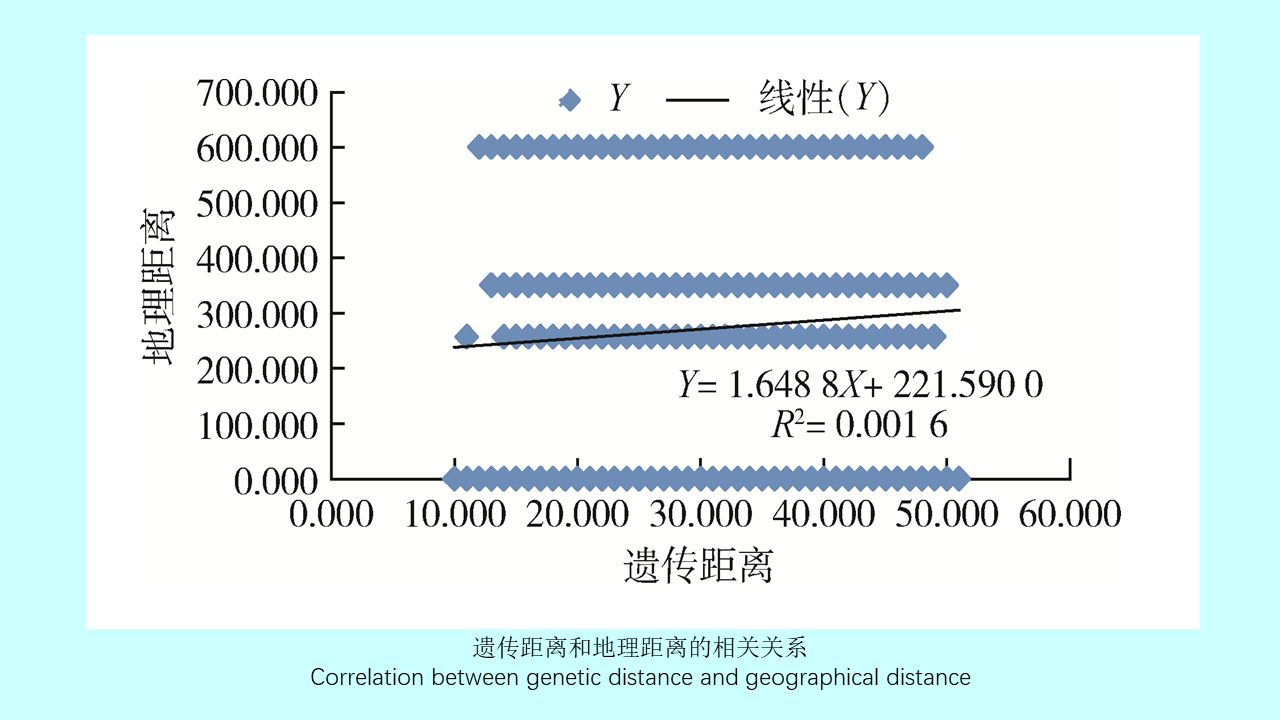
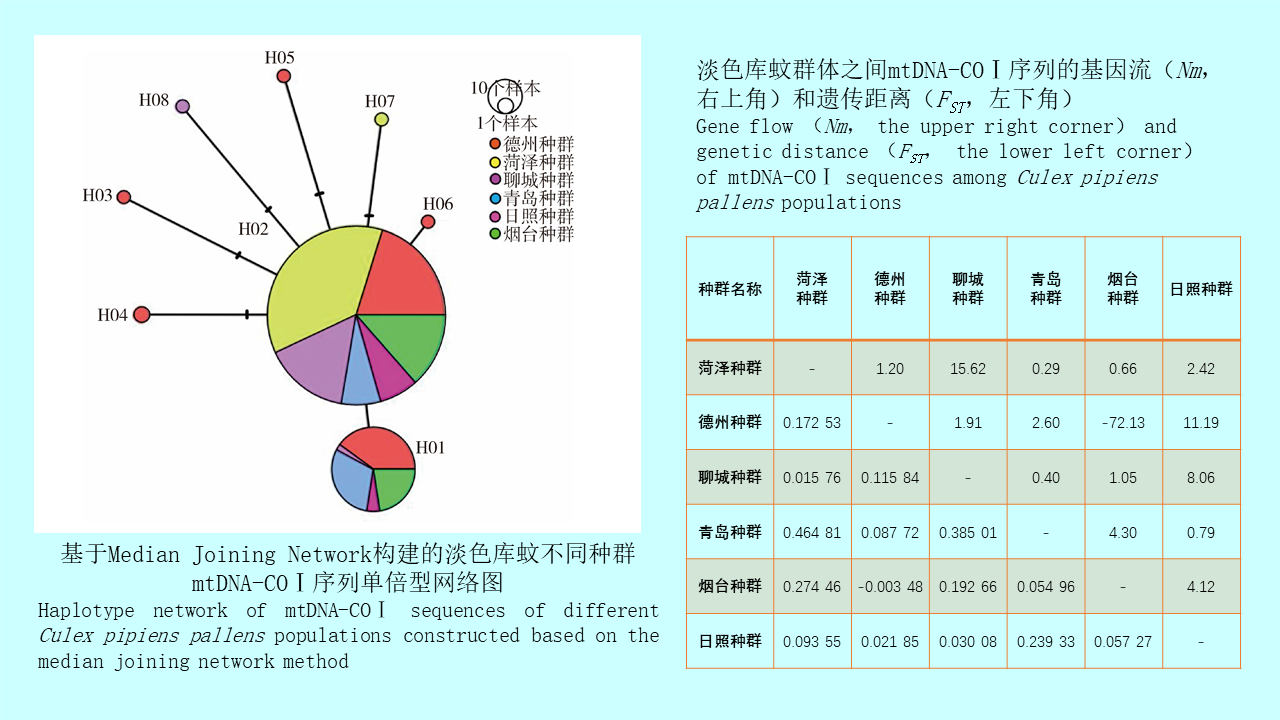
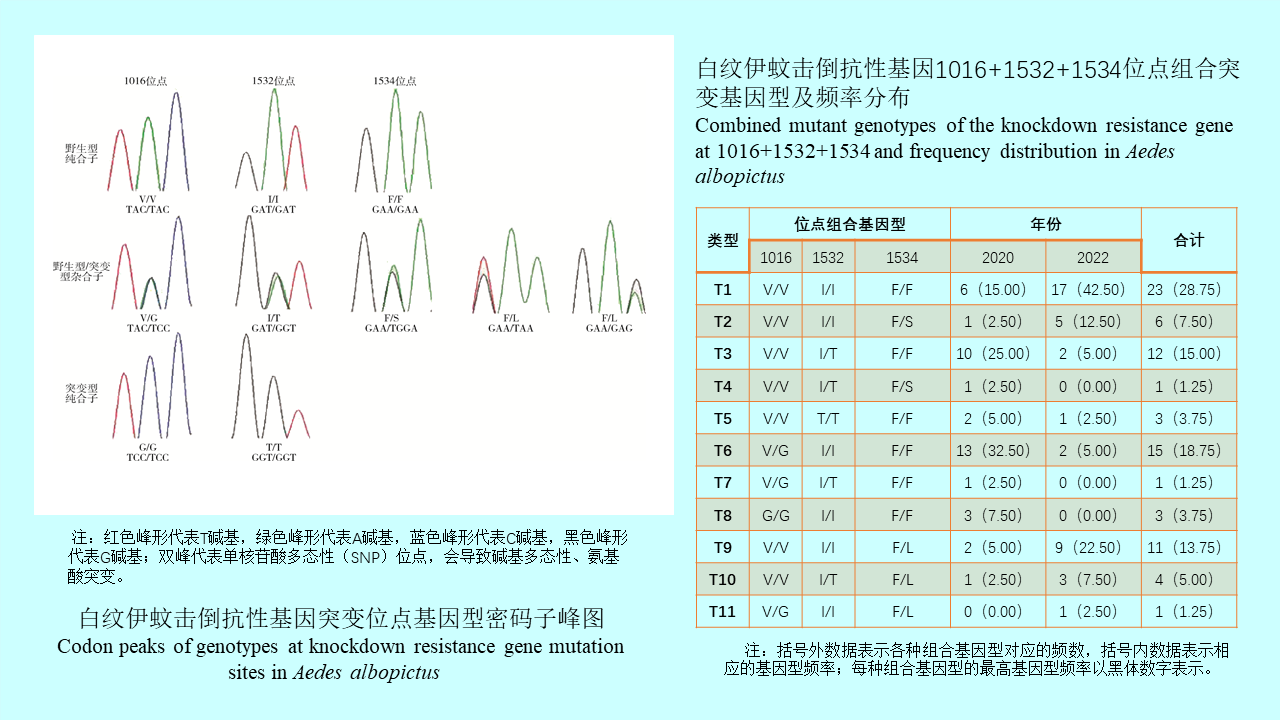
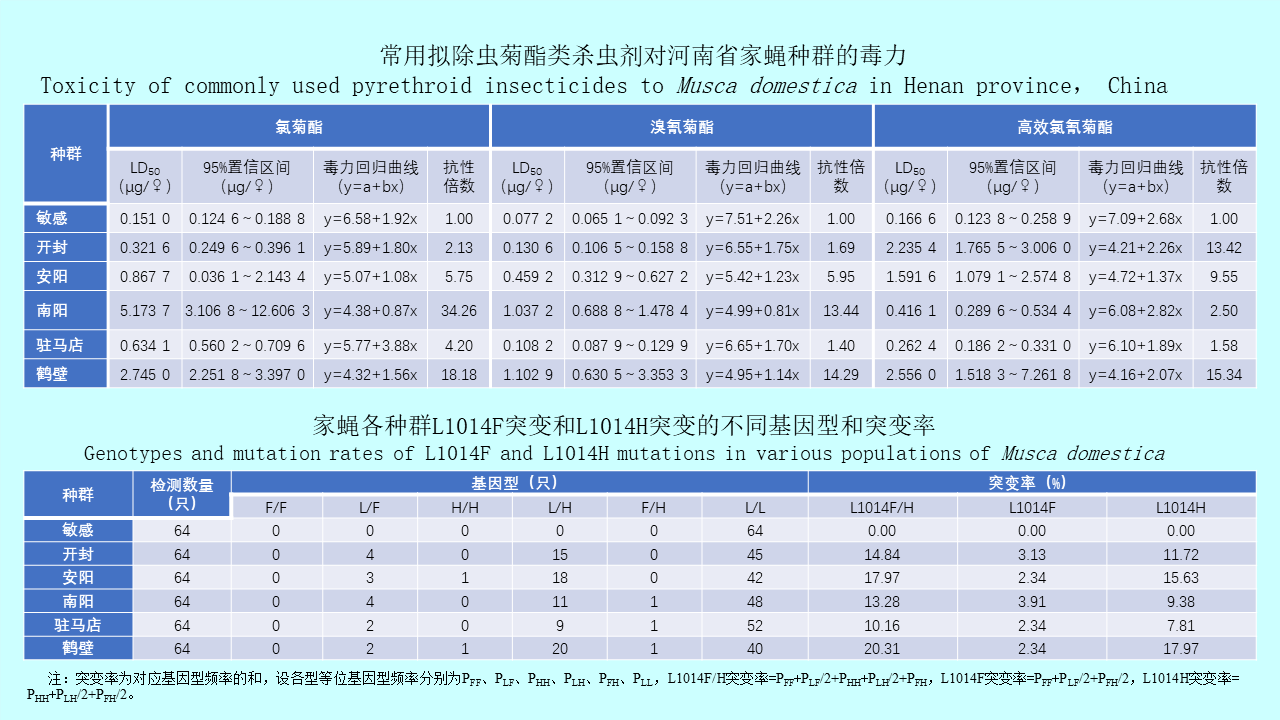
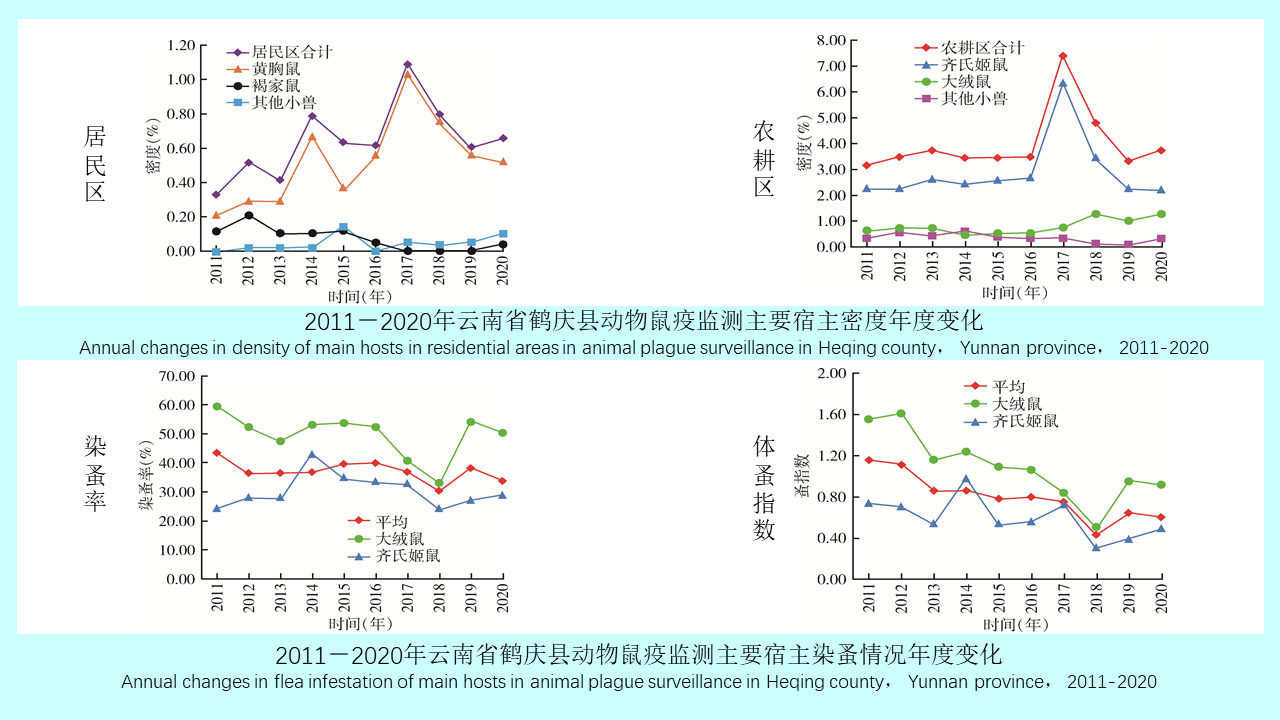
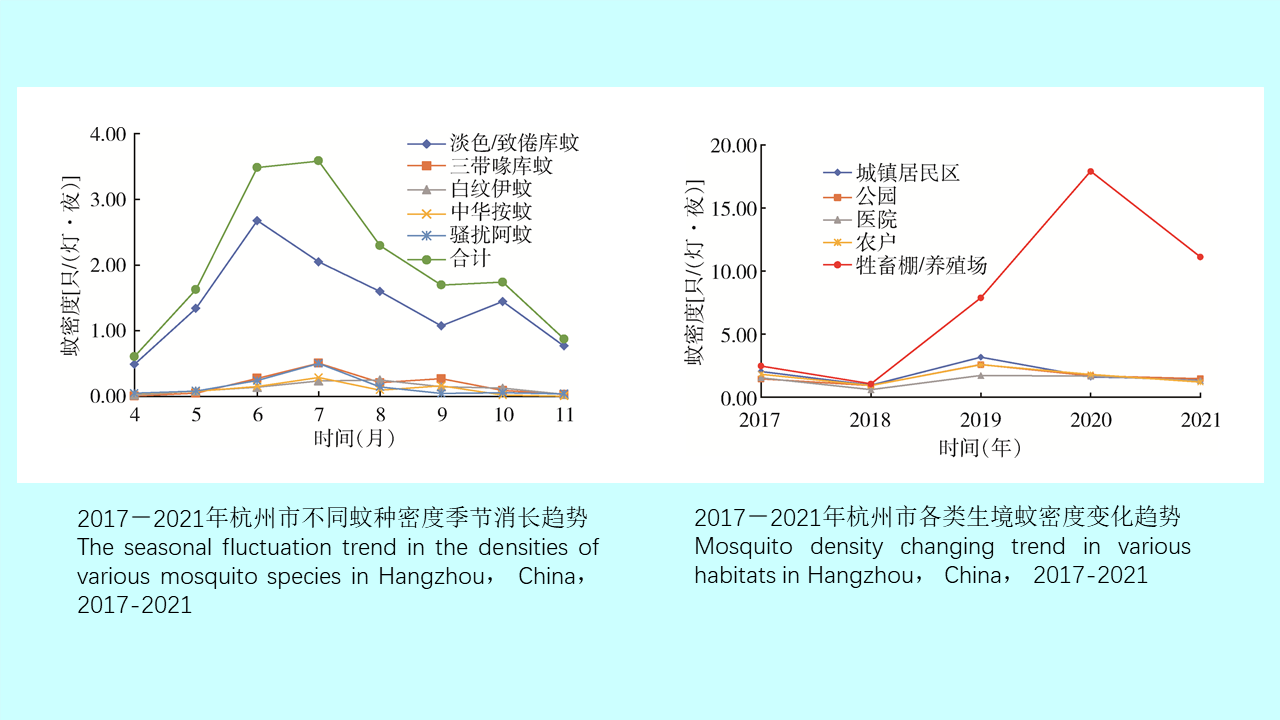
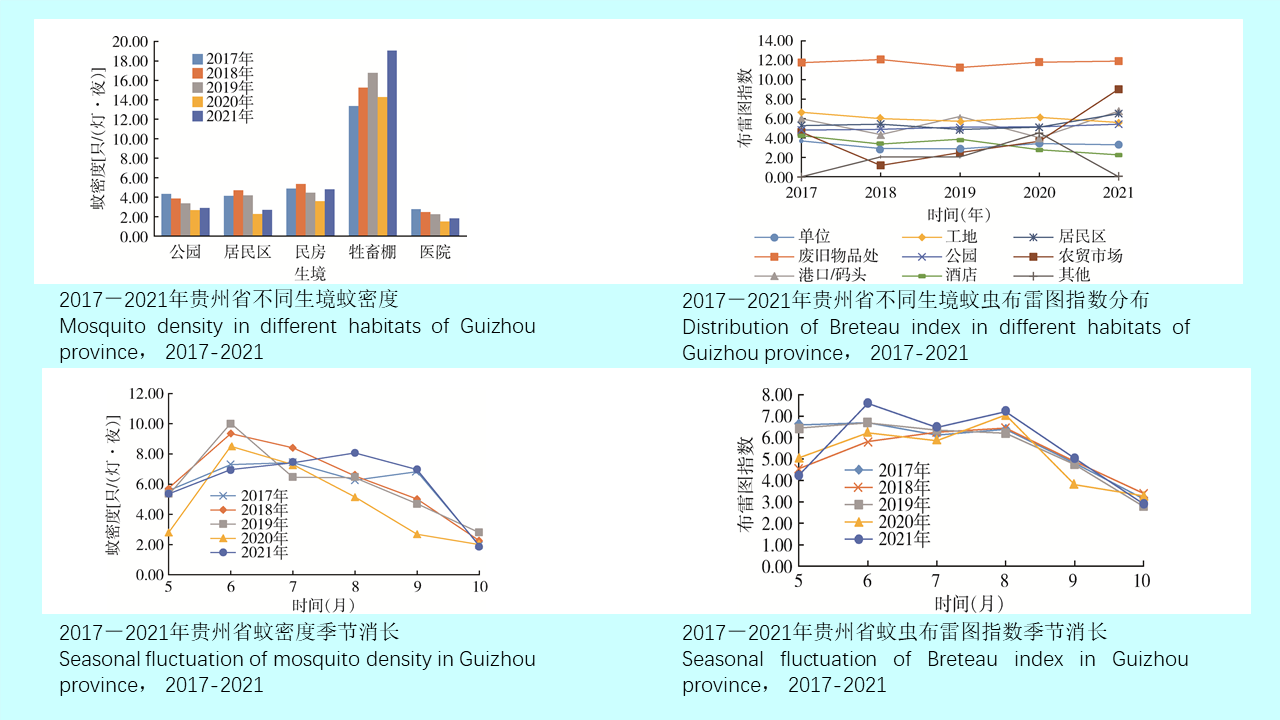
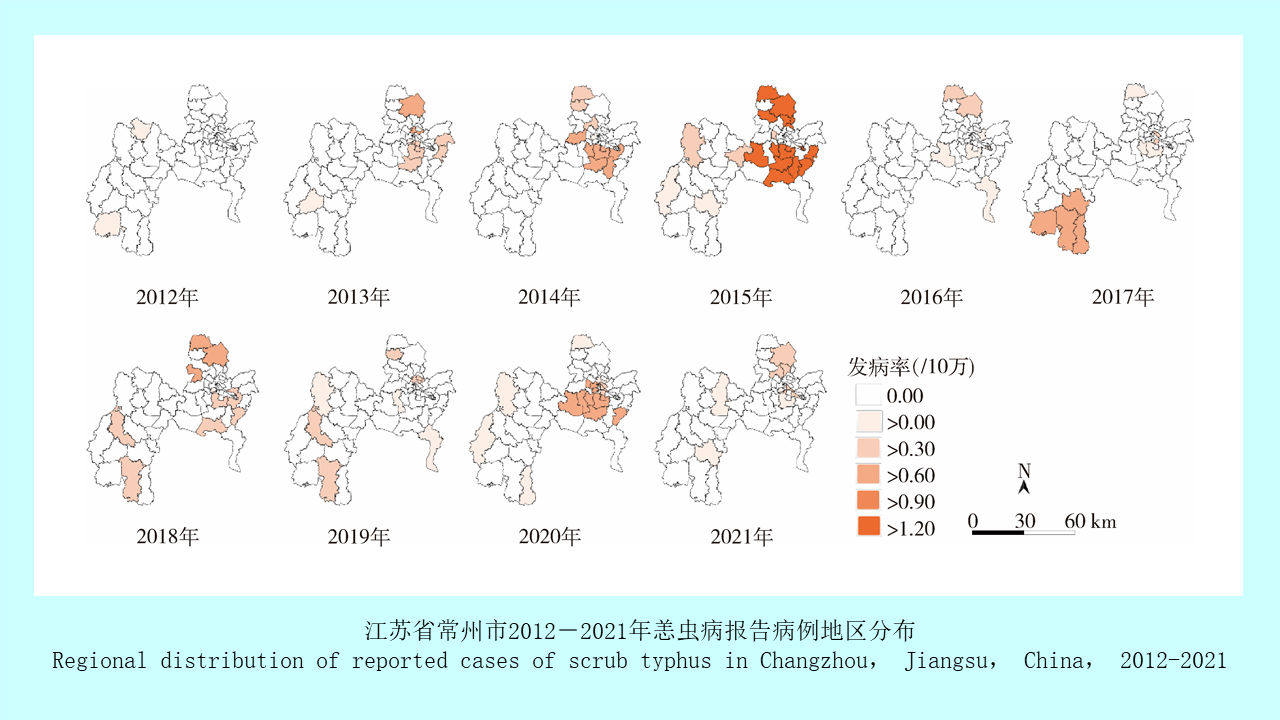
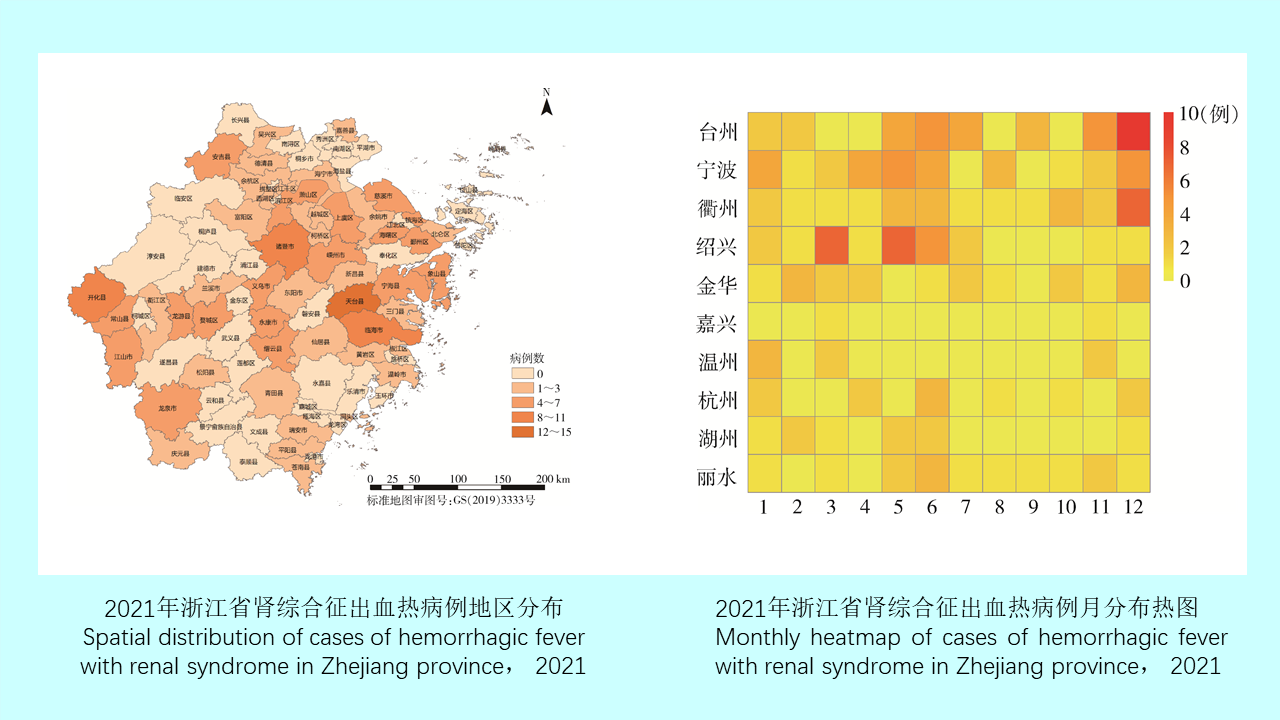
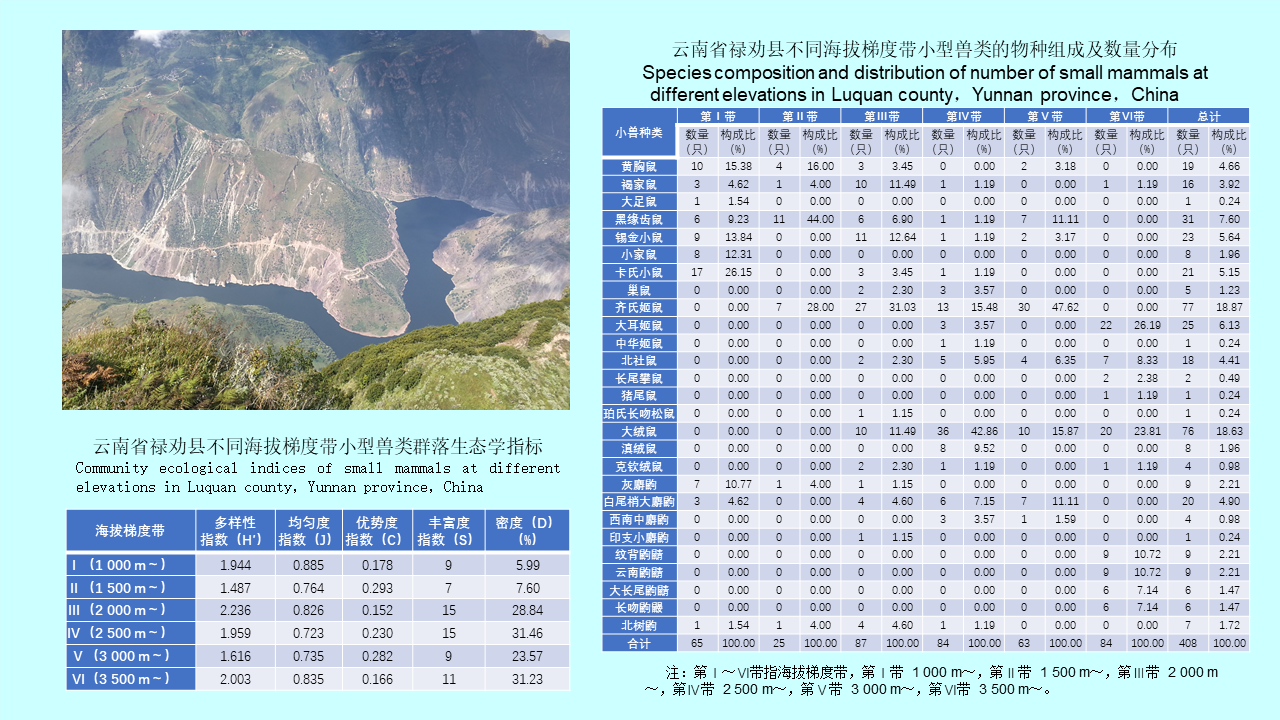
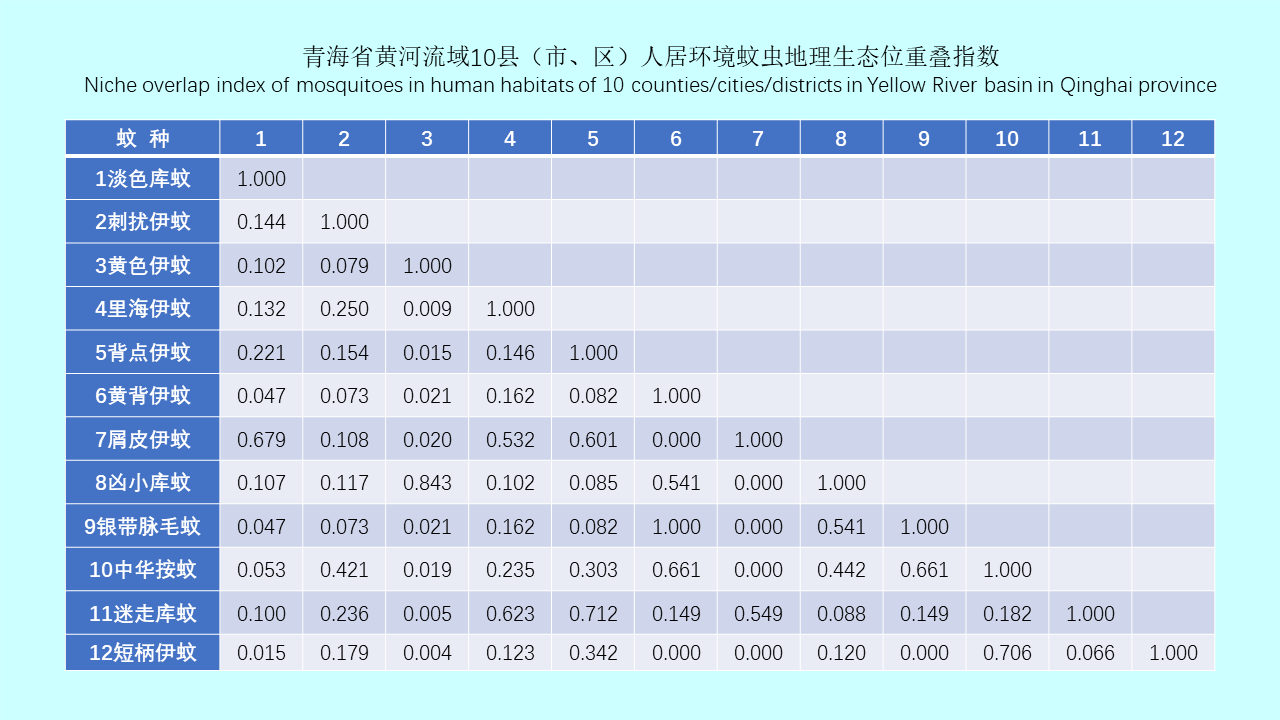
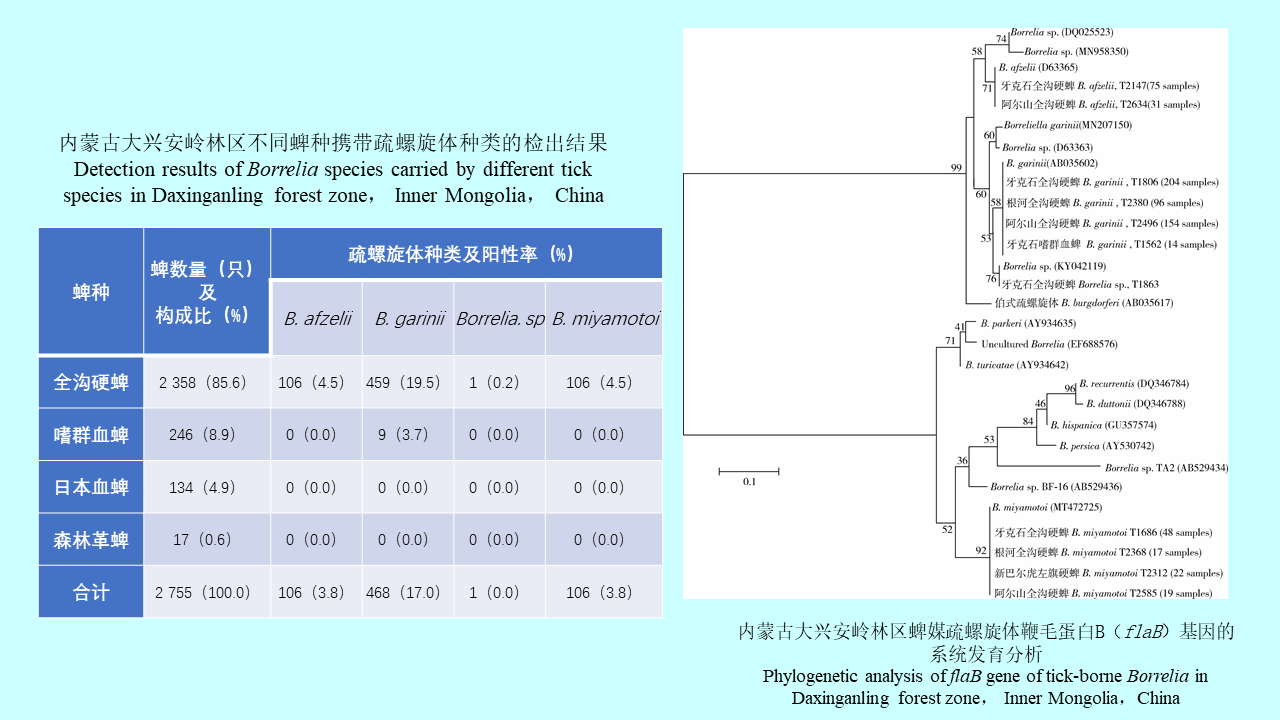
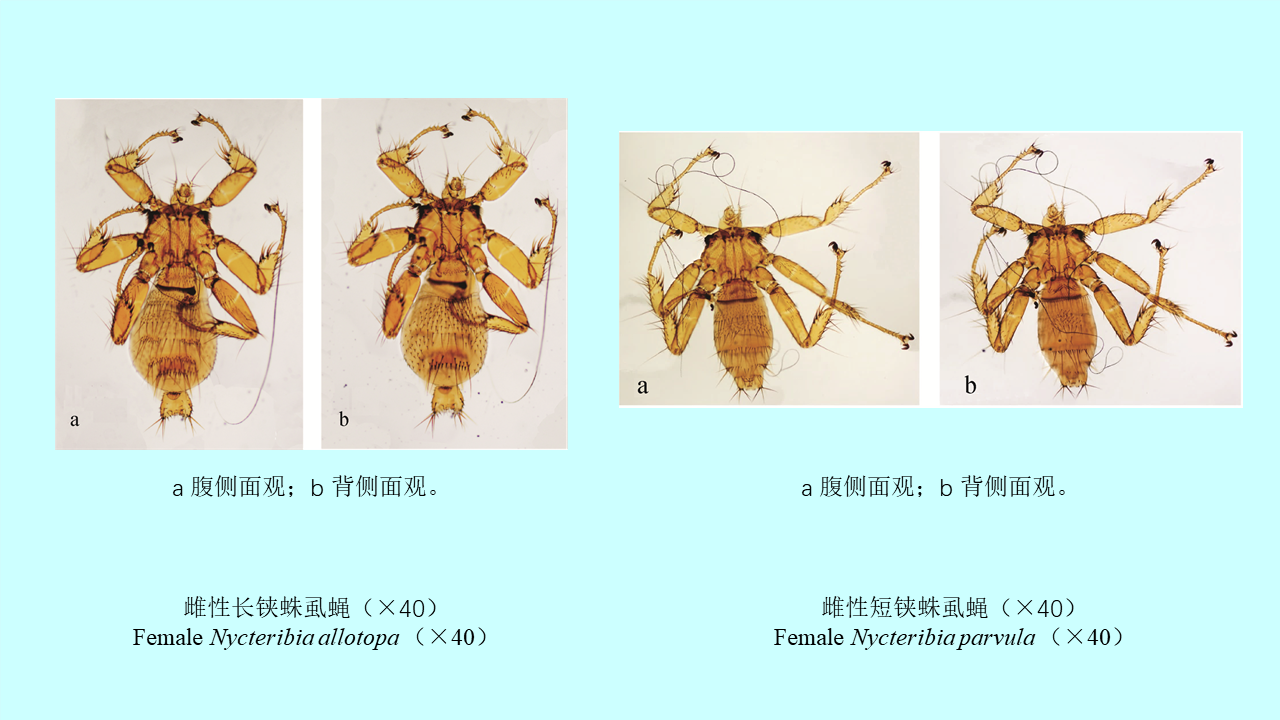
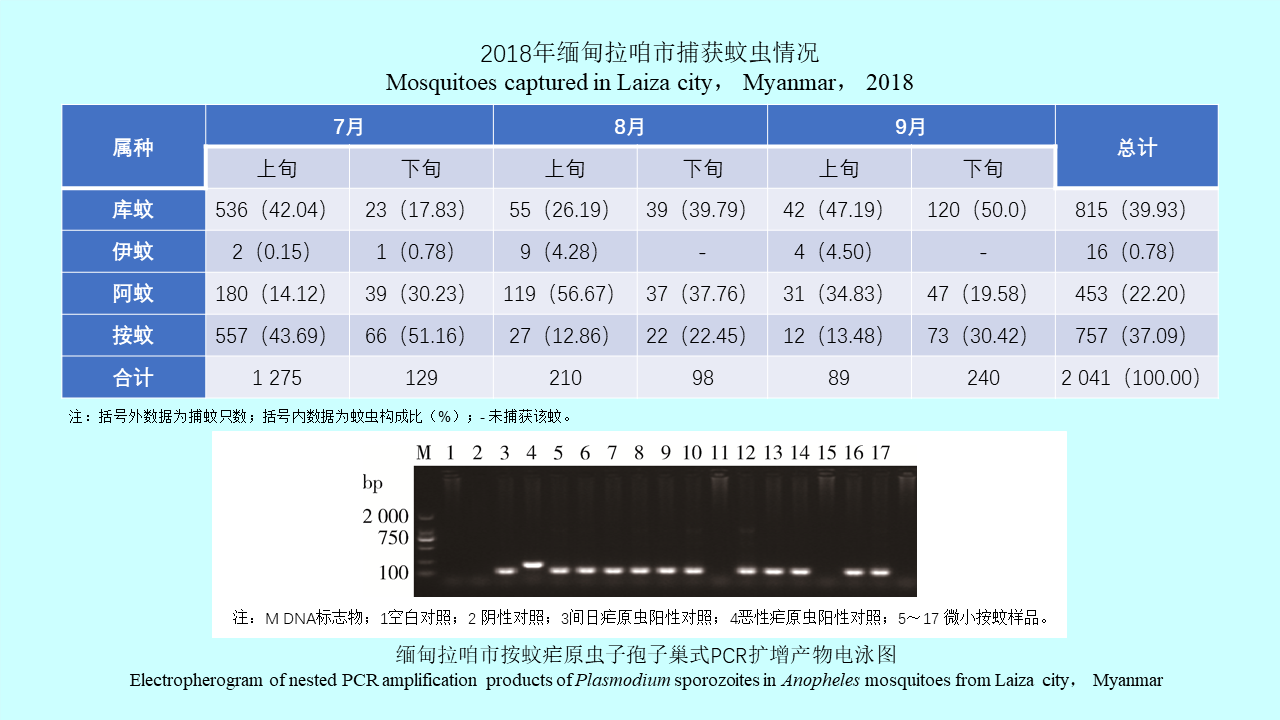
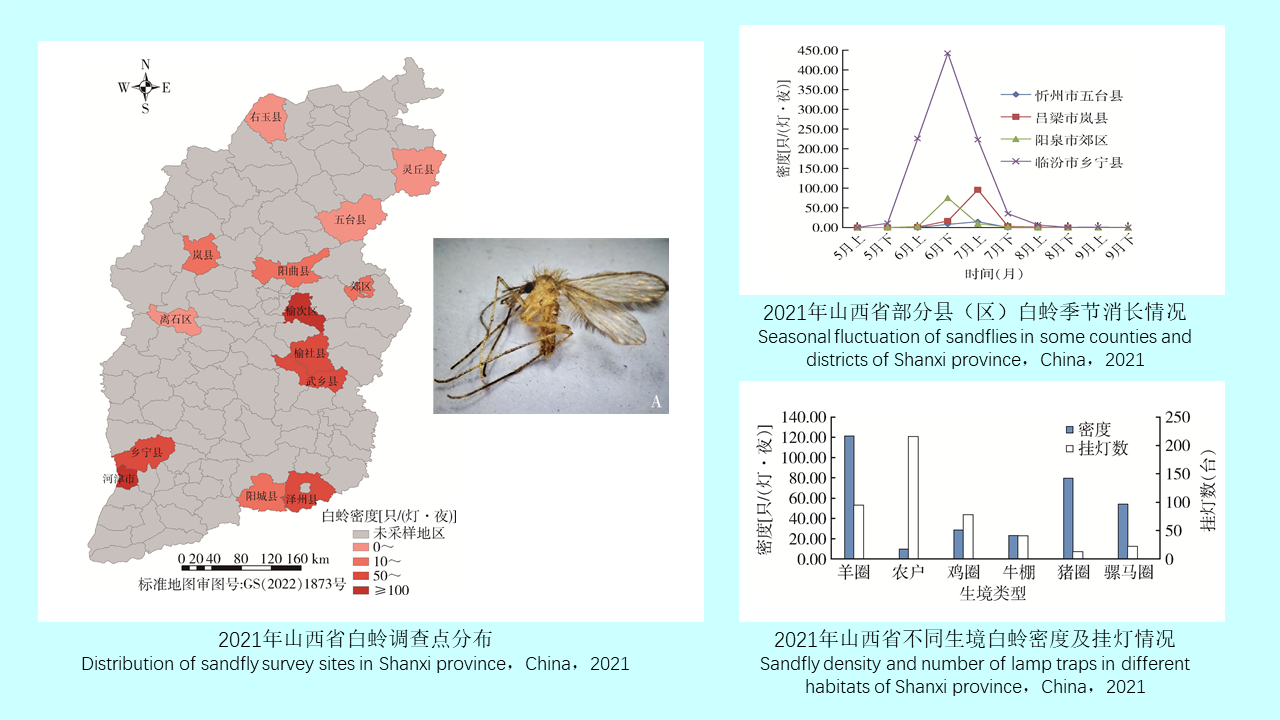
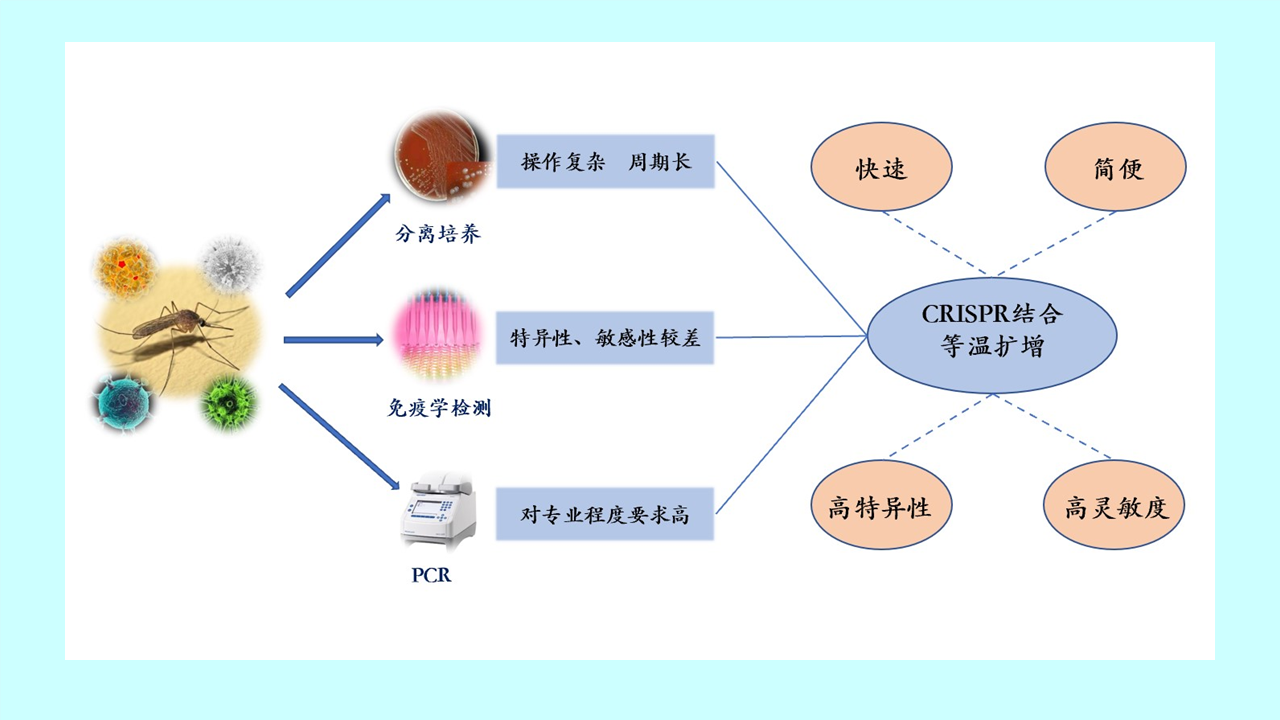
GAO Yi, MAO Yi-ping, WANG Xiao-lin, CHEN Yi-nan, ZHANG Xin-wei, GONG Zhen-yu
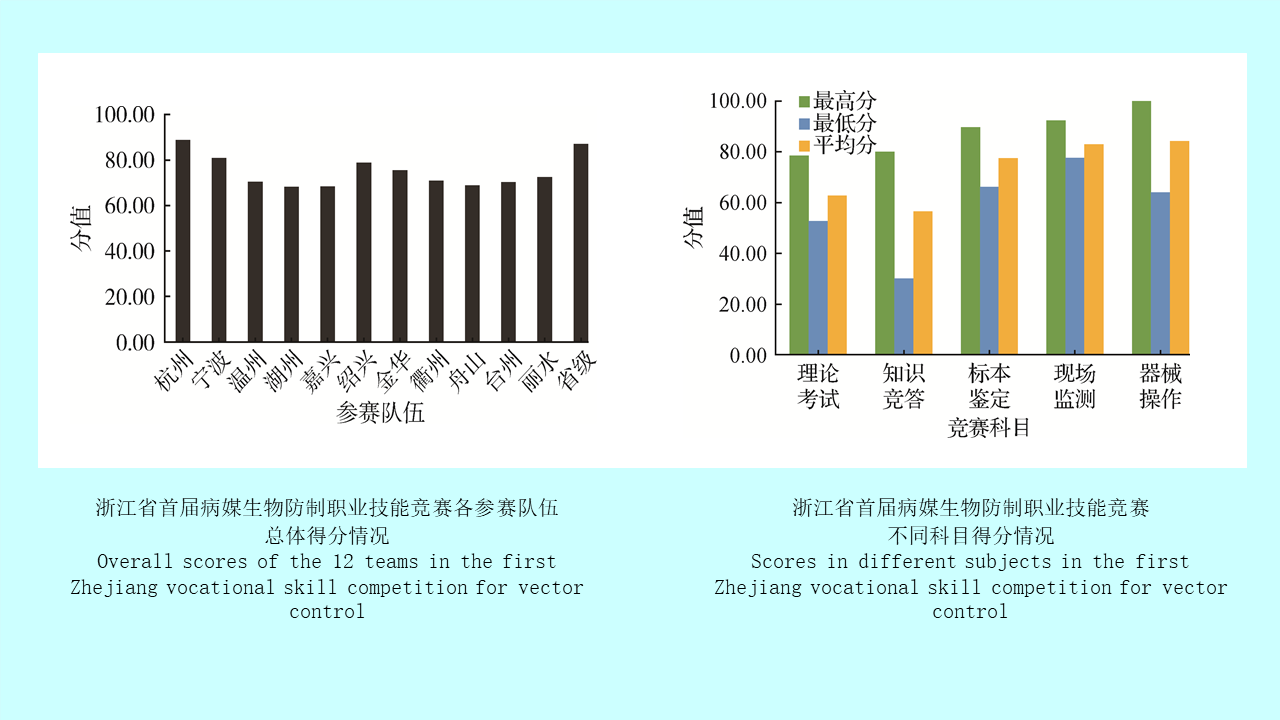
Objective To analyze the theoretical knowledge, on-site disposal, and comprehensive analysis capacity for vector control in professional technicians in Zhejiang disease control and prevention (disease control) institutions, China, and to provide a decision-making basis for strengthening the capacity building of teams in disease control institutions.Methods Based on the first Zhejiang vocational