 PDF(572 KB)
PDF(572 KB)


1901-2020年新疆维吾尔自治区鼠疫流行和防控回顾性分析
贵有军, 王信惠, 王启果, 张晓兵, 王诚, 李冰, 古丽阿依·包开西, 罗勇军, 王效俊
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6) : 843-848.
 PDF(572 KB)
PDF(572 KB)
 PDF(572 KB)
PDF(572 KB)
1901-2020年新疆维吾尔自治区鼠疫流行和防控回顾性分析
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}A retrospective analysis of plague prevalence and control in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China, 1901-2020
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}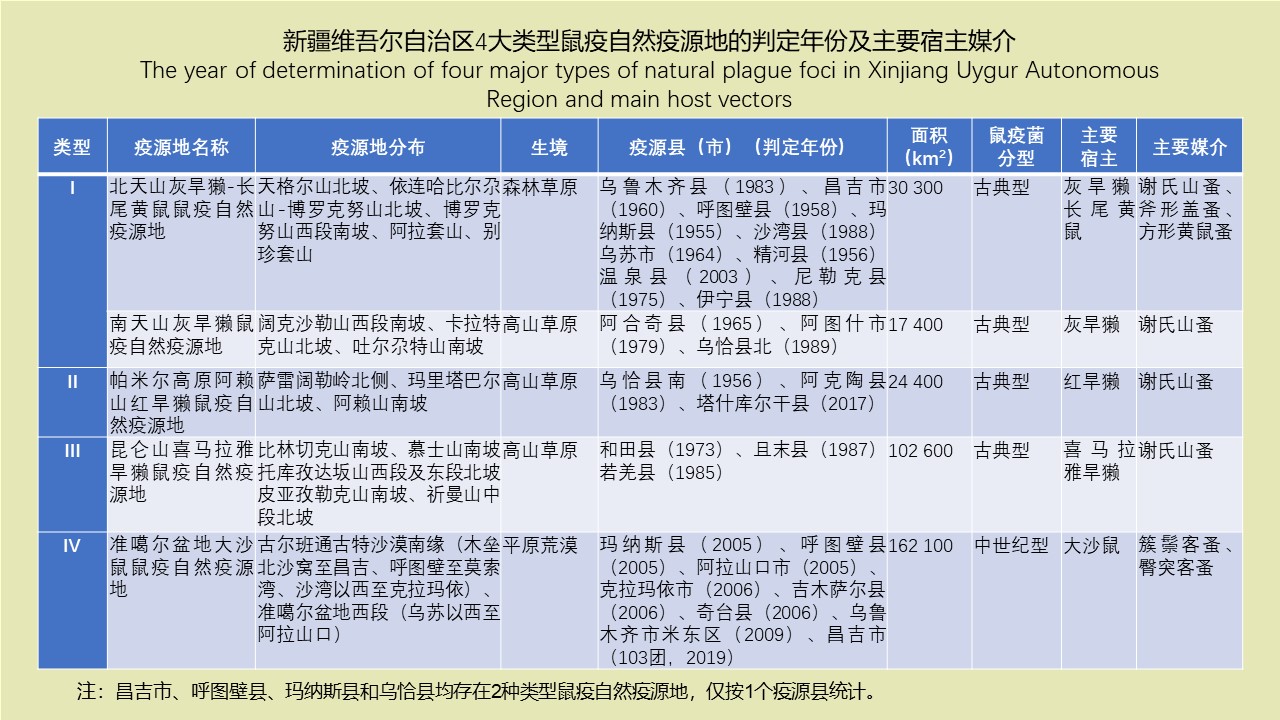
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |