 PDF(8757 KB)
PDF(8757 KB)


气候变化背景下按蚊伊丽莎白菌全球和中国适生区分布预估研究
韦晓慧, 王晓旭, 冀好强, 梁莹, 刘起勇
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2) : 165-175.
 PDF(8757 KB)
PDF(8757 KB)
 PDF(8757 KB)
PDF(8757 KB)
气候变化背景下按蚊伊丽莎白菌全球和中国适生区分布预估研究
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Prediction of suitable habitat distribution of Elizabethkingia anophelis in the world and China under climate change
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}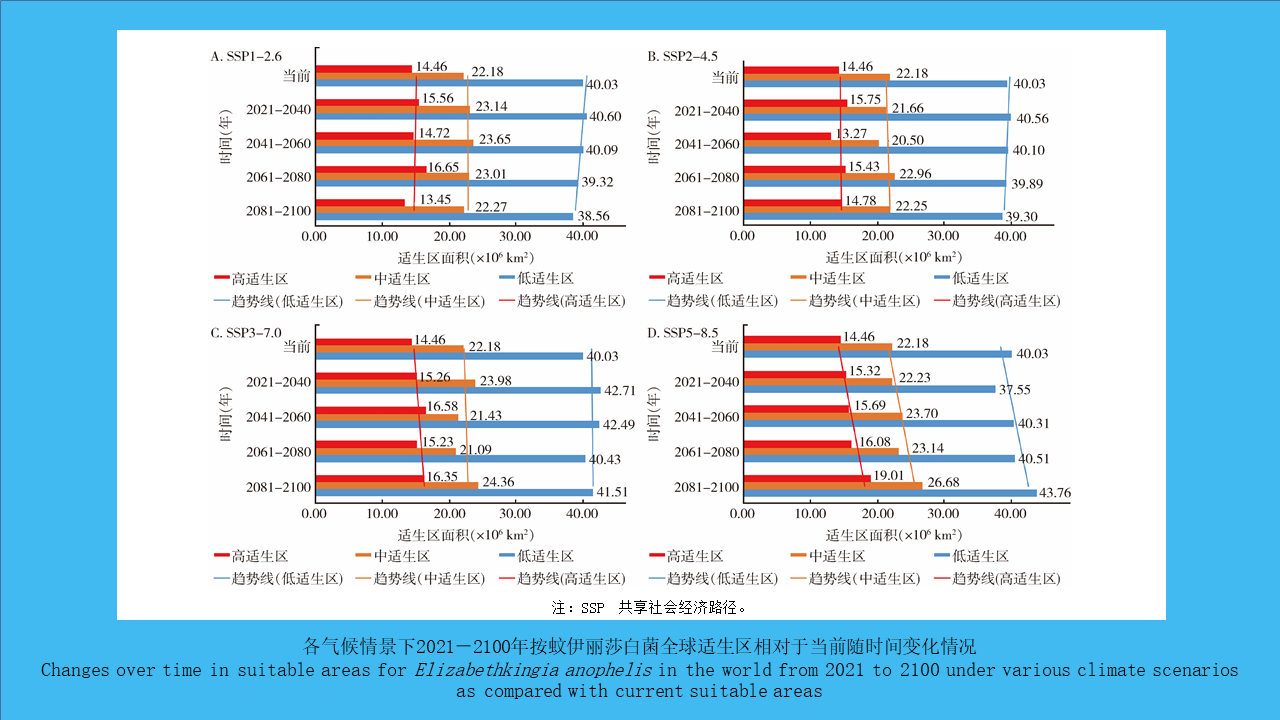
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |