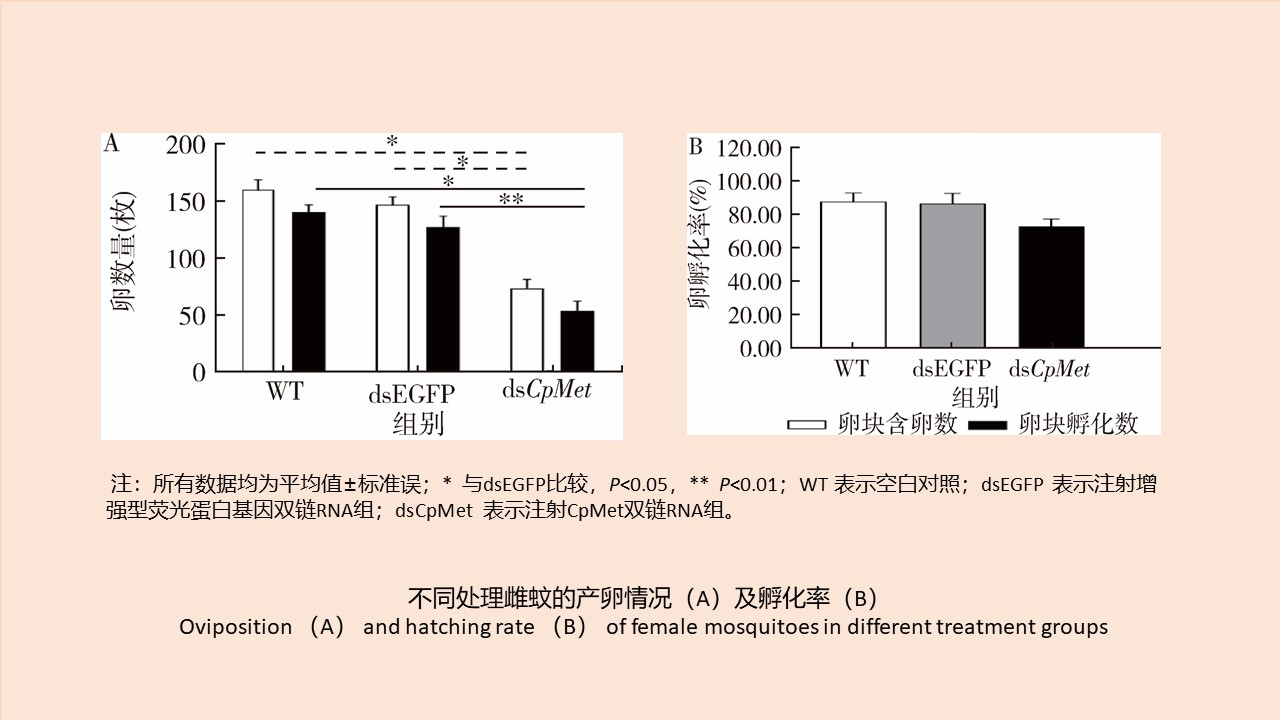
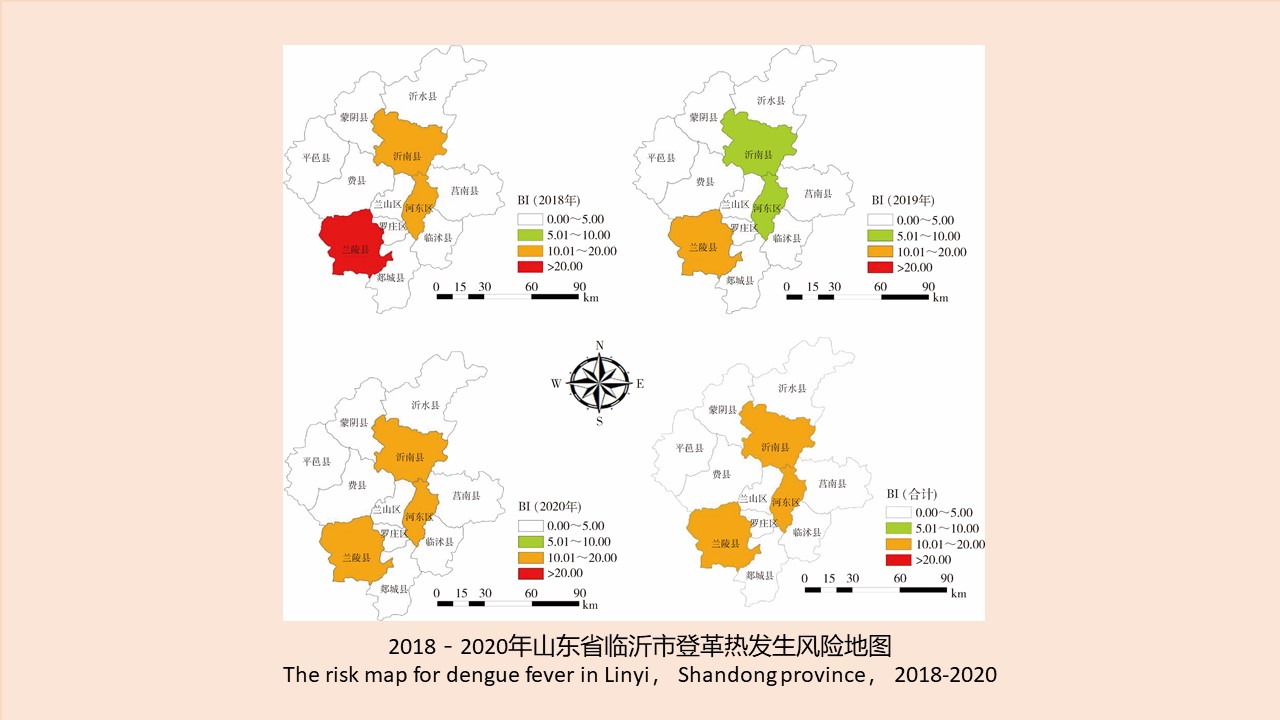
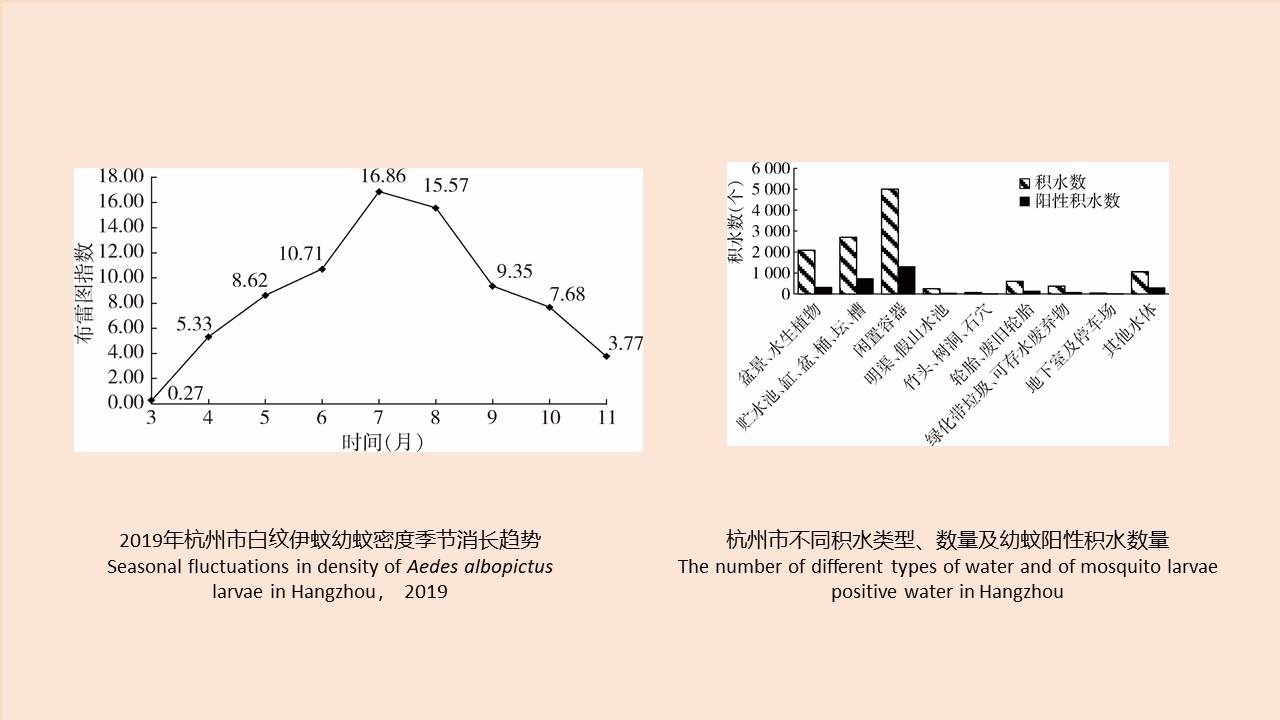
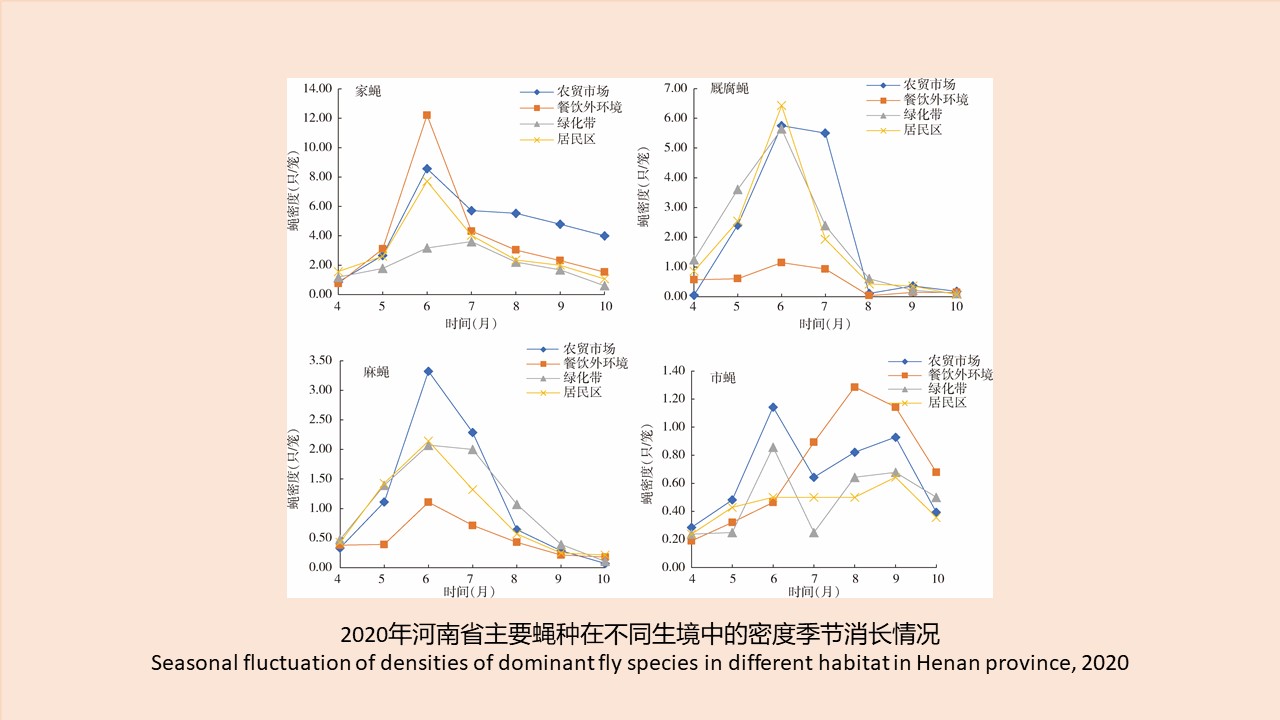
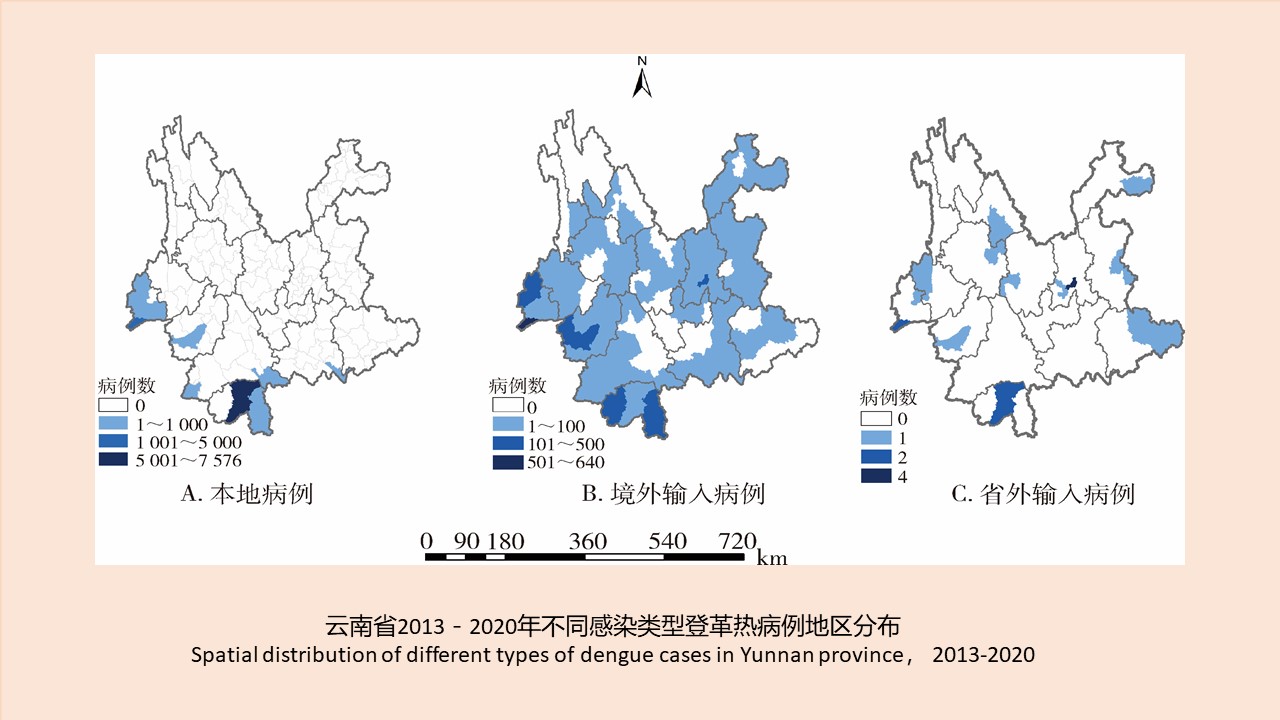
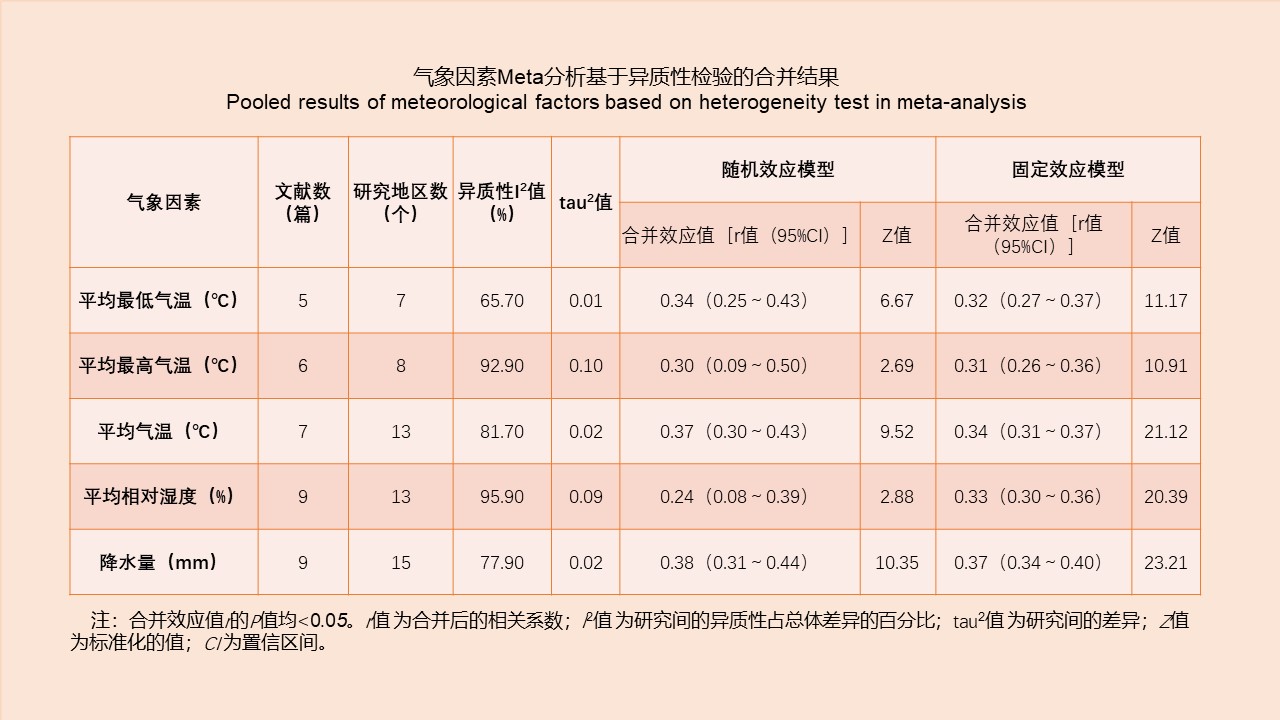
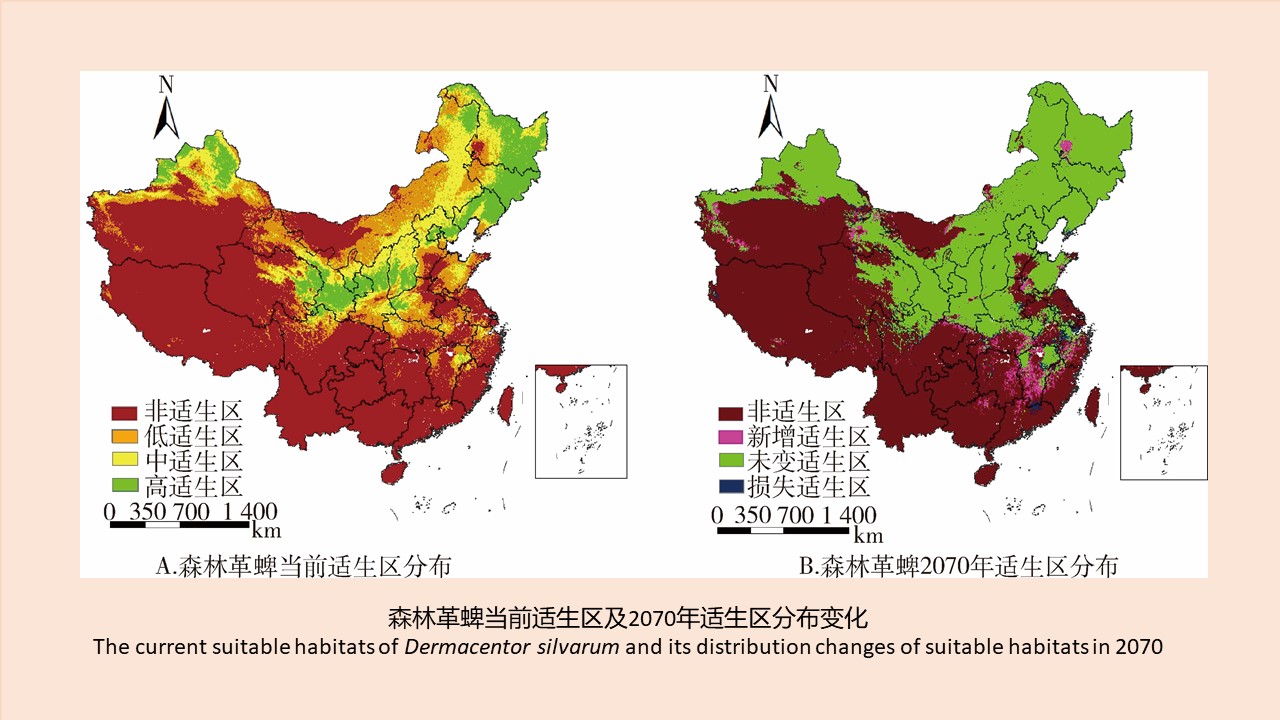
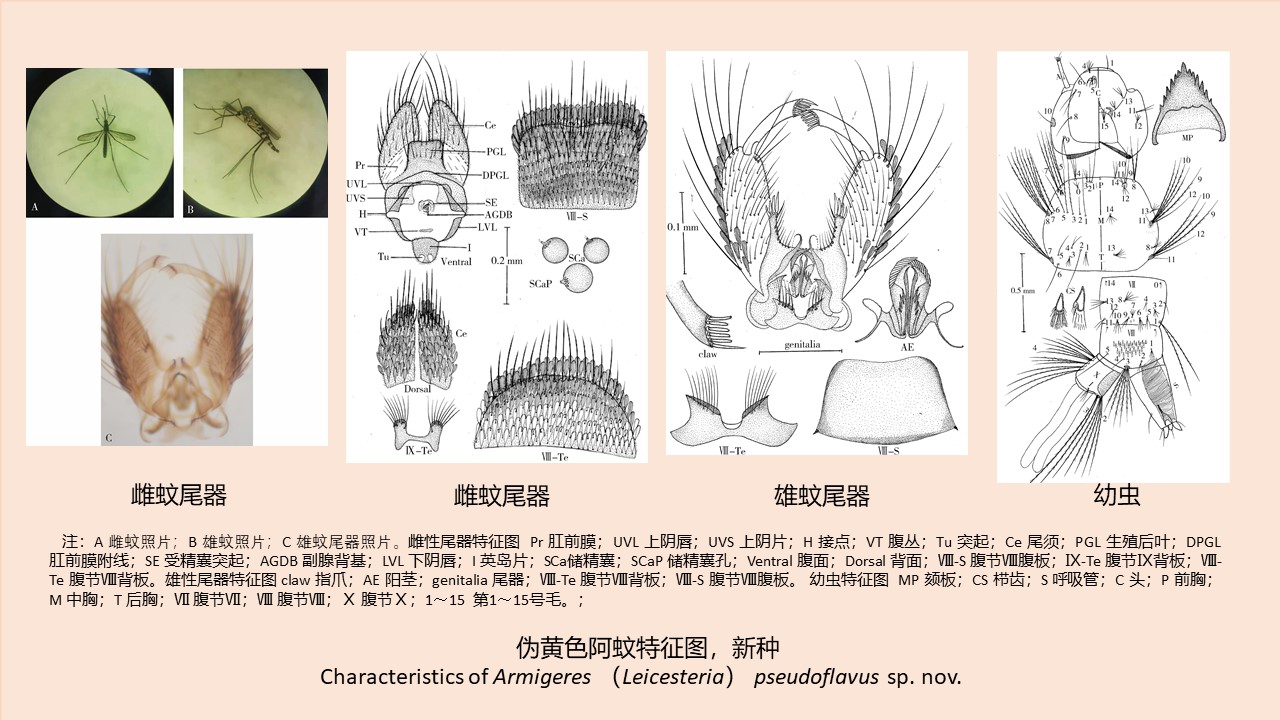
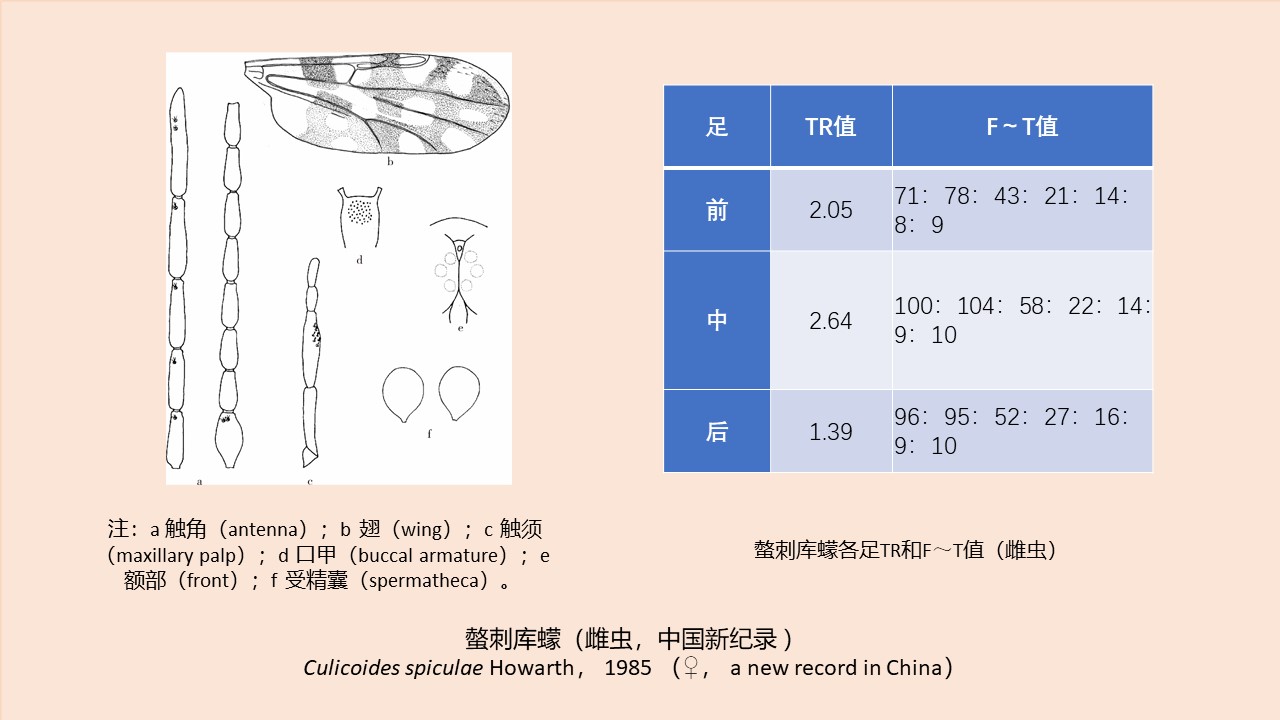
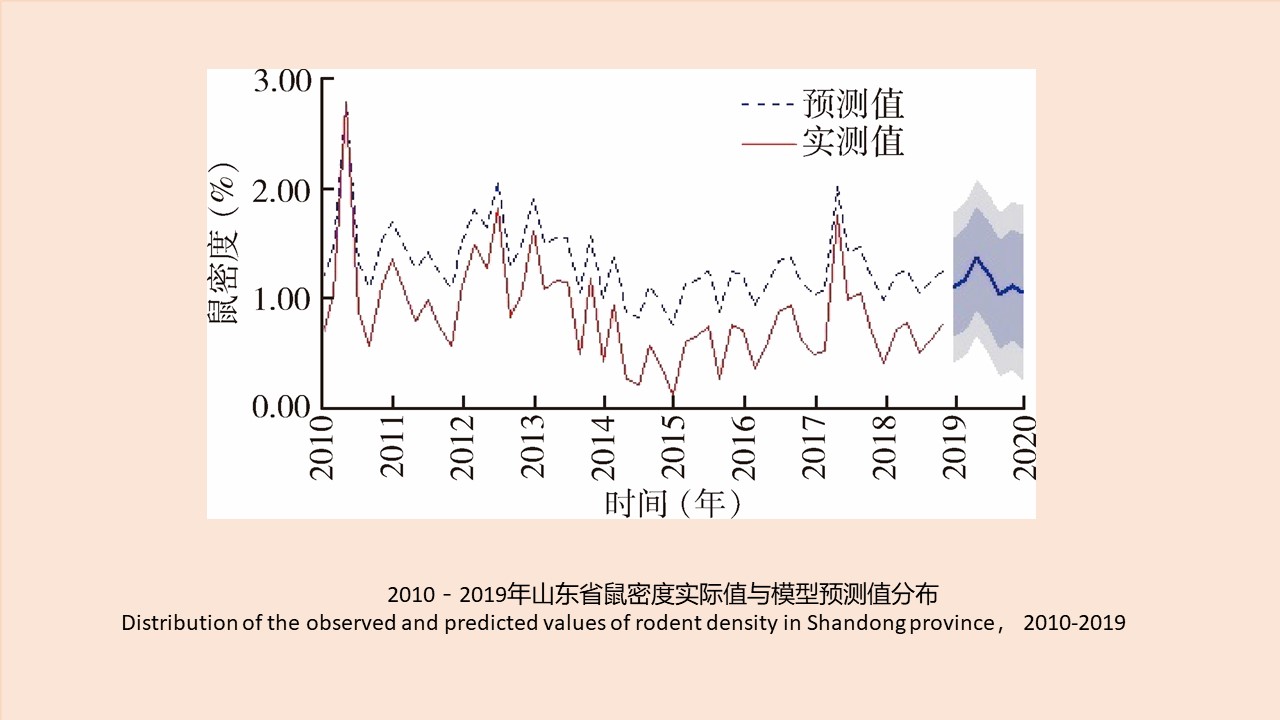
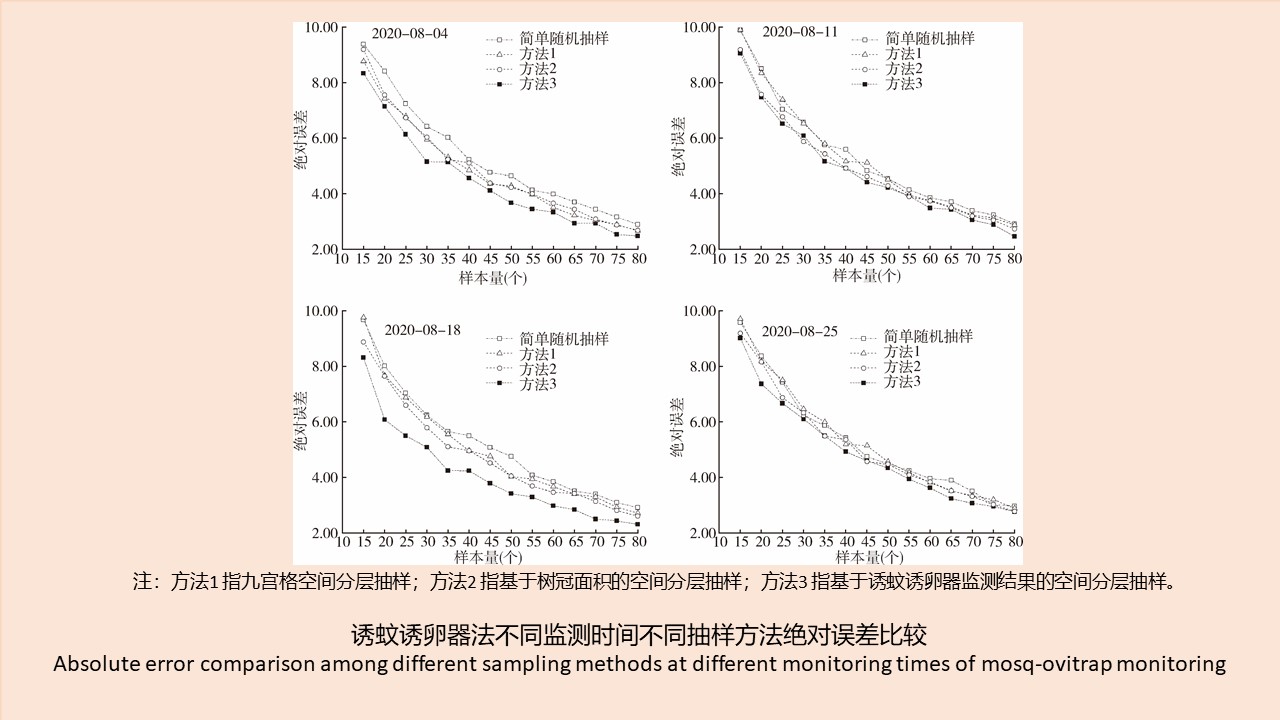
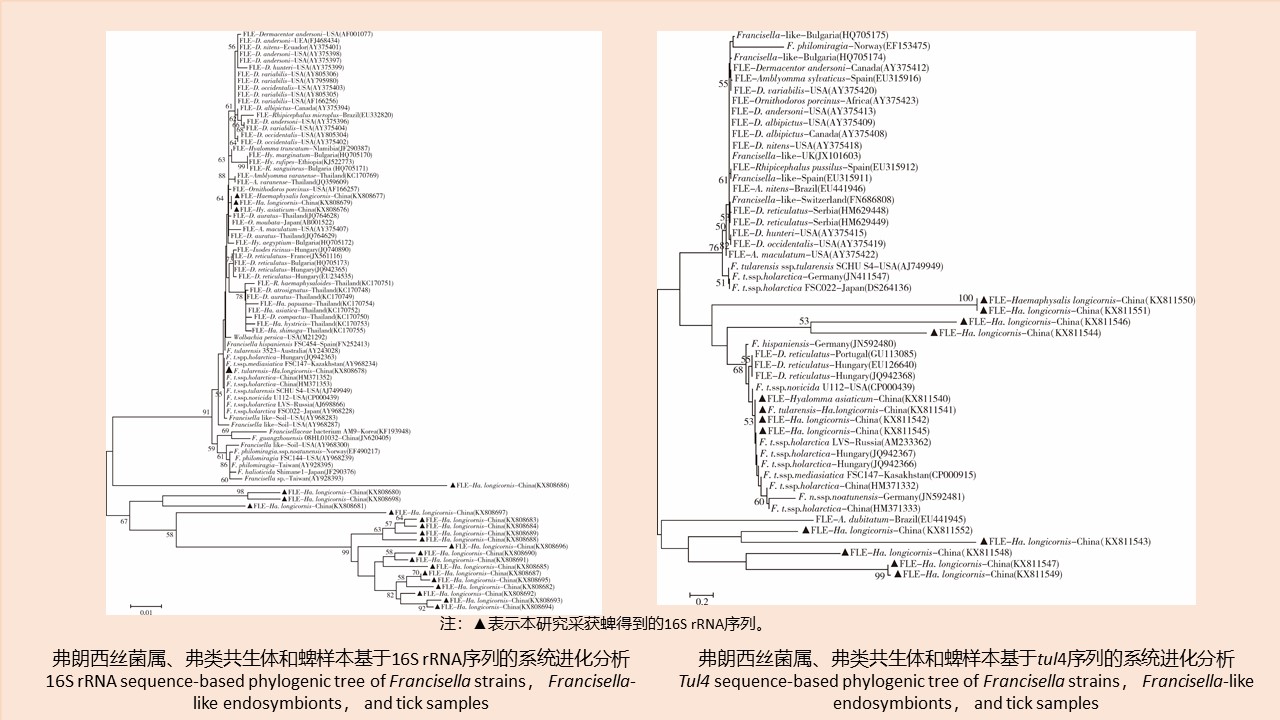
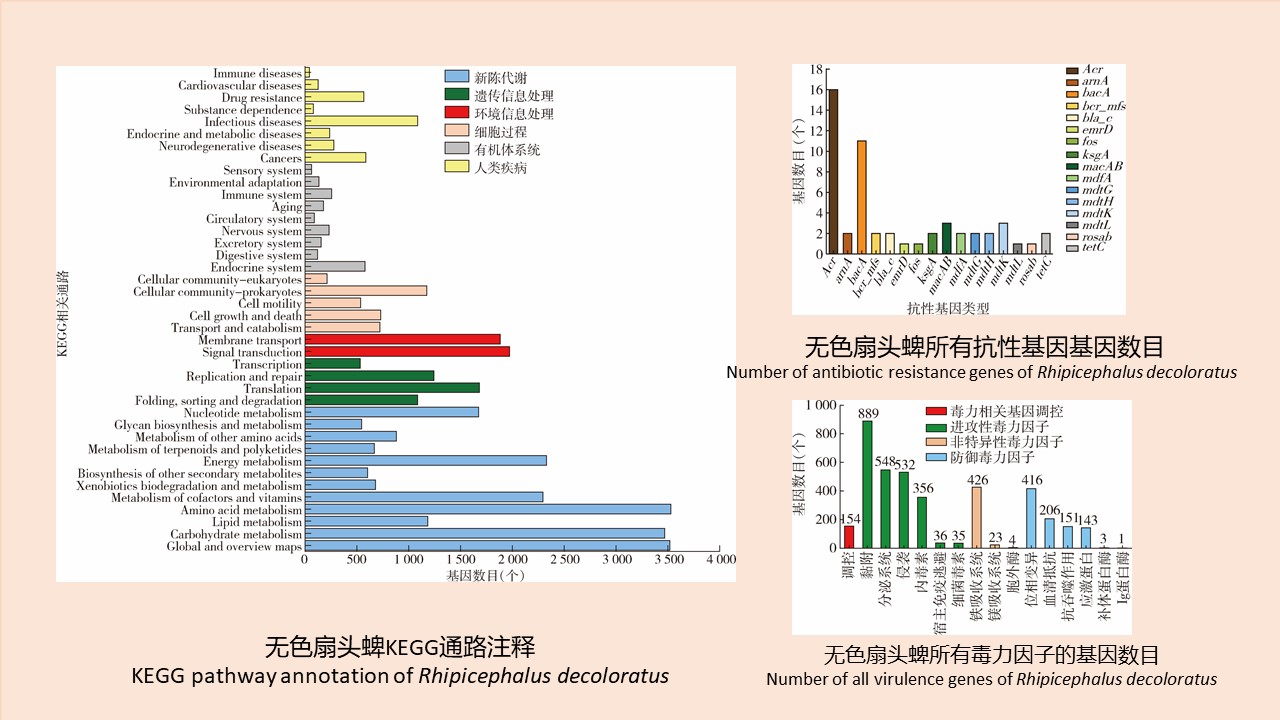
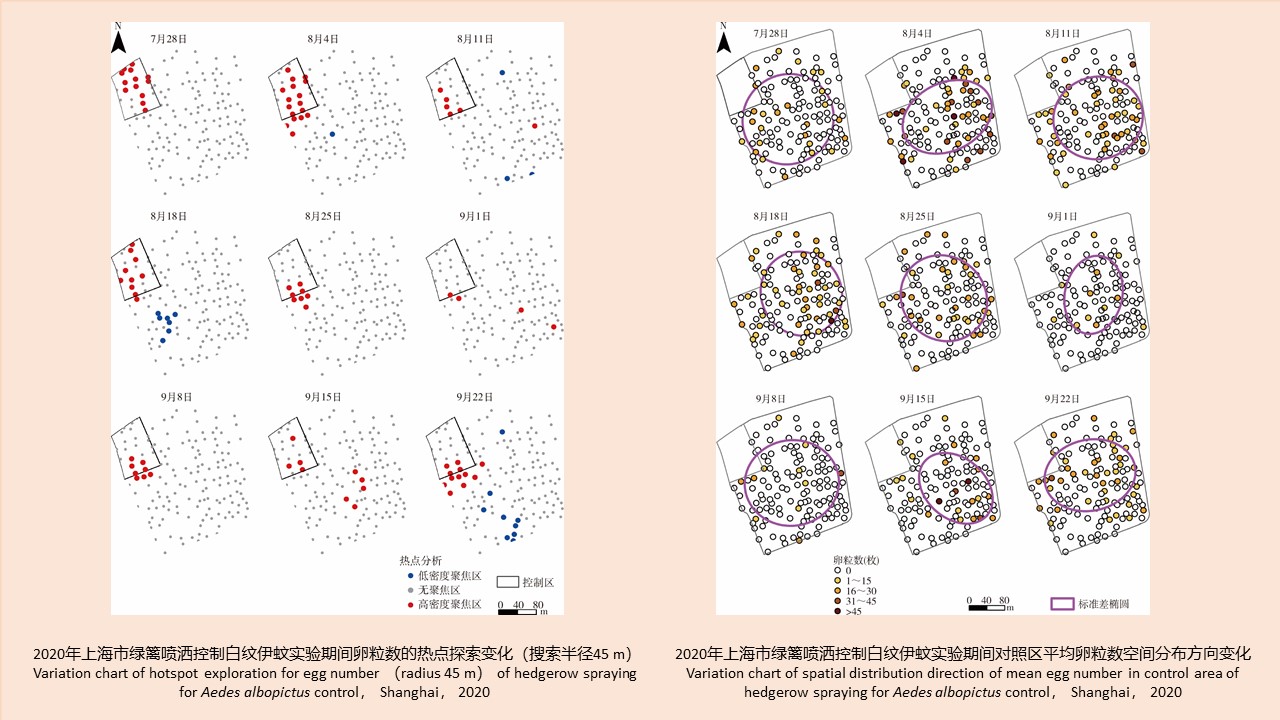
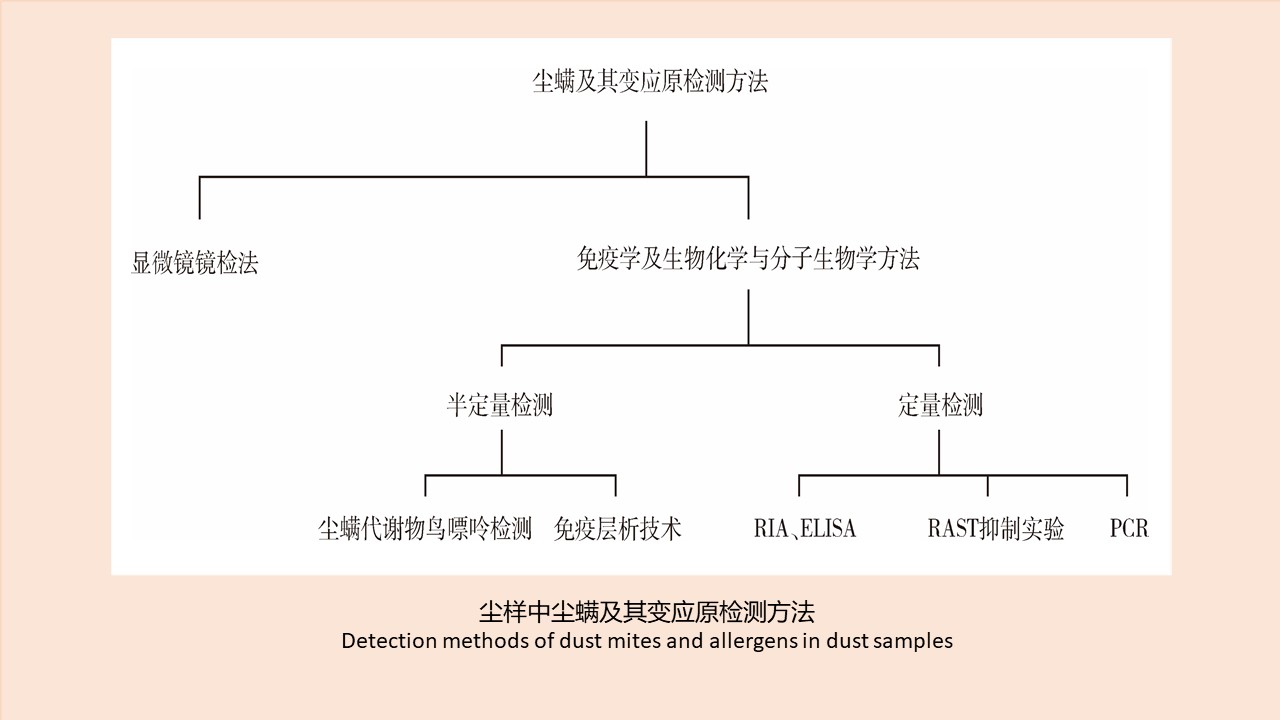
CAO Yang, WEI Ling-ya, SHAO Han-wen, WANG Hui-min, KONG Qing-xin
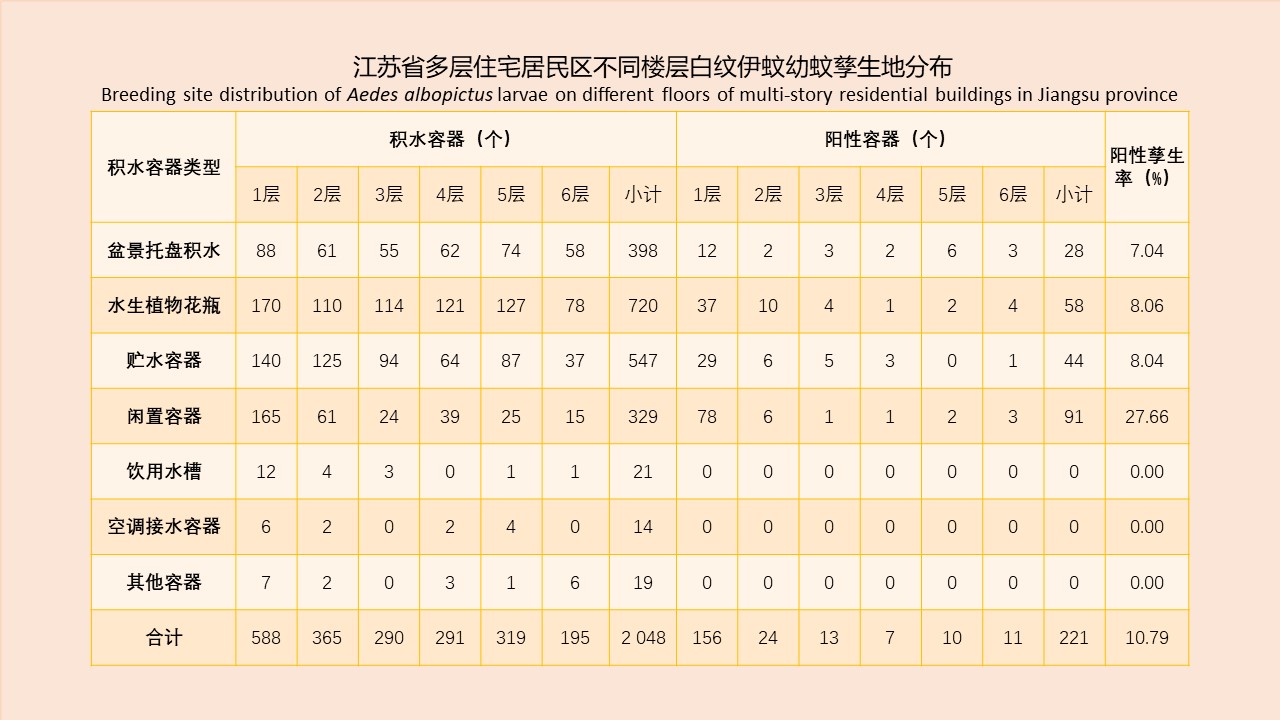
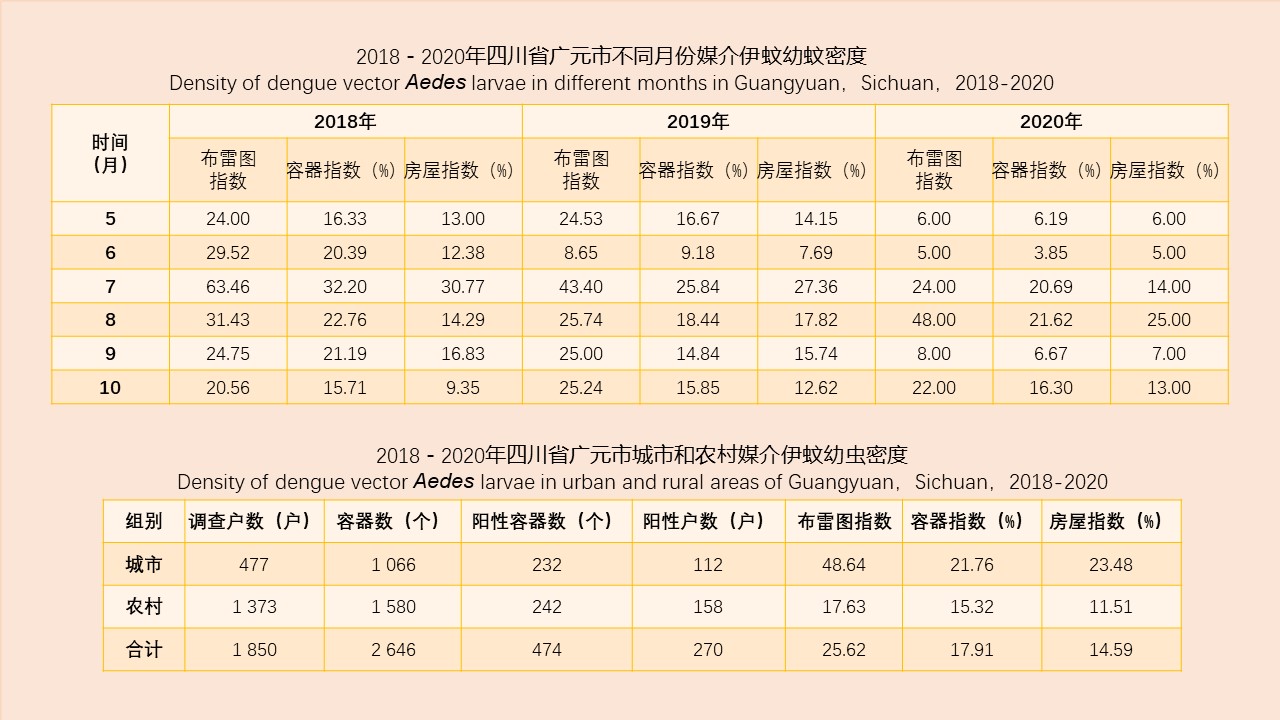
Objective To investigate the species composition, the mixed population density, and seasonal variation of vector mosquitoes in Hangzhou, Zhejiang province, China, 2019, and to provide a reference for the prevention and control of mosquito-borne diseases. Methods In 2019, 