skill competition for vector control in 2019, the knowledge of vector control, average score, and loss of points in individual item in 36 contestants from eleven municipal and one provincial disease control institutions were evaluated, and the differences in scores in different regions, different competition subjects, different knowledge categories, theoretical knowledge, and on-site operation were analyzed. SPSS 25.0 was used for difference comparison and variance analysis.Results The results were converted and standardized according to 100 points. The average score of 12 teams was 75.01 (68.13-88.77) points. The analysis of five different subjects of theory test, knowledge quiz, specimen identification, monitoring technique, and device operation showed significant differences in the scores between the theory test and the other four subjects and between the knowledge quiz and the other four subjects (all P<0.05). There were significant differences in individual scores between the contestants with different job types (full-time and part-time) and between those from institutions with different structures and personnel allocations (F=11.897, P=0.002; F=14.737, P=0.001; F=10.627, P=0.003). The analysis of theory test and knowledge quiz according to different knowledge categories showed significant differences in the scores between drug and device use and the other three knowledge categories, and between comprehensive analysis and the other three knowledge categories in the theory test (all P<0.05); for the knowledge quiz, there were significant differences in the scores between the basic knowledge and monitoring evaluation, between the basic knowledge and disposal technique, between species identification and monitoring evaluation, between species identification and disposal technique, between monitoring evaluation and drug and device use, and between drug and device use and disposal technique (all P<0.05). The species identification showed that there were significant differences in the scores between mosquito feature description and the other three key assessment points, and between cockroach or fly feature description and the other three key assessment points (all P<0.05). There were significant differences in the scores between rodent monitoring records and the other key assessment points, and between fly monitoring records and the other key assessment points (all P<0.05). In the device operation subject, significant differences were observed in the scores between drug liquid preparation and personal protection, between drug liquid preparation and post-treatment, and between actual operation and post-treatment (all P<0.05).Conclusions The competition shows that the professional technicians from Zhejiang province’s disease control institutions are generally at a high level. However, there are still insufficient knowledge coverage of the contestants, certain differences in the mastery degree between regions. The vector control teams construction are weakened in the disease control institutions. There are shortcomings and weaknesses in some knowledge categories, especially species identification, basic knowledge, and drug and device use. It suggests that it is necessary to strengthen the systematic training of professionals, highlight basic knowledge and skills training such as on-site operation, and strengthen the construction of internal teams and personnel allocation, so as to improve the overall level of vector prevention and control in Zhejiang province.