 PDF(1475 KB)
PDF(1475 KB)


青海省三江源地区1958-2021年人间鼠疫流行特征分析
蒋可, 熊浩明, 田富彰, 何多龙, 张爱萍, 杨建国, 李翔, 郭文涛, 李伟
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6) : 838-842.
 PDF(1475 KB)
PDF(1475 KB)
 PDF(1475 KB)
PDF(1475 KB)
青海省三江源地区1958-2021年人间鼠疫流行特征分析
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Epidemiological characteristics of human plague in the Sanjiangyuan region, Qinghai province, China, 1958-2021
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}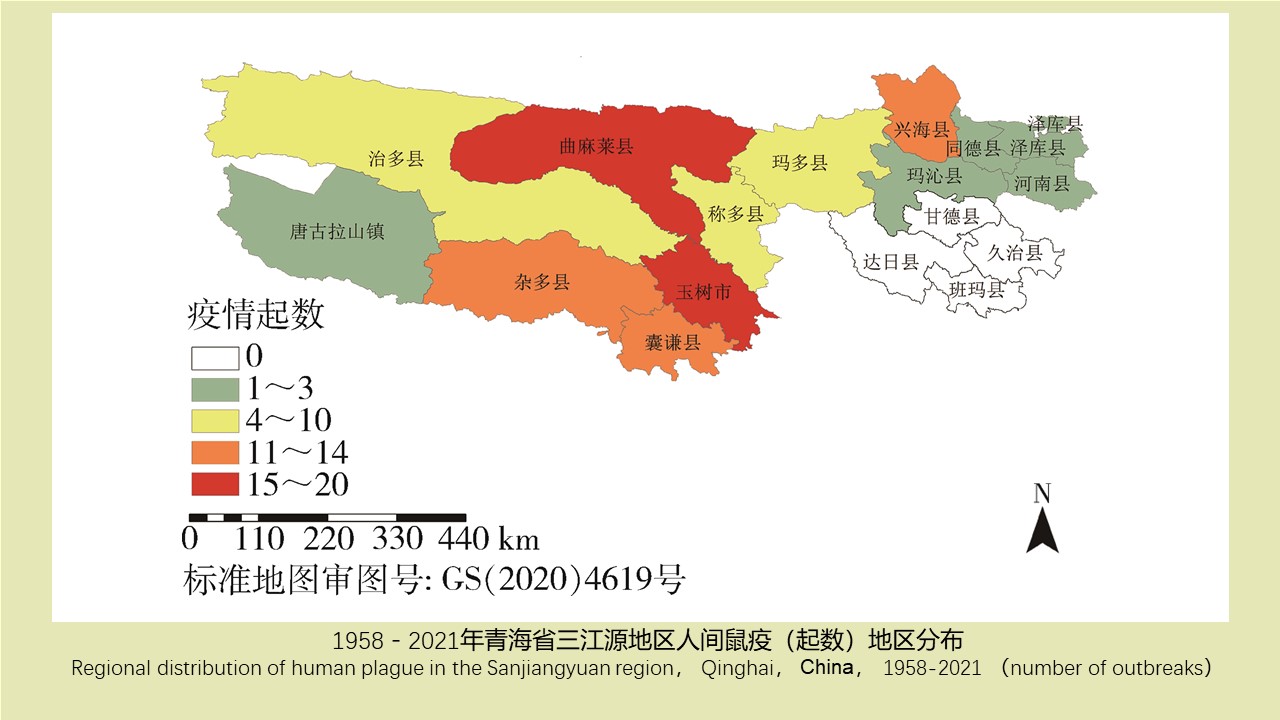
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |