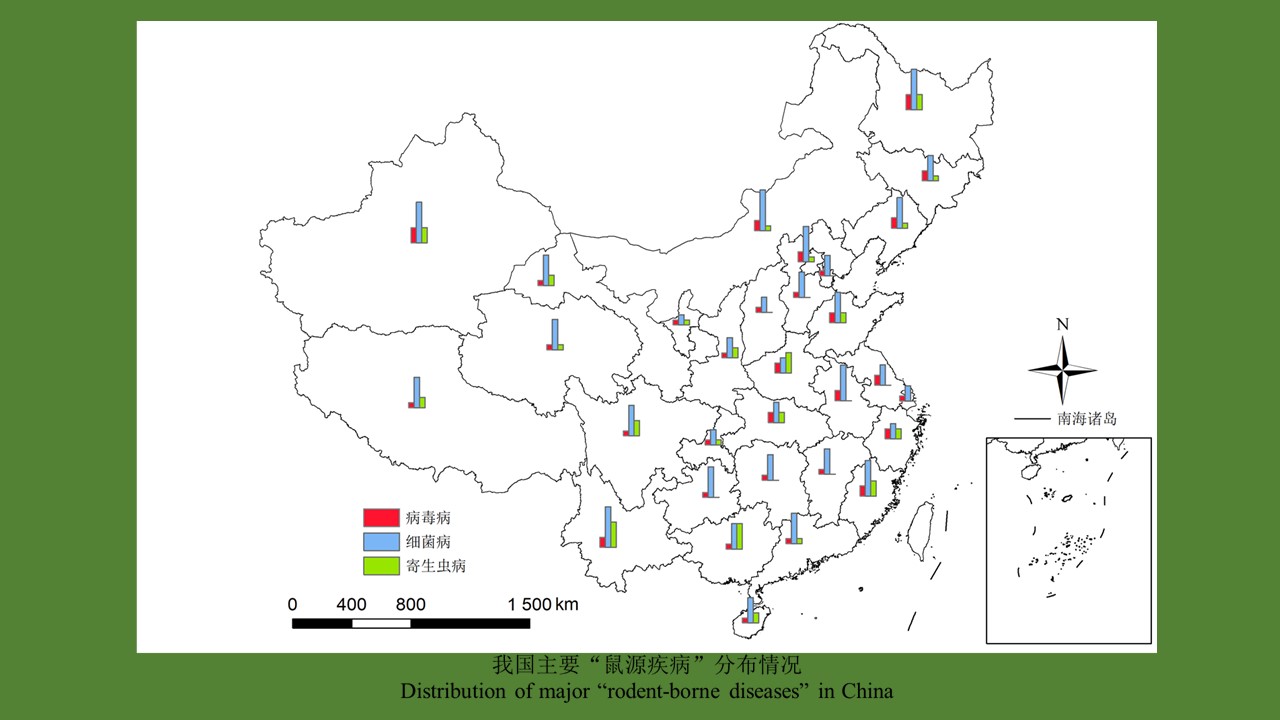
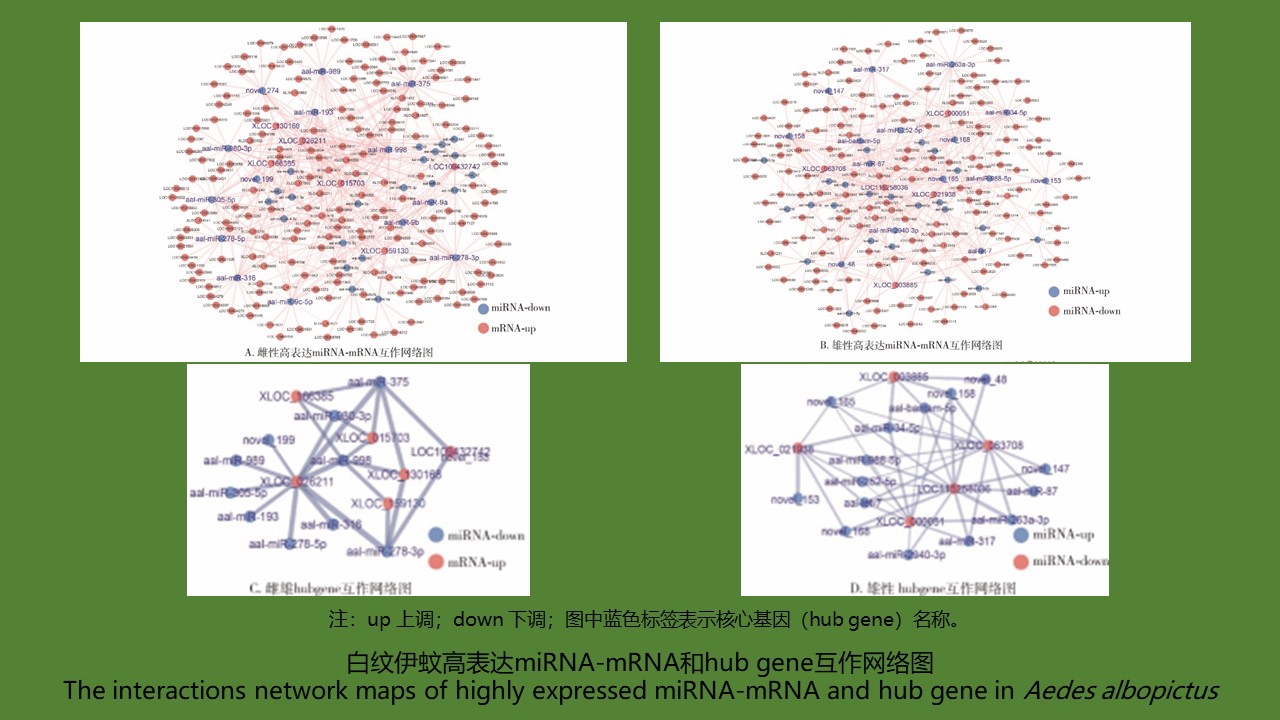
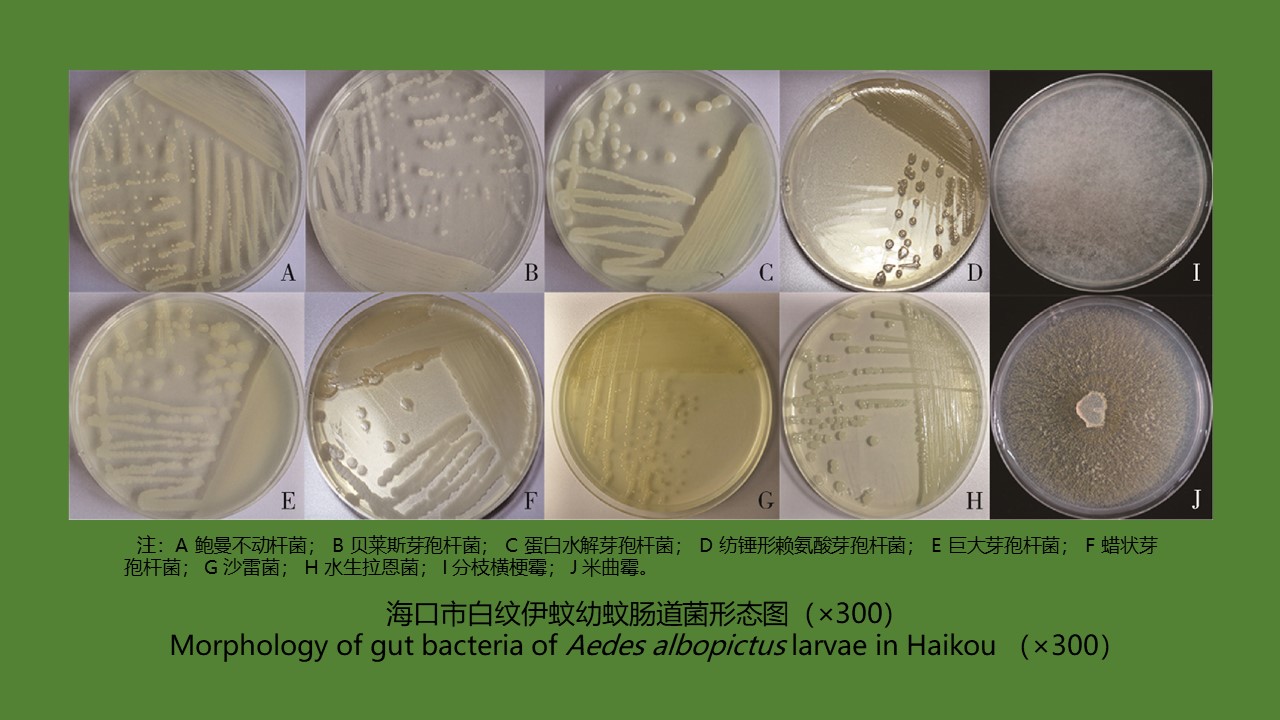
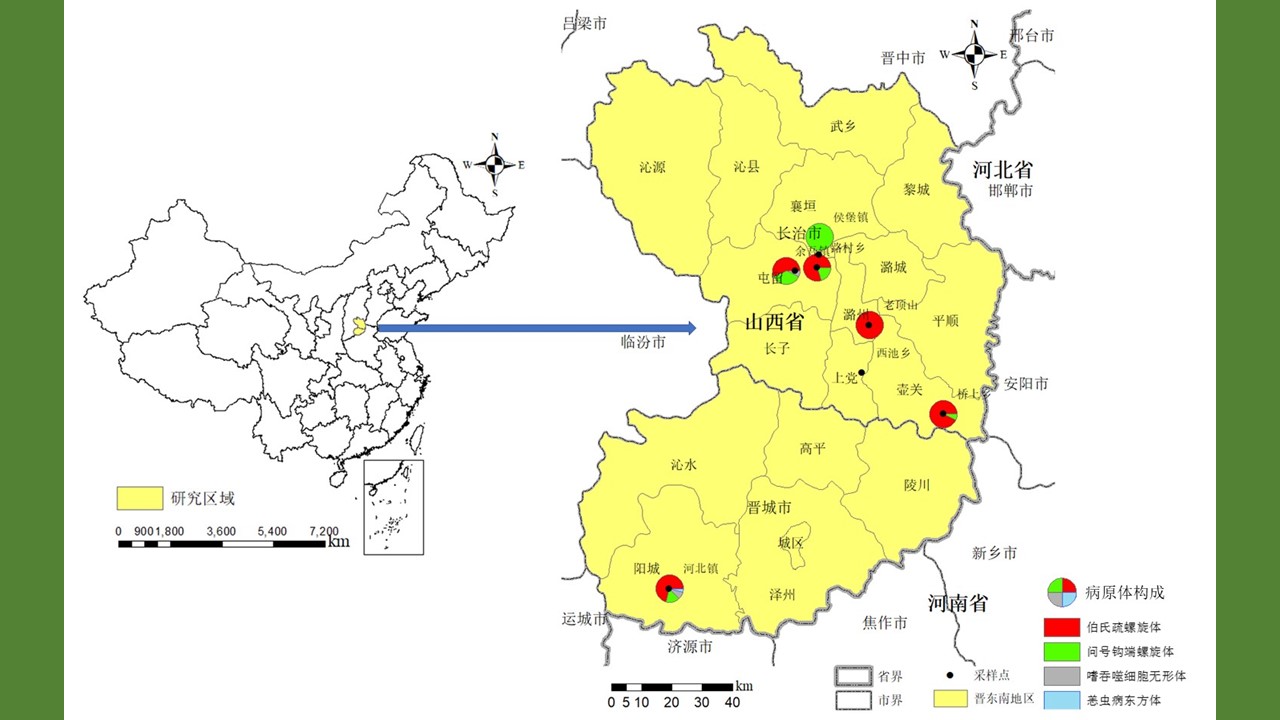
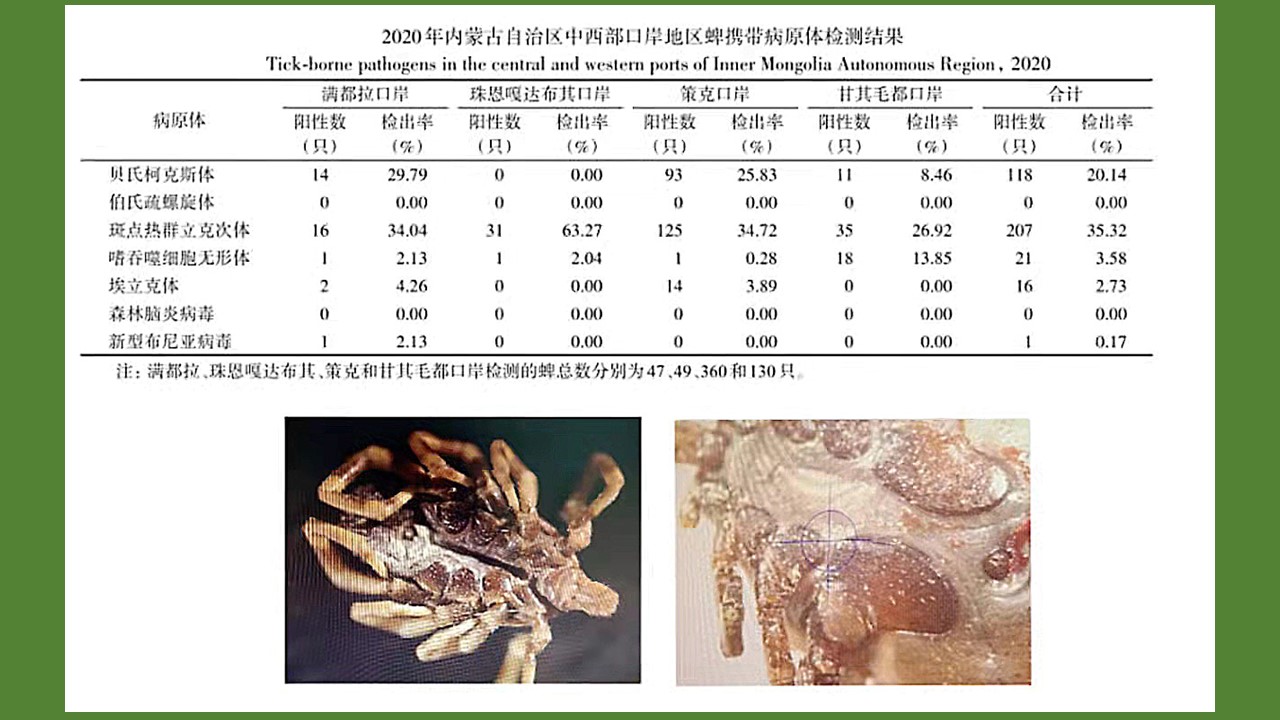
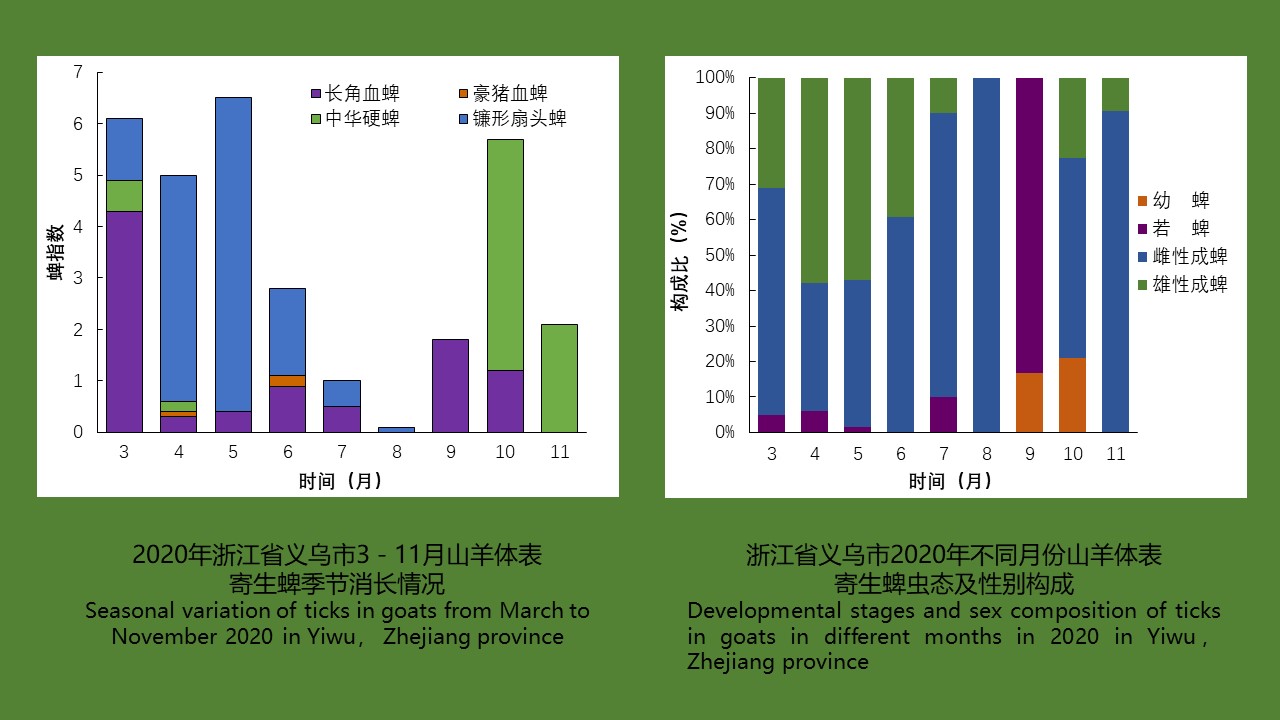
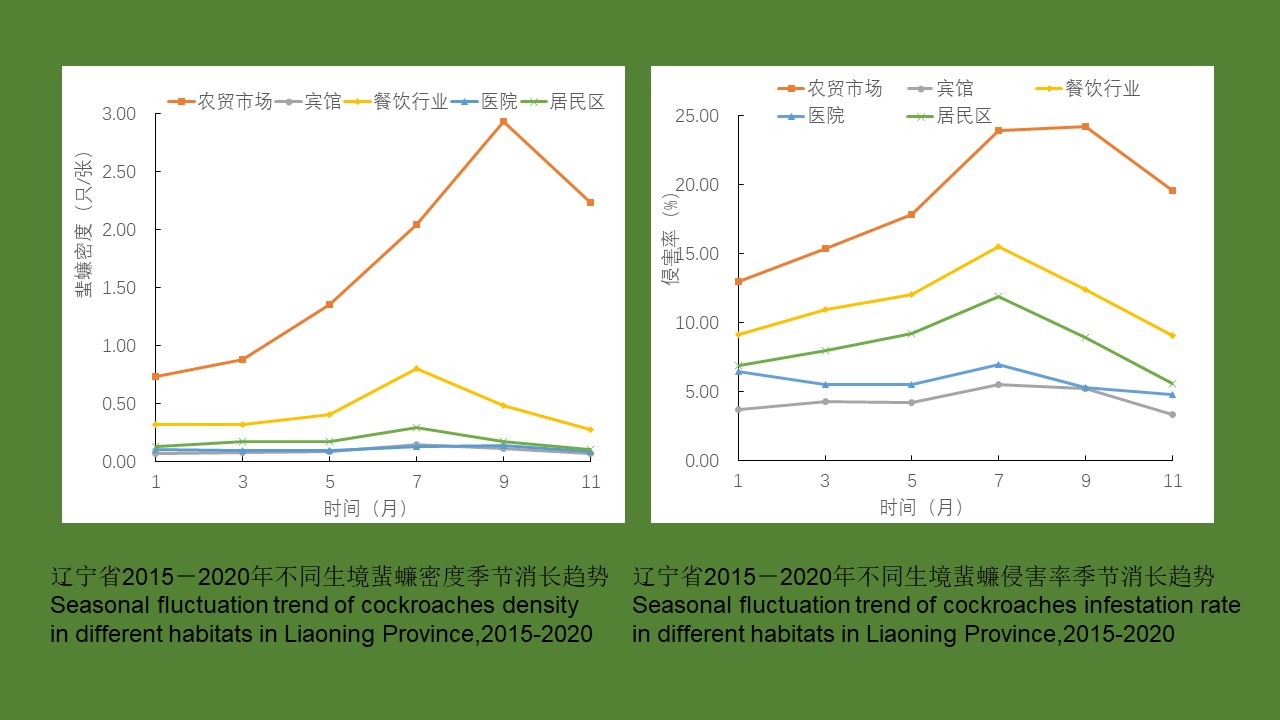
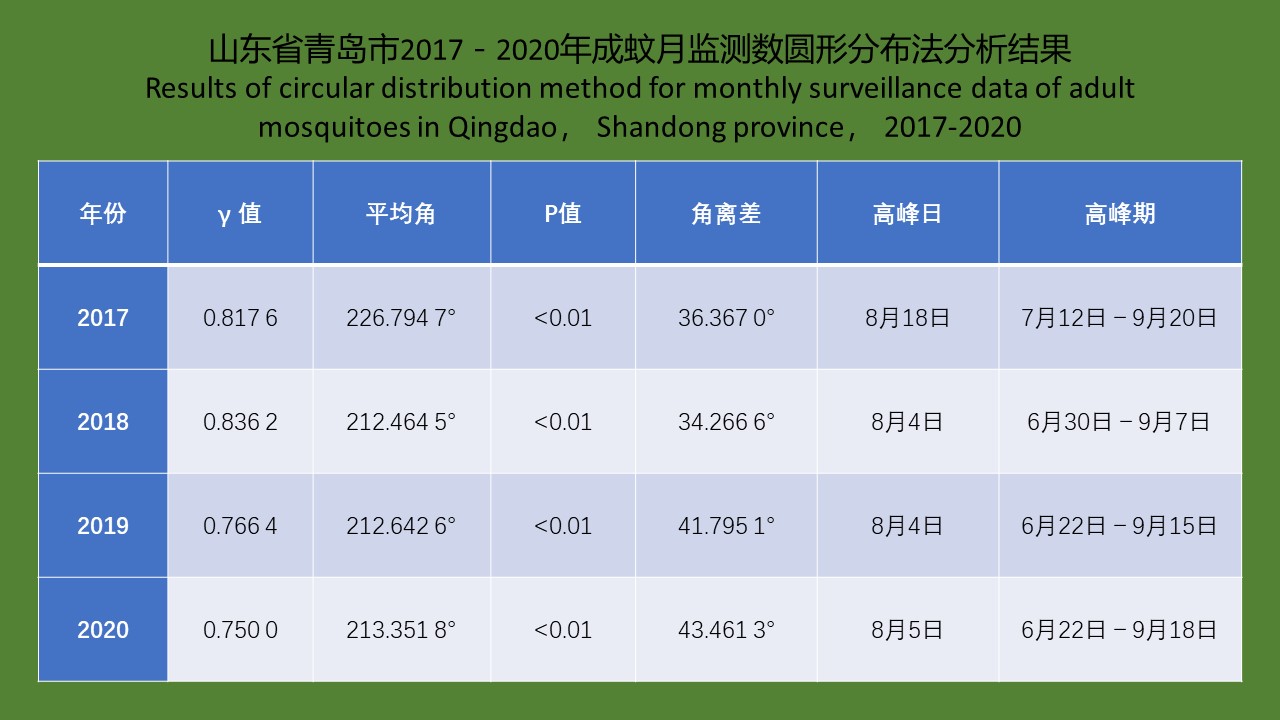
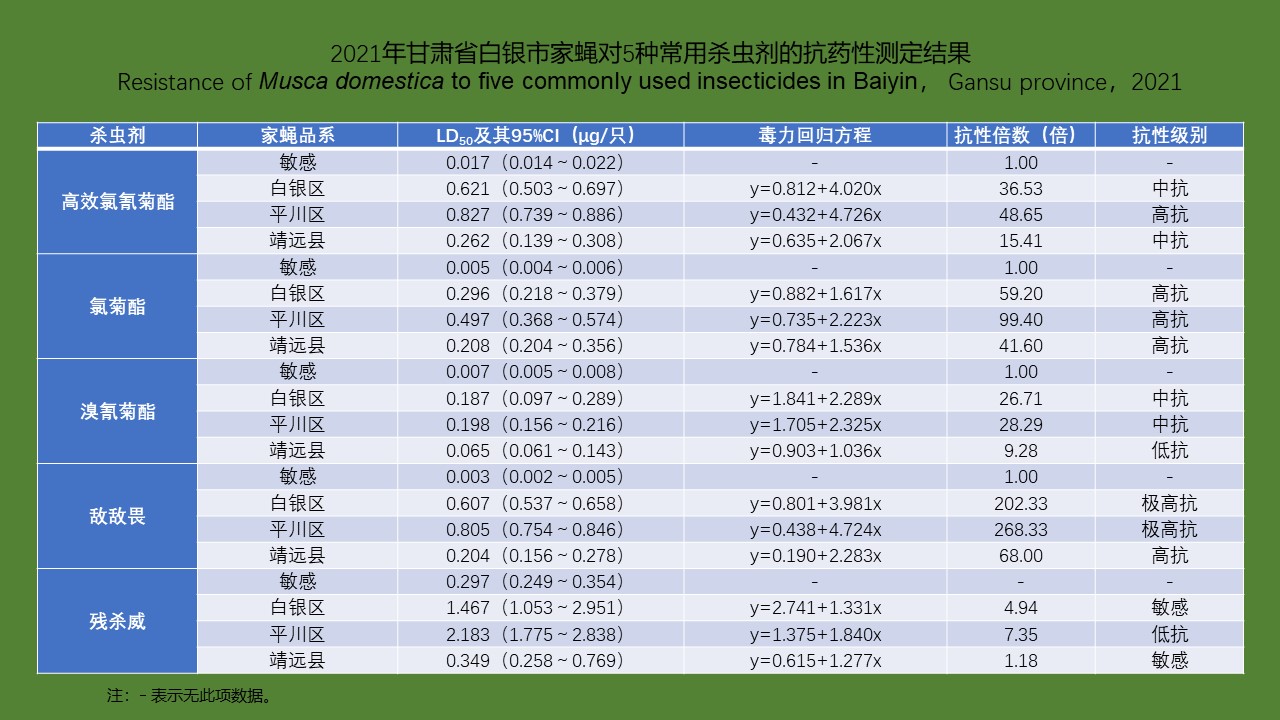
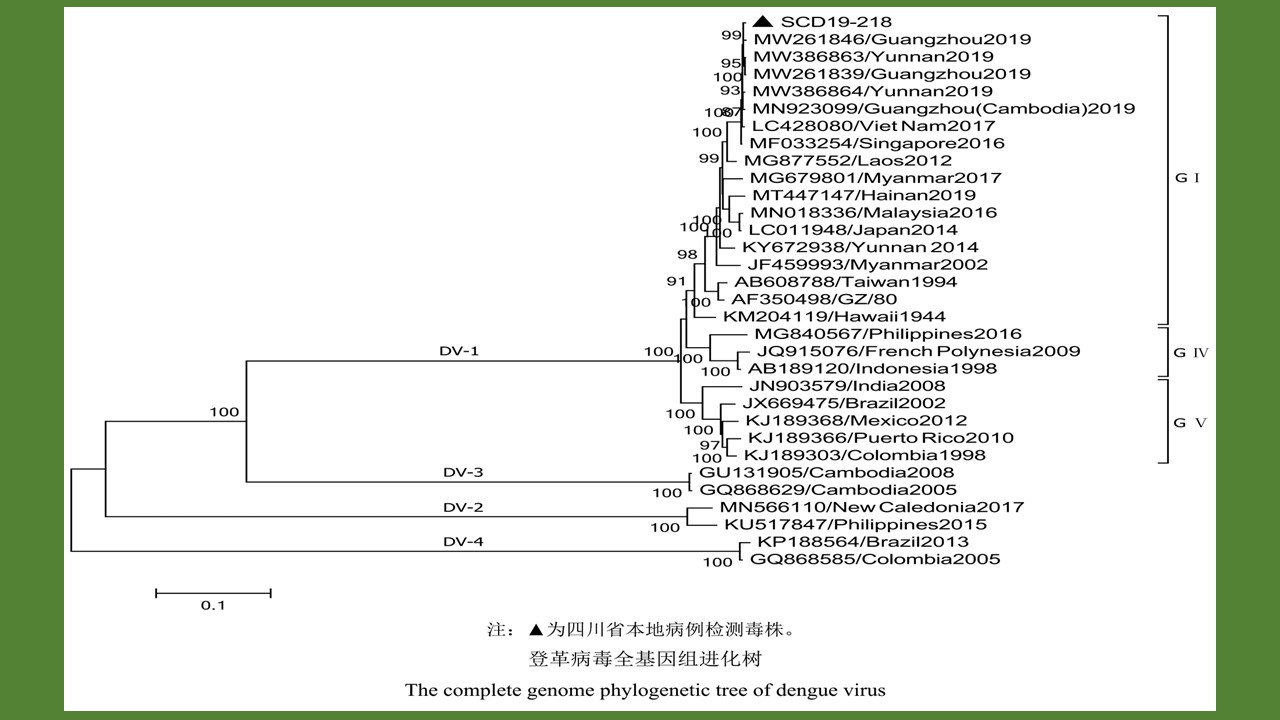
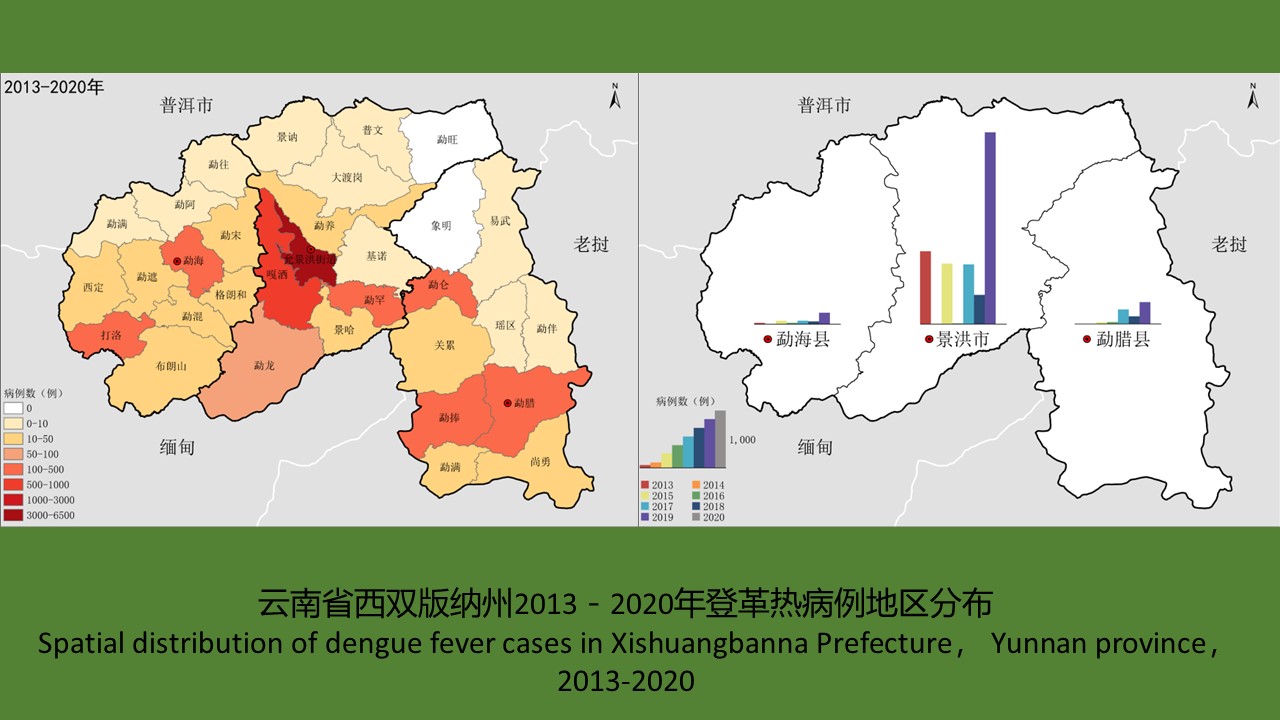
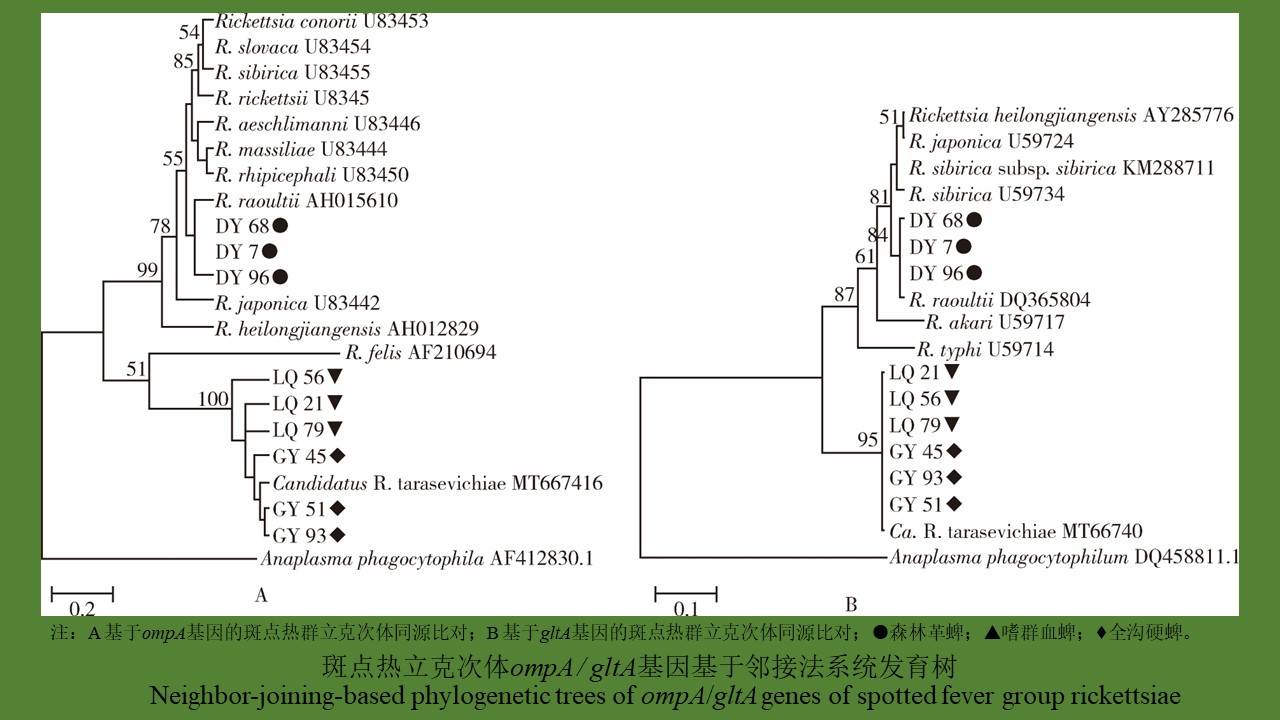
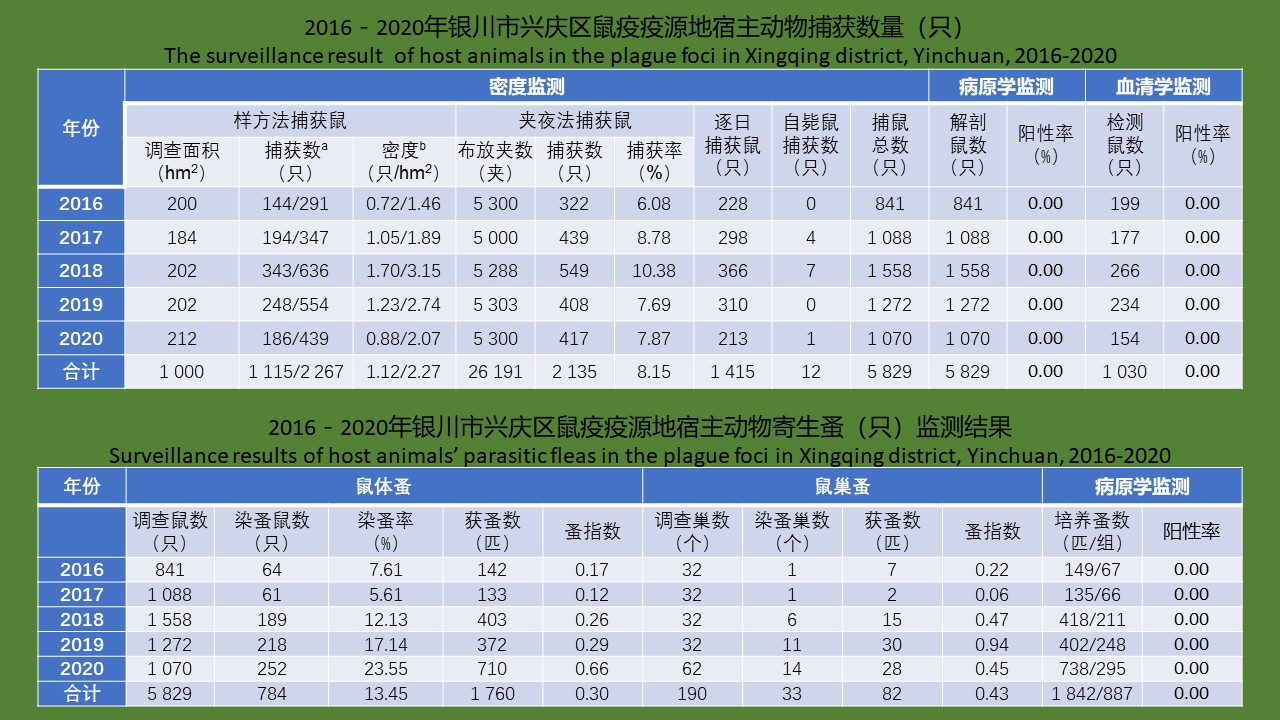
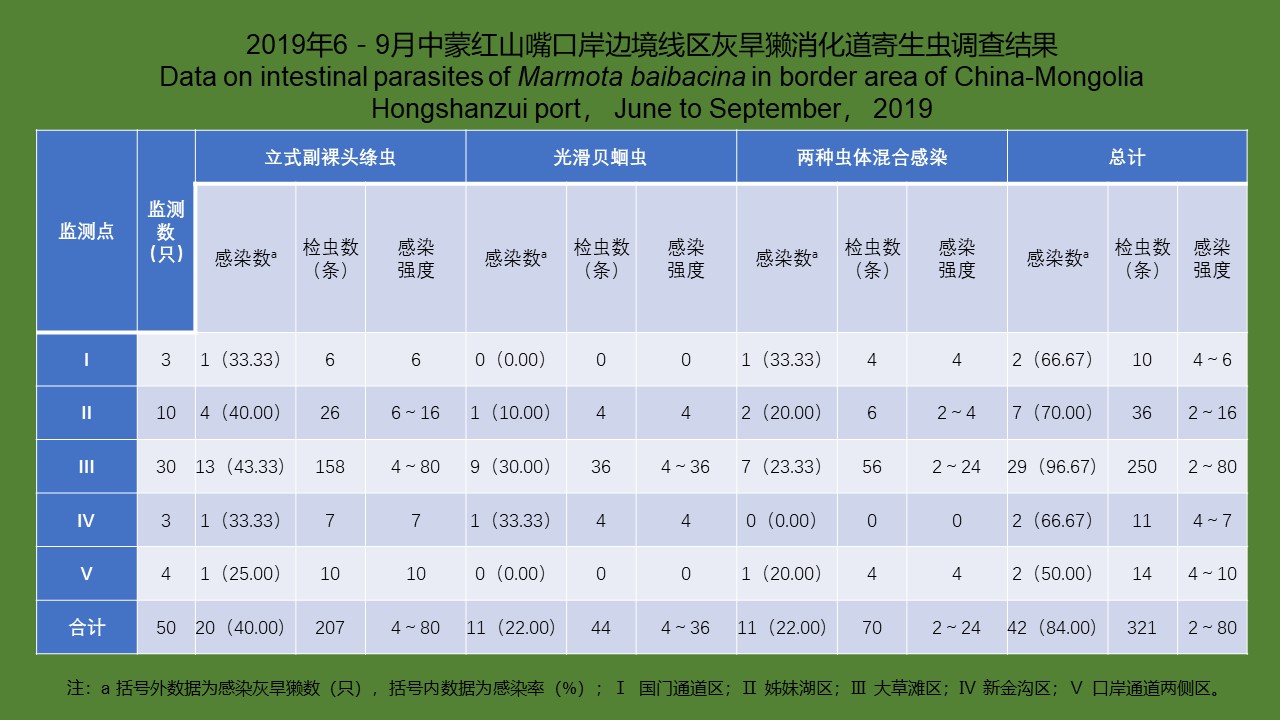
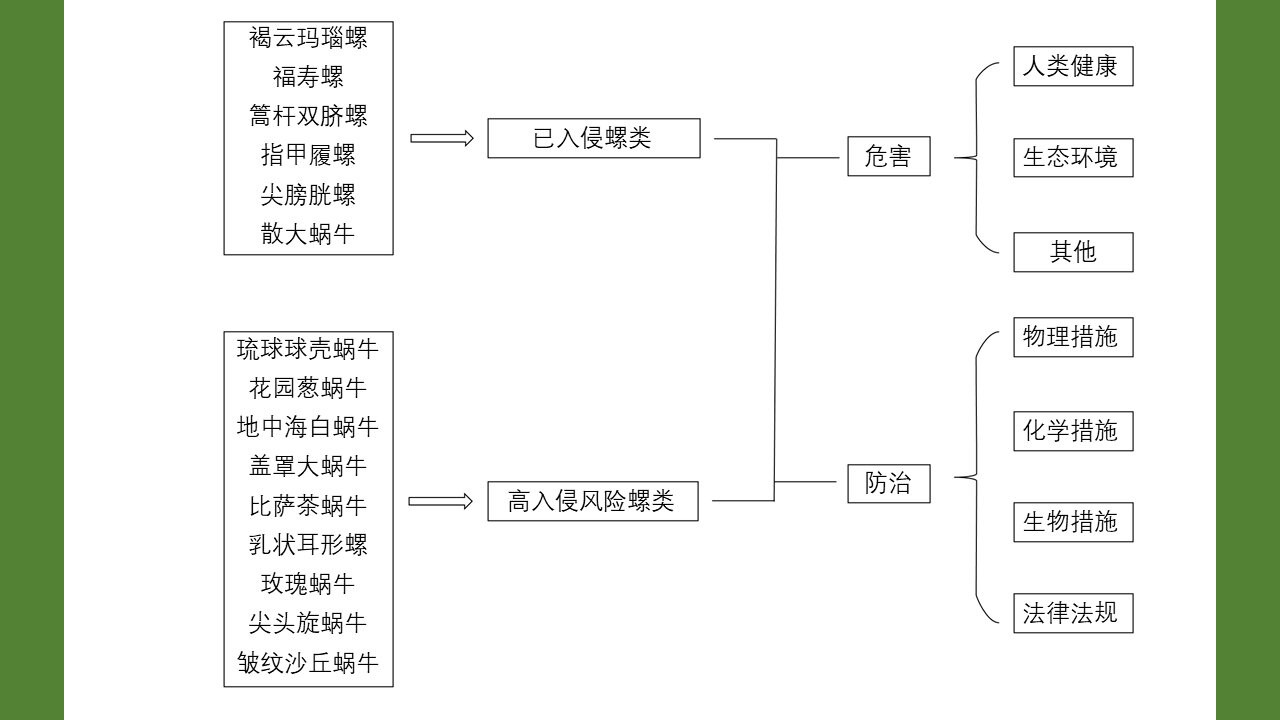
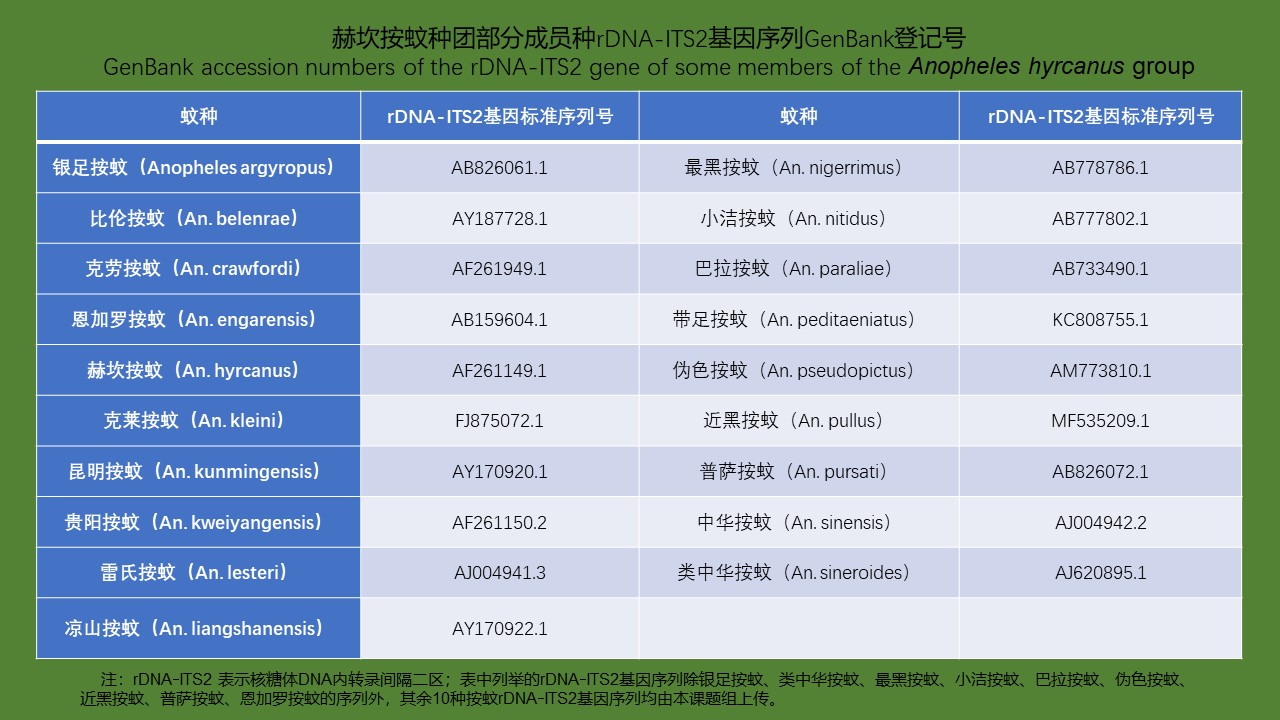
YU Juan, BIAN Xiang, XIE Bing, ZHAO Yong-bo, BI Ge-yue, DU Xia-yan, BI Li-fang, LI Dong-mei, RAO Hua-xiang
Objective To investigate the prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi, Leptospira interrogans, Rickettsia typhi, Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Orientia tsutsugamushi, and Francisella tularensis in rodents in the southeast of Shanxi province, China, and to provide a scientific basis for the prevention and control of local natural focal diseases. Methods Seven sampling sites were selected in the southeastern region of Shanxi province in July 2020 and May 2021, and rodents were captured by the night trapping method. The spleen and kidney tissues of rodents were collected under aseptic conditions for detection of the above six pathogens by real-time polymerase chain reaction. The difference in pathogen detection rate among different species, sexes, tissues, and habitats of rodents was analyzed by the χ2 test or Fisher's exact test. Results In total, 248 rodents from 8 species were captured, including Mus musculus, Apodemus agrarius, Niviventer confucianus, Caryomys inez, A. draco, Rattus tanezumi, Cricetulus triton, and A. peninsulae. Except A. peninsulae, four pathogens namely B. burgdorferi, L. interrogans, A. phagocytophilum, and O. tsutsugamushi were detected in the other 7 species of rodents, with detection rates of 21.77% (54/248), 5.24% (13/248), 1.21% (3/248), and 0.40% (1/248), respectively (χ2=200.097, P<0.001). R. typhi and F. tularensis were not detected. The detection rate of B. burgdorferi was the highest in the forest region and was statistical different between different habitats (χ2=17.906, P<0.001). B. burgdorferi was mainly detected in N. confucianus and A. agrarius, with a higher detection rate in kidney tissue than in spleen tissue (χ2=5.310, P=0.021). The detection rate of L. interrogans was the highest in the village, but was comparable between different habitats (Fisher's exact test, P=0.971). L. interrogans was mainly detected in R. tanezumi, with no statistical difference in the detection rate between spleen and kidney tissues (χ2=0.773, P=0.379). In addition, 11 rodents were found to have mixed infection with two pathogens. Conclusion B. burgdorferi and L. interrogans are the main pathogens prevalent in the rodents in southeastern Shanxi, which may have the possibility to cause human diseases. Therefore, corresponding prevention and control measures should be taken into consideration by relevant authorities.