15 districts (counties or county-level cities) of Hangzhou carried out mosquito surveillance according to the "National Vector Surveillance Implementation Plan" and "Vector Surveillance Program in Zhejiang". The national surveillance sites included Shangcheng district, Xiacheng district, Gongshu district, Jianggan district, and Xihu district; The provincial surveillance sites included Yuhang district and Jiande city; the other districts were routine surveillance sites. Adult mosquitoes were monitored from April to November, and the larvae from March to November. Adult mosquitoes were monitored using the light trap method (twice a month at the national and provincial surveillance sites and once a month at the routine surveillance sites) and double mosquito net method (twice a month at the national surveillance sites and once a month at the other surveillance sites). Larval mosquitoes were monitored using the Breteau index (BI) method (twice a month at the provincial surveillance sites and once a month at the other surveillance sites). The monitoring data of the 15 districts (counties or county-level cities) were collected and analyzed using Excel 2019 software. The mosquito density, net trapping index, and BI were computed. Results In 2019, Culex pipiens pallens/quinquefasciatus was the main mosquito species, accounting for 76.88% of the total number of mosquitoes captured, followed by Armigeres subalbatus, Aedes albopictus, Cx. tritaeniorhynchus, and Anopheles sinensis. The density of mosquitoes in Hangzhou averaged 3.09 mosquitoes/light·night, with a single peak at 7.42 mosquitoes/light·night in July, after which the density decreased gradually. Among different habitats, livestock sheds/livestock farms had the highest mosquito density, followed by urban residential areas, and hospitals had the lowest density of 1.72 mosquitoes/light·night. The net trap index averaged 2.70 mosquitoes/net·h, and peaked in July at 5.69 mosquitoes/net·h. All mosquitoes captured with the net method were Ae. albopictus. The net trap index differed greatly between different habitats, with the highest index at waste and old goods location/construction sites, which was 4.32 mosquitoes/net·h. BI averaged 8.84, with a single peak at 16.86 in July. BI exceeded 10.00 from June to August, and rapidly declined after August. Positive waters mainly included miniascape, aquatic plants, water tanks, water vats, basins, barrels, and unused containers (the number of unused containers with positive water was 1 304, which was the greatest). Conclusion In 2019, the dominant mosquito species in Hangzhou was Cx. pipiens pallens/quinquefasciatus, and the density of mosquitoes showed clear seasonal fluctuations, with the peak of activities occurring between June and October for both adult and larval mosquitoes. The mosquito vector capacity might sustain mosquito-borne diseases transmission such as dengue. Mosquito control measures should be taken based on the surveillance results and local climate conditions, so as to control mosquito density and prevent the spread of mosquito borne diseases.