 PDF(2509 KB)
PDF(2509 KB)


云南省西双版纳州2006-2020年登革热流行特征及媒介伊蚊监测分析
范建华, 高阳, 朱进, 黄强, 李俊明, 苏梅惠, 张海林
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2) : 245-251.
 PDF(2509 KB)
PDF(2509 KB)
 PDF(2509 KB)
PDF(2509 KB)
云南省西双版纳州2006-2020年登革热流行特征及媒介伊蚊监测分析
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Epidemiological characteristics of dengue fever and surveillance results of Aedes mosquitoes in Xishuangbanna Prefecture, Yunnan province, China, 2006-2020
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}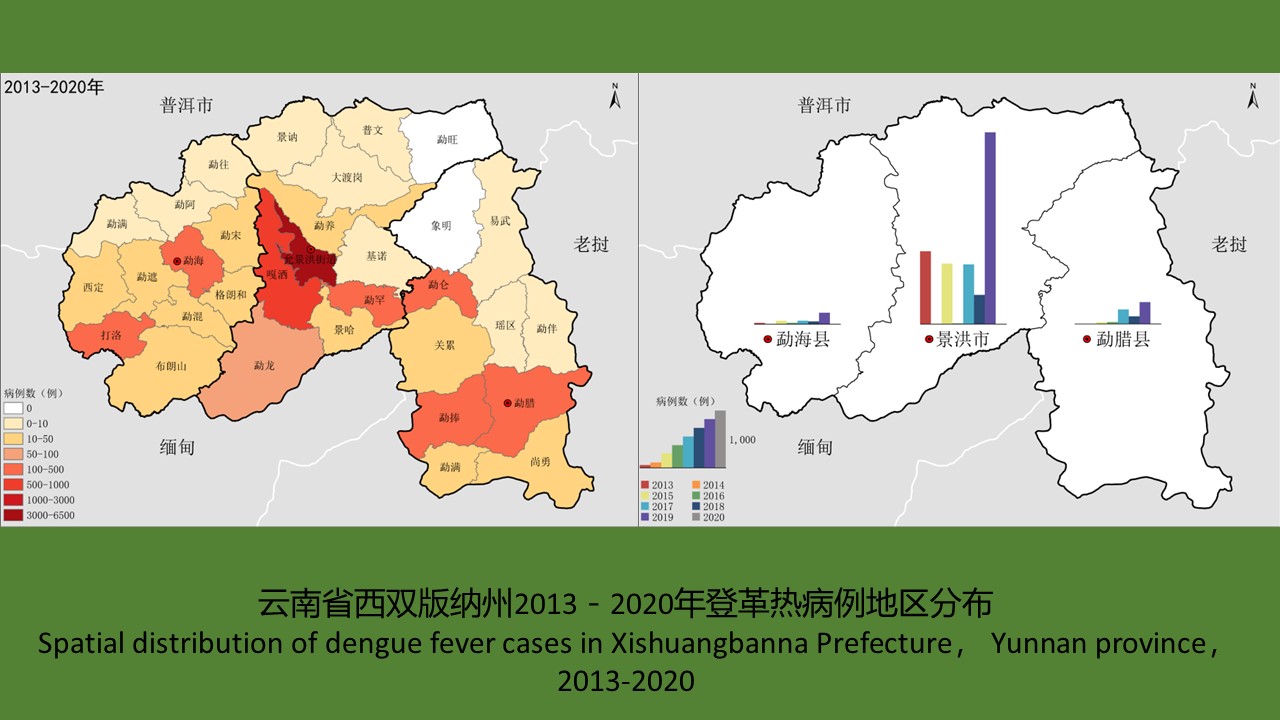
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |