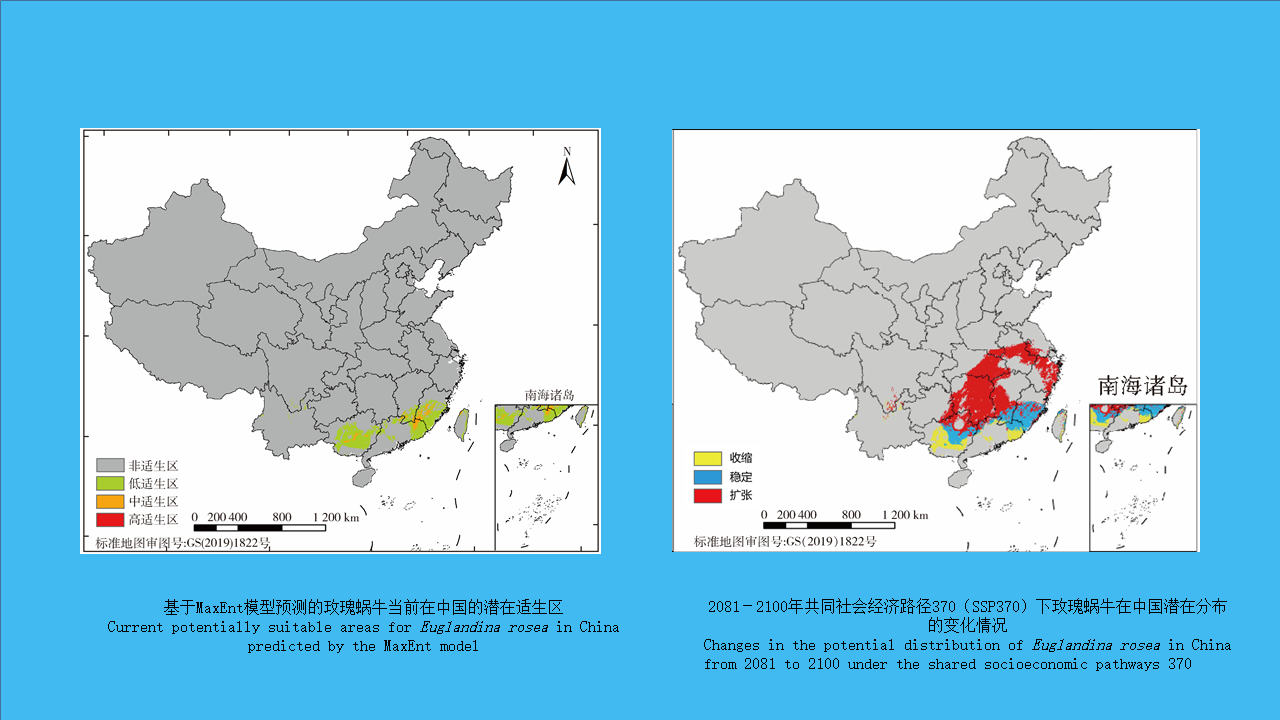
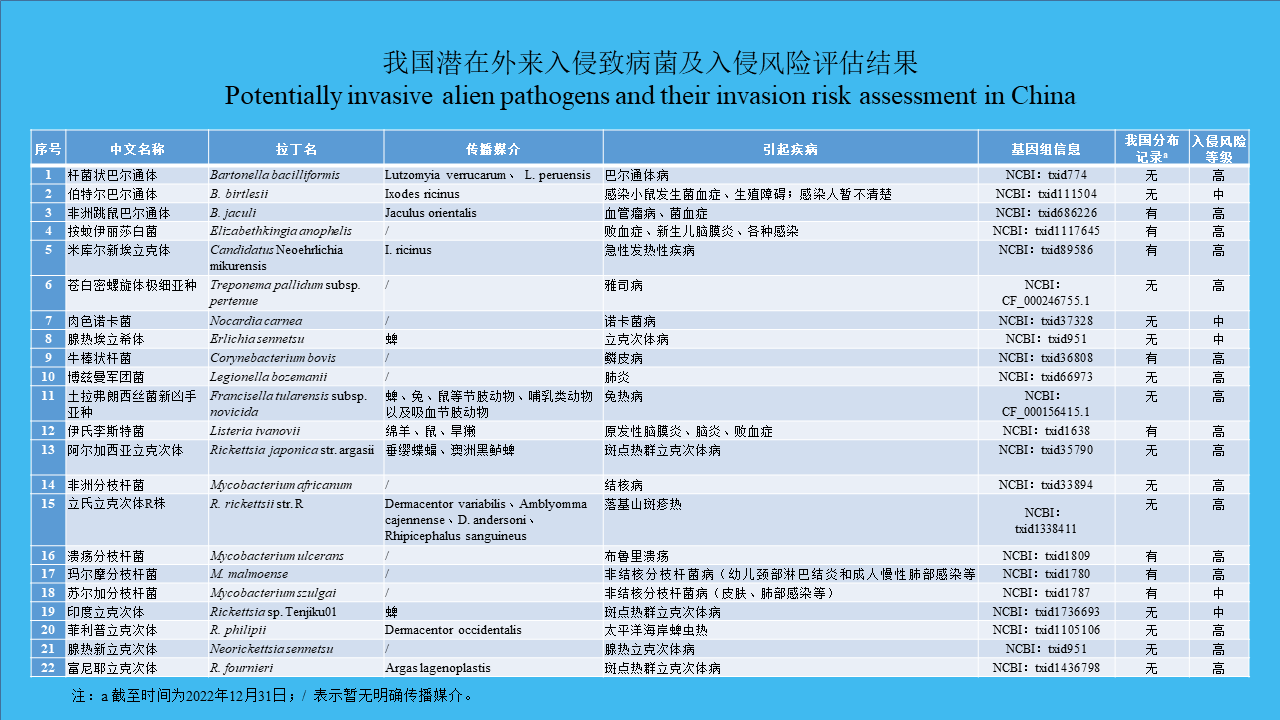
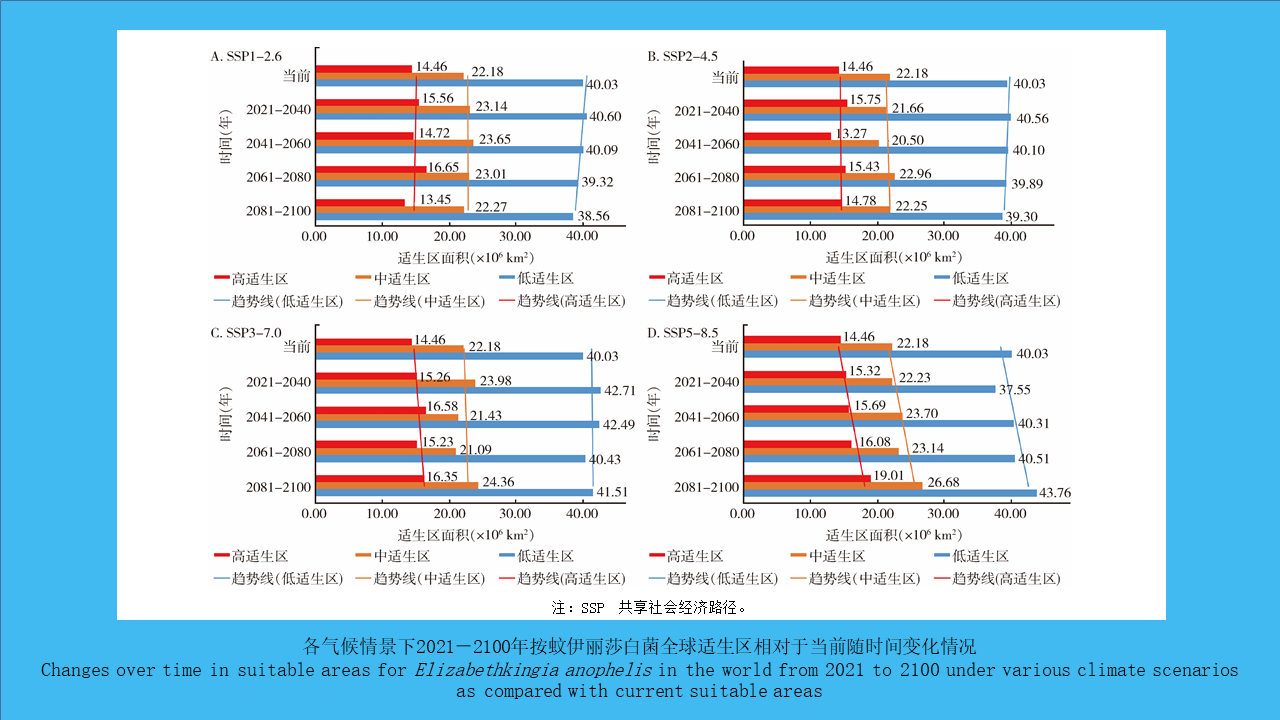
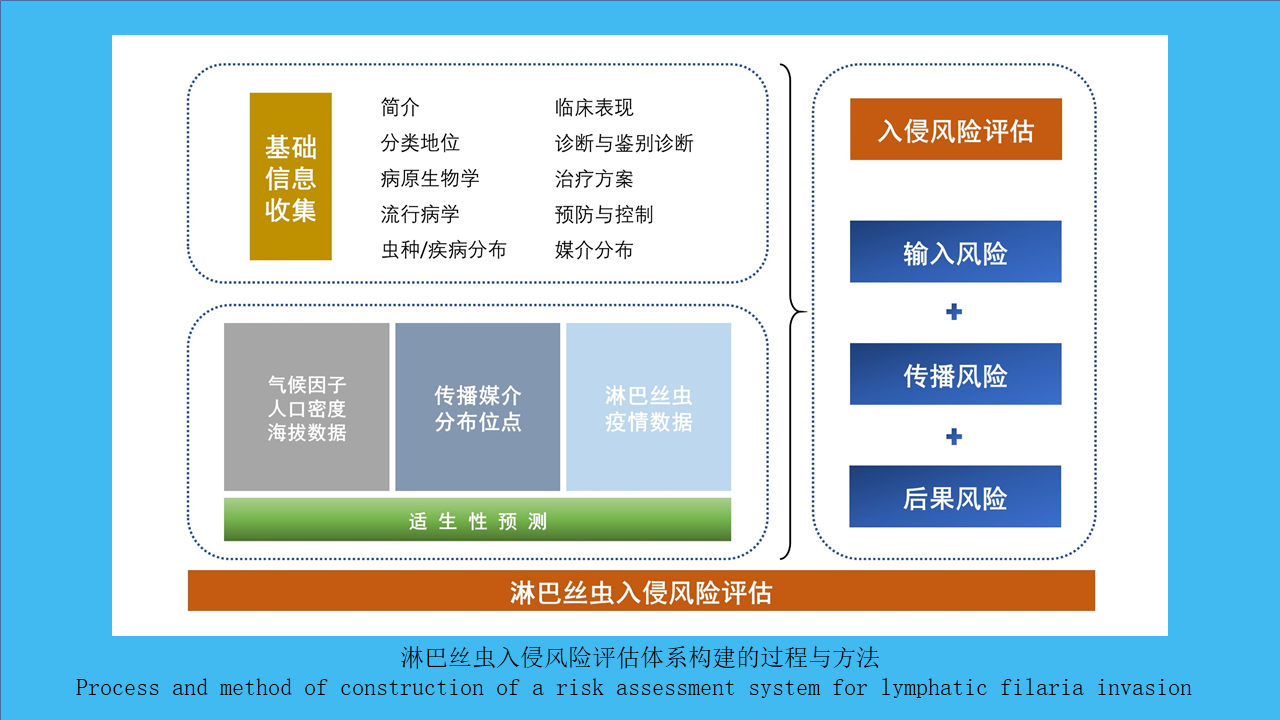
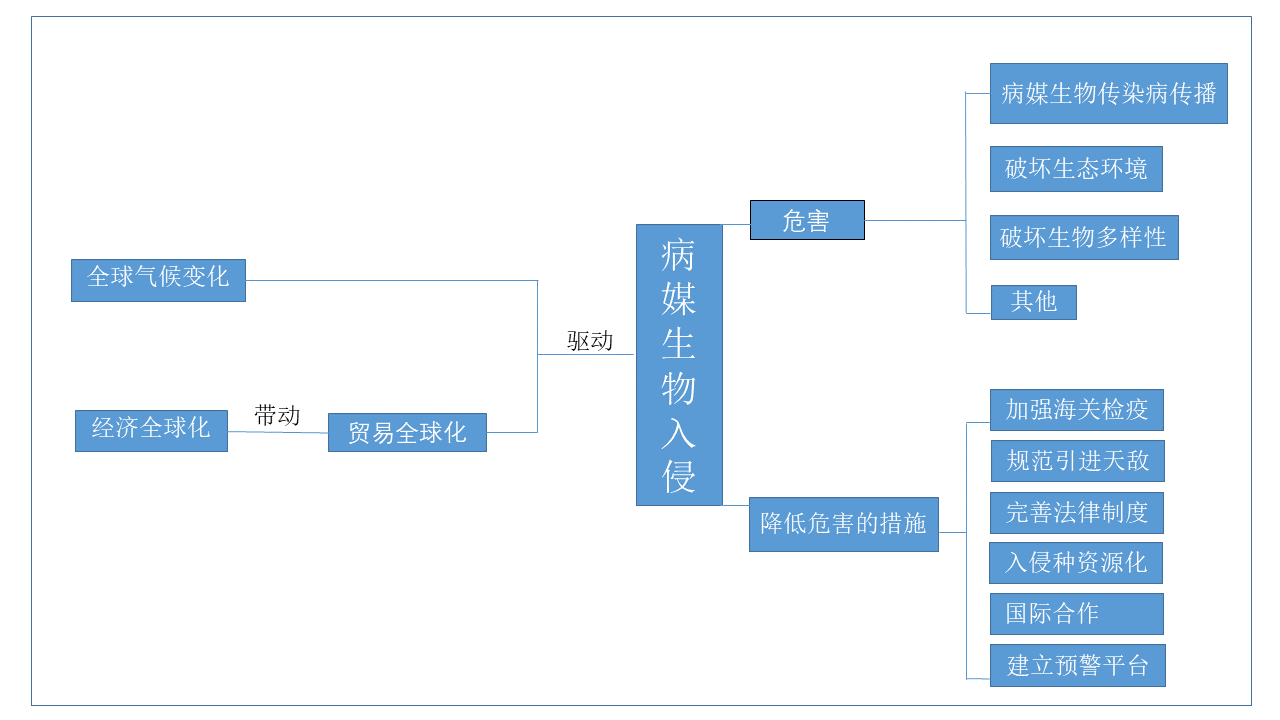
XIAO Qiu-qiu, LI Wei-yi, HE Shan, CHENG Jin-zhi, PENG Zhe-hui, WU Jia-hong
Objective To identify the insulin-like peptide (ILP) genes from the whole genome of Aedes albopictus, and to analyze the gene structure and its expression profiles at various developmental stages and in different tissues. Methods The ILP gene family was identified by homology comparison in the whole genome database of Ae. albopictus on the Vectorbase website. Signal peptide prediction was performed by SignalP 6.0 software. The structural features of ILP genes were analyzed by MEGA 11.0 software. The phylogenetic tree was constructed by the maximum likelihood method. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to detect the changes in ILP gene expression at different mosquito developmental stages (eggs, fourth instar larvae, pupae, and adults) and in different tissues (head, fat body, midgut, thorax, and ovary) of female mosquitoes before and after blood feeding. SPSS 20.0 software was used for statistical analysis. The Tukey’s HSD test was used to analyze the expression of AalbILPs at different developmental stages, and the t-test was used to compare the expression of AalbILPs in different tissues before and after blood feeding. Results Seven AalbILP open reading frame sequences were identified from the whole genome of Ae. albopictus. The seven AalbILP sequences had the conserved characteristics of the insulin superfamily, and the propeptide consisted of continuous signal peptides, B, C, and A chains; AalbILP6 had a truncated C chain and carboxy-terminal extension, similar to the insulin growth factor in vertebrates. The clustering evolutionary tree demonstrated that AalbILP1, 2, 3, and 5 were most conservative among mosquitoes, followed by AalbILP6, and both AalbILP4 and 7 were unique to Aedes. The results of qRT-PCR showed that AalbILP1, 2, 3, and 5 were expressed at different developmental stages. Compared with other developmental stages, AalbILP5 was the highest expressed in male adult mosquitoes (1.358 3±0.576 9; qegg=6.572, qlarva=5.771, qpupa=5.409, qfemale=3.115, all P<0.05). AalbILP 3 and 4 were specifically expressed in the head of the whole mosquito, and AalbILP6 was principal expressed in the ovaries of female adult mosquitoes. AalbILP7 is a pseudogene and is not transcribed. Compared to the non-blood mosquitoes, the expression level of AalbILP3 and AalbILP4 in the head of female mosquitoes were significantly upregulated by 2.60 and 1.68 times (tAalbILP3- head=9.596, PAalbILP3- head<0.001; tAalbILP4-head=4.524, PAalbILP4-head=0.001); The expression of AalbILP1 in the head, fat body and midgut was up-regulated by 10.33, 6.07, and 3.79 times(thead=4.255, Phead=0.001; tfat body=4.305, Pfat body=0.001; tmigut=10.480, Pmigut<0.001), but the expression of throax and ovary decreased 4.24 and 2.17 times (tthroax=7.922, Pthroax<0.001; tovary=3.752, Povary=0.003); The expression of AalbILP6 in midgut and ovary was up-regulated 11.91 and 2.16 times (tmigut=5.799, Pmigut<0.001; tovary=9.074, Povary<0.001). Conclusions Six ILP sequences have been identified in the whole genome of Ae. albopictus and the spatiotemporal expression profiles of ILPs have been constructed.