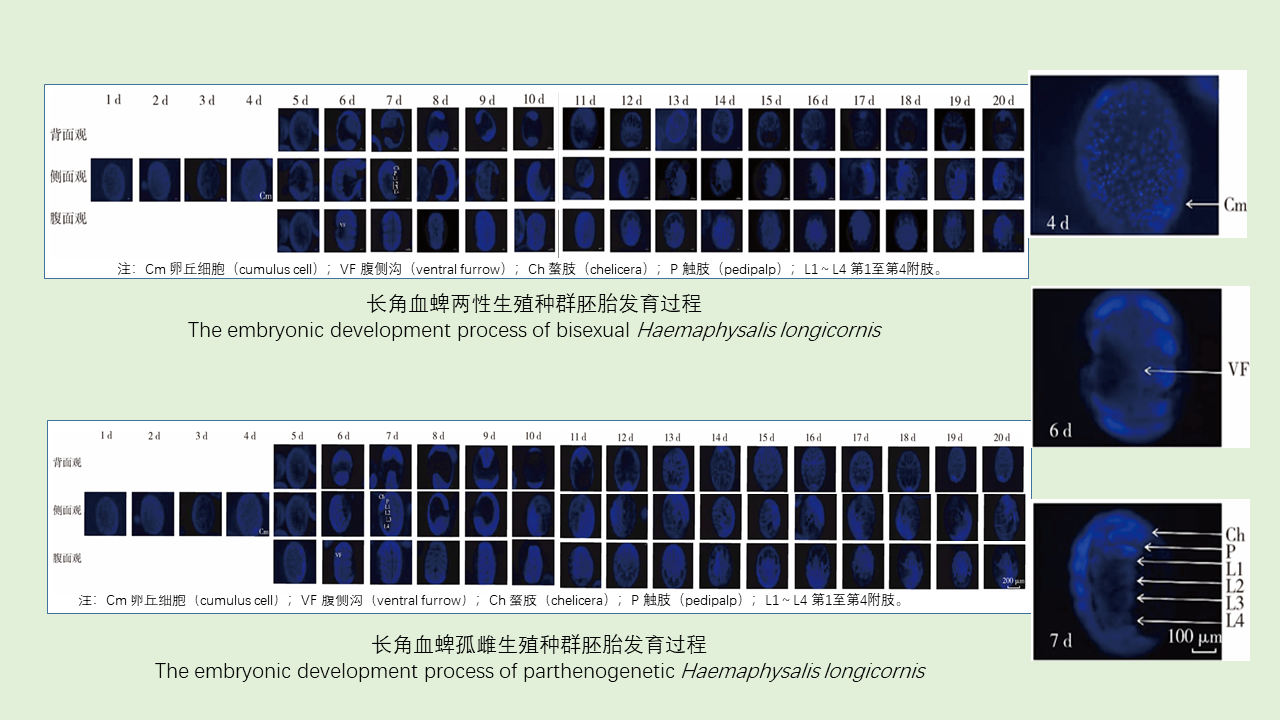
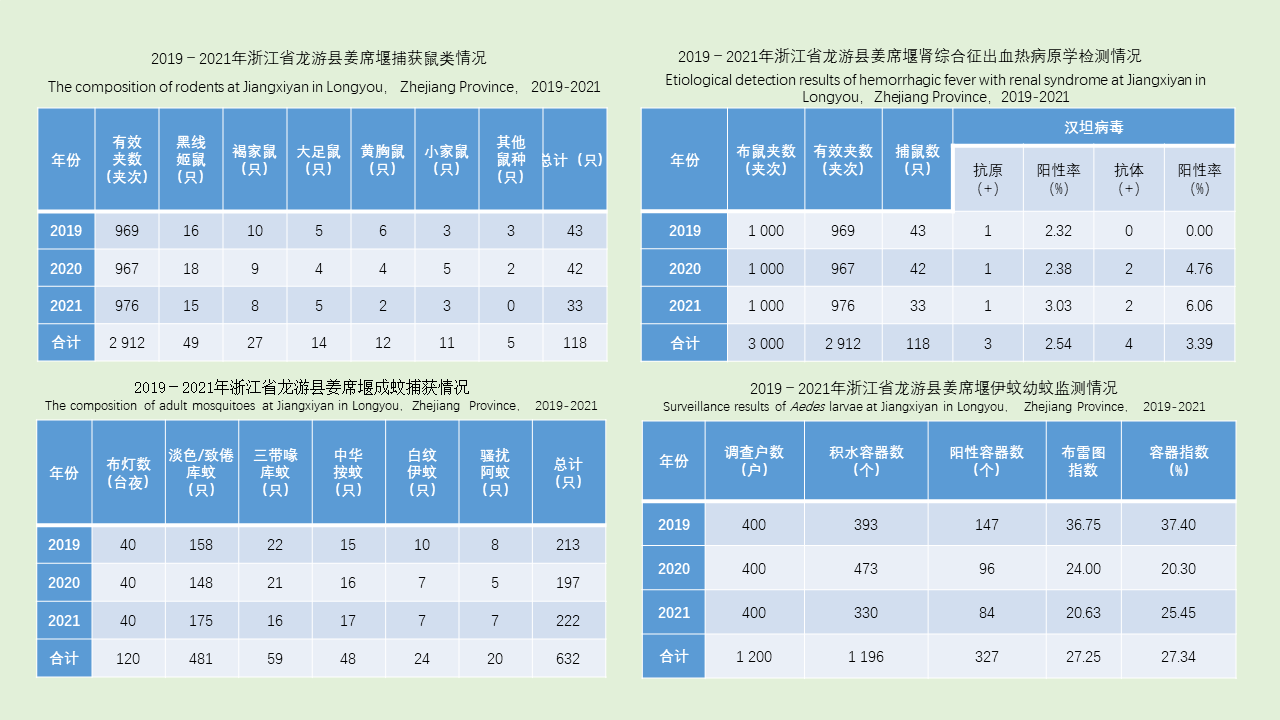
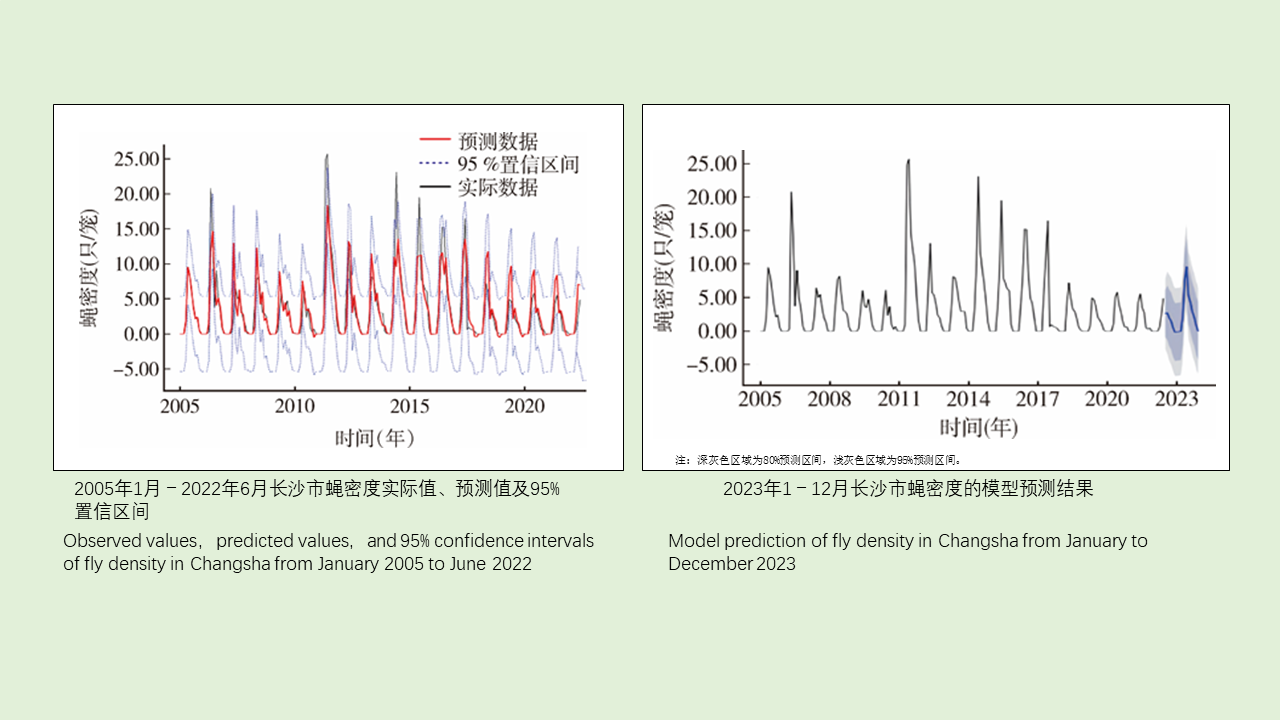
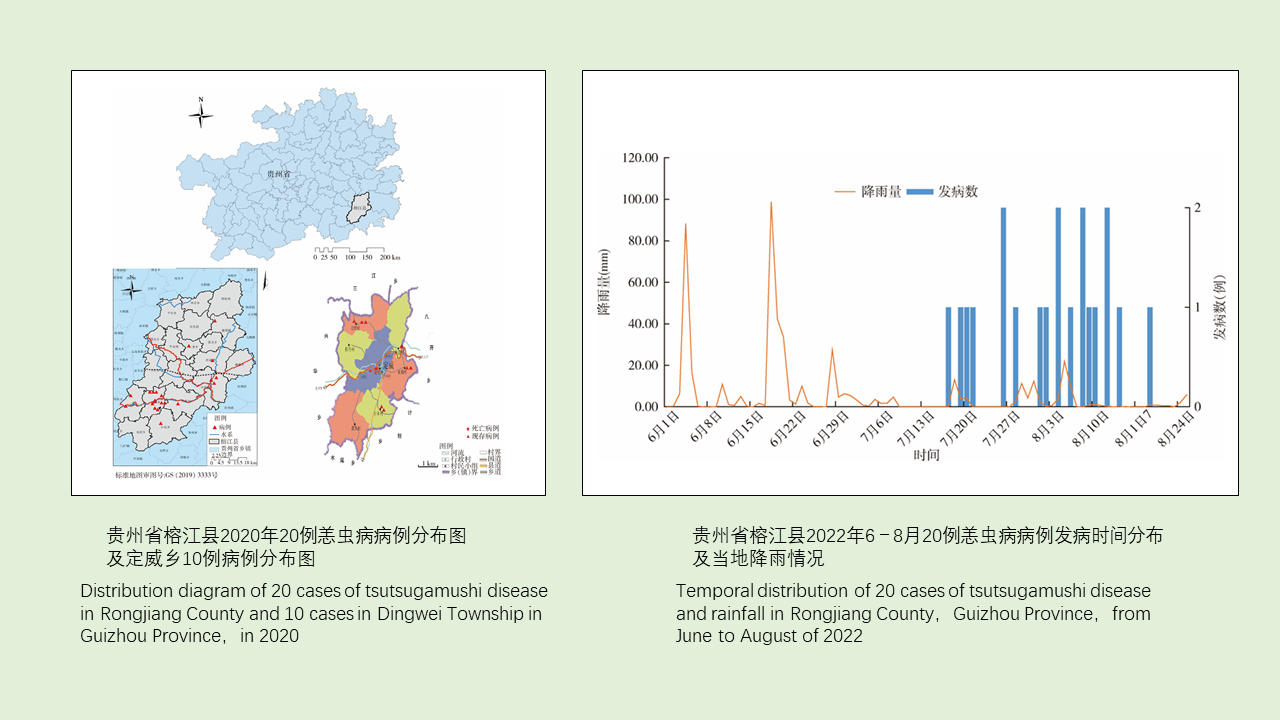
HOU Yin-xu, ZHANG Yan-jie, WANG Wen-jun, YANG Feng-tao, LIU Xiao-bo, MENG Feng-xia, XU Qing-hua
Objective To investigate the resistance levels of the dengue vector Aedes albopictus collected in 2021 to commonly used insecticides in Hefei, Anhui Province, China, so as to provide a scientific basis for the control of Aedes vectors and the formulation of standardized insecticide use strategies.Methods The resistance levels of Ae. albopictus collected in 2021 to commonly used insecticides were determined using the dipping method for larvae and the WHO tube method for adult mosquitoes. Using the Probit module of SPSS 22.0 software, the data from the bioassays were analyzed for the toxicity regression equation, Chi-squared value, median lethal concentration (LC50), and 95% confidence interval (CI). The mortality rate and resistance ratio were calculated to evaluated the resistance level.Results In 2021, the LC50 values of propoxur, temephos, dichlorvos, chlorpyrifos, Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti), permethrin, deltamethrin, and beta-cypermethrin against Ae. albopictus larvae in Hefei were 2.984, 0.015, 0.055, 0.004, 0.037 (259 ITU/L), 0.235, 0.103, and 0.019 mg/L, respectively. The resistance ratios were 8.29, 9.25, 0.91, 0.33, 0.84, 117.79, 257.50, and 21.13 times, respectively. Ae. albopictus larvae in Hefei were sensitive to Bti, dichlorvos, and chlorpyrifos, lowly resistant to propoxur and temephos, moderately resistant to beta-cypermethrin, and highly resistant to permethrin and deltamethrin. Adult Ae. albopictus mosquitoes in Hefei were resistant to fenitrothion and deltamethrin (24 h mortality: 21.43% and 71.60%, respectively), sensitive to chlorpyrifos and bendiocarb (24 h mortality: 100%), and possibly resistant to permethrin, beta-cypermethrin, lambda-cyhalothrin, propoxur, and malathion.Conclusions Chlorpyrifos can be used for the control of adult Ae. albopictus, while temephos and Bti can be used as the first-choice insecticides for larval control. Bendiocarb can be combined or mixed with the sensitive pyrethroids for adult mosquito control in key environments. The use of pyrethroids and fenitrothion should be reduced to delay the development of resistance and gradually restore sensitivity.