 PDF(5760 KB)
PDF(5760 KB)


白纹伊蚊性别差异miRNA筛选及miRNA-mRNA调控网络分析
刘文娟, 张可心, 程鹏, 张心雨, 张倩, 张忠, 张瑞玲
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2) : 191-200.
 PDF(5760 KB)
PDF(5760 KB)
 PDF(5760 KB)
PDF(5760 KB)
白纹伊蚊性别差异miRNA筛选及miRNA-mRNA调控网络分析
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Deciphering sex differentially expressed miRNAs and miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks of Aedes albopictus
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}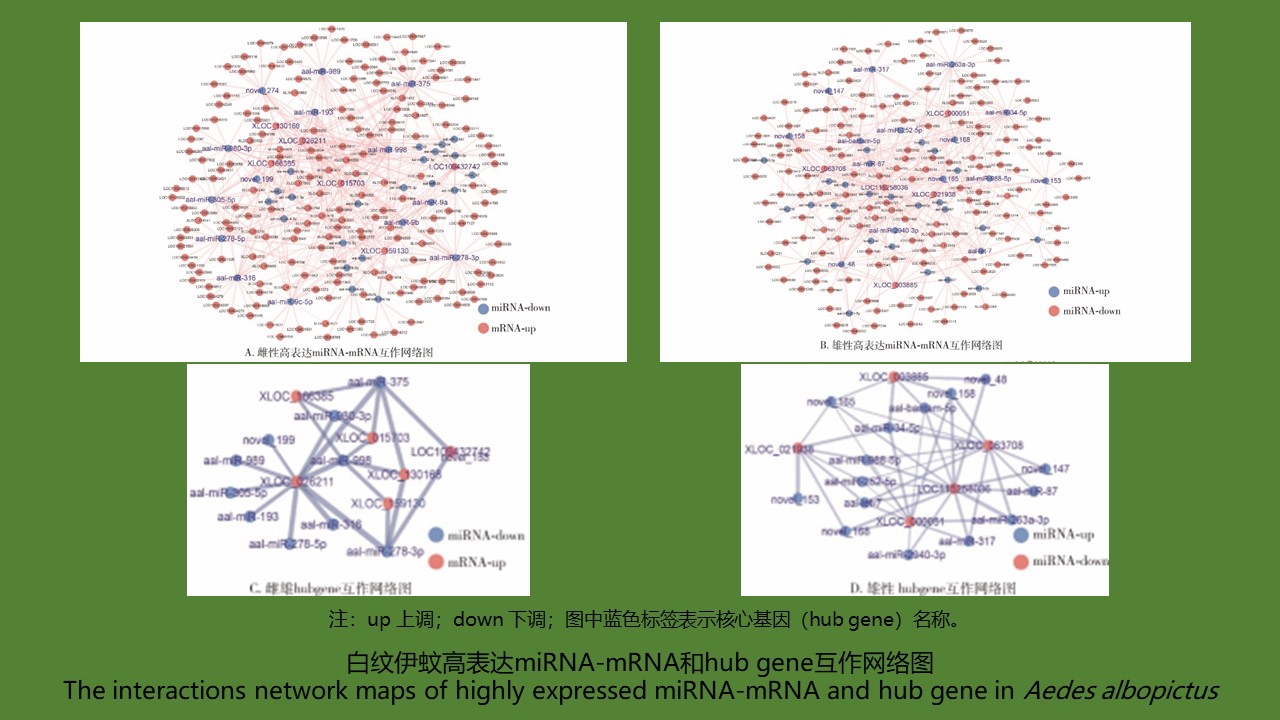
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |