 PDF(1069 KB)
PDF(1069 KB)


黑龙江省佳木斯市2004-2021年肾综合征出血热流行特征及发病趋势预测
王艳旭, 赵继民, 刘翠玉, 吴晓敏, 王彦富, 肖虹
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (4) : 536-541.
 PDF(1069 KB)
PDF(1069 KB)
 PDF(1069 KB)
PDF(1069 KB)
黑龙江省佳木斯市2004-2021年肾综合征出血热流行特征及发病趋势预测
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Epidemiological characteristics and trend prediction of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Jiamusi, Heilongjiang, China, 2004-2021
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}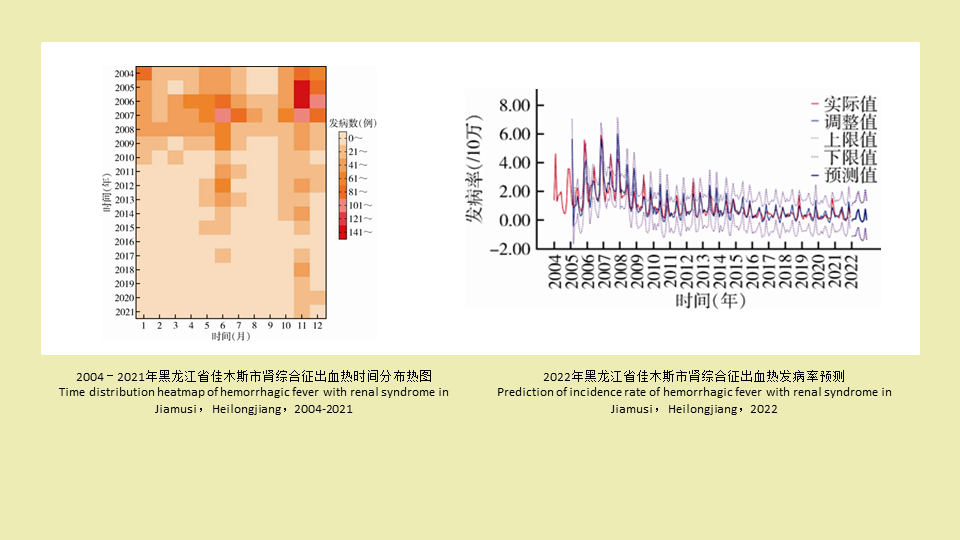
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |