 PDF(1541 KB)
PDF(1541 KB)


广西壮族自治区2016-2020年登革热流行特征分析
王晶, 罗飞, 何为涛, 蒋丽娜, 张超, 林玫, 曾竣
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1) : 65-69.
 PDF(1541 KB)
PDF(1541 KB)
 PDF(1541 KB)
PDF(1541 KB)
广西壮族自治区2016-2020年登革热流行特征分析
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Epidemiological characteristics of dengue fever in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China, 2016-2020
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}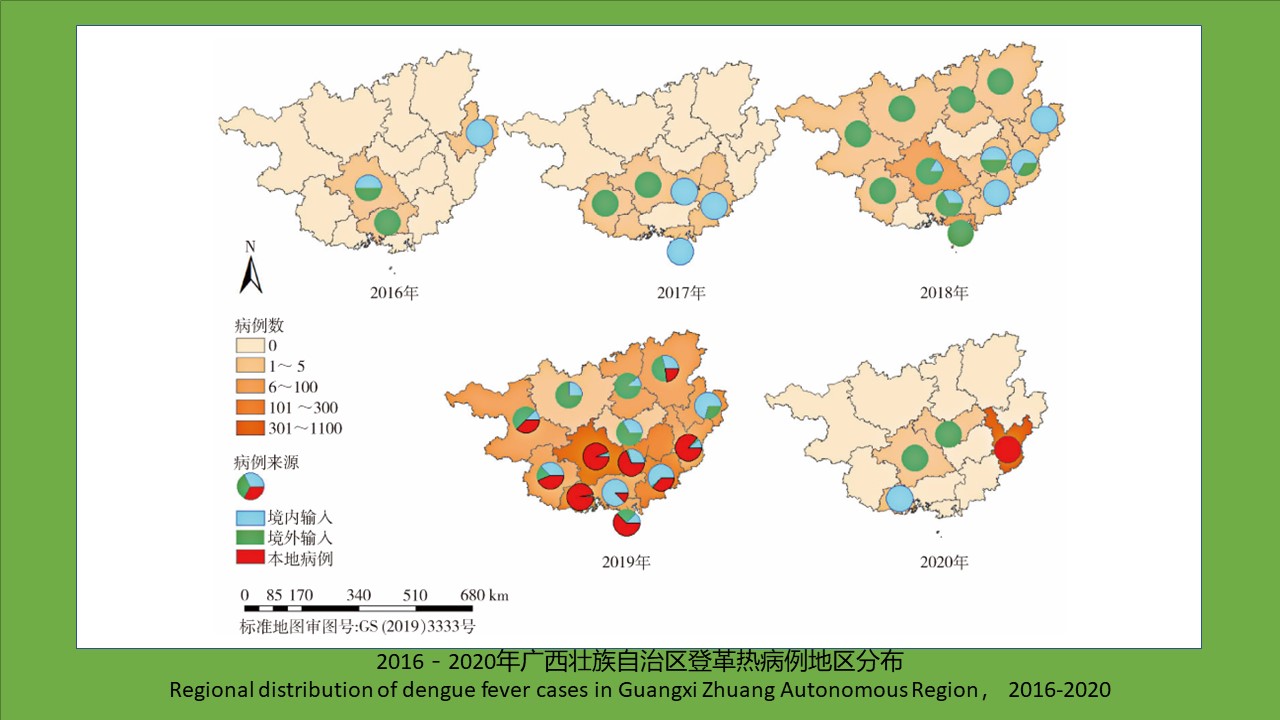
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |