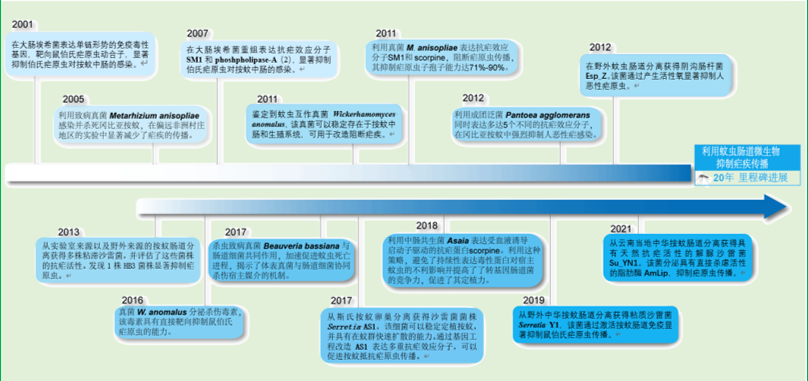
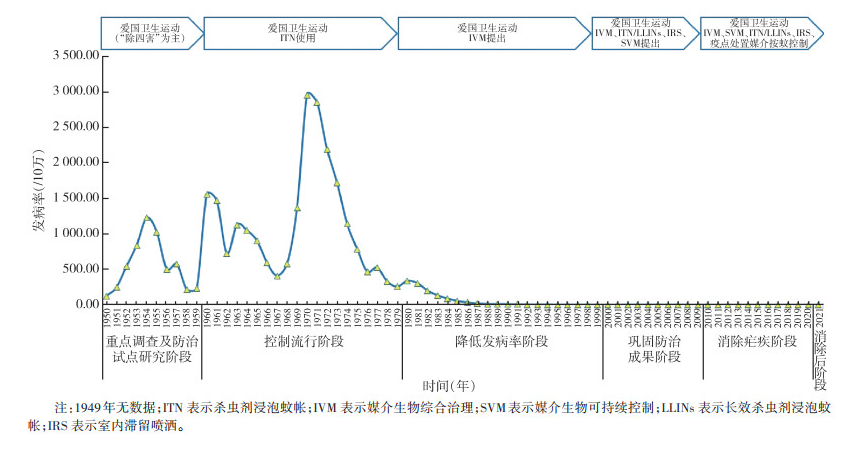
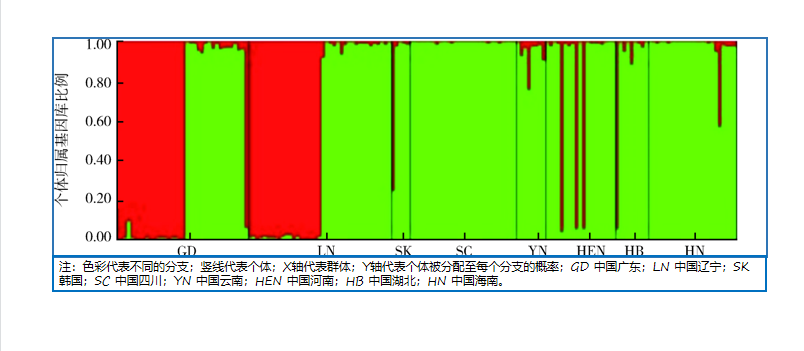
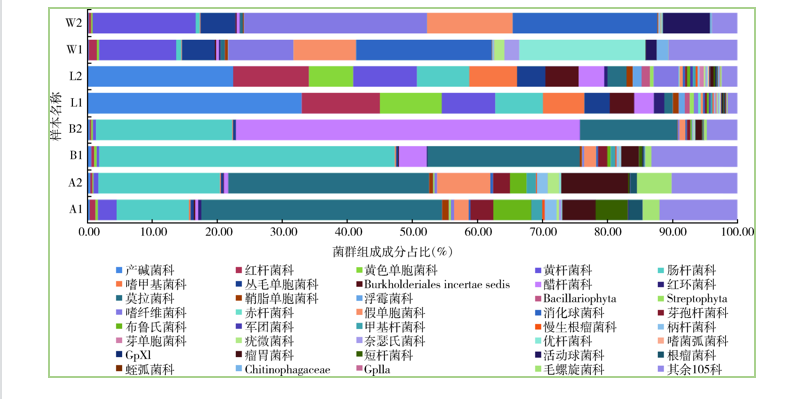
HU Yuan-feng, TAN Liang-fei
Objective To investigate the density, infestation rate, seasonal variation, distribution, and population composition of cockroaches in Ezhou of Hubei province, China, and the insecticide resistance of Blattella germanica to eight insecticides, and to provide a scientific basis for the prevention and control of cockroach. Methods In 2016-2020, the sticky trap method was used to monitor the density of cockroaches in six types of habitats, i.e., farmers’ market, supermarket, hotel, catering environment, hospital, and residential area, in Ezhou, and in 2018 and 2020, the residual film method recommended by the World Health Organization was used to determine the insecticide resistance of B. germanica. Excel 2007 software was used for statistical analysis, SPSS 17.0 software was used to perform the Chi-square test of the density, infestation rate, and composition ratio of cockroaches, and median knockdown time (KT50) was calculated for the results of insecticide resistance. Results The density and infestation rate of cockroaches showed a trend of gradual reduction year by year in Ezhou in 2016-2020, with the highest density of 0.28 cockroaches/trap and the highest infestation rate of 14.37% in 2016, and the lowest density of 0.14 cockroaches/trap and the lowest infestation rate of 6.37% in 2020. Seasonal variation was observed for cockroaches, and a peak was observed in July, with a density of 0.41 cockroaches/trap and an infestation rate of 17.37%. The highest density and infestation rate of cockroaches were observed in catering environment (with a density of 0.46 cockroaches/trap and an infestation rate of 19.51%) and farmers’ market (with a density of 0.31 cockroaches/trap and an infestation rate of 15.57%), followed by hotel and supermarket, and the low density and infestation rate were observed in residential area and hospital. B. germanica was the most numerous species and accounted for 93.55% of total catch, followed by Periplaneta fuliginosa and P. americana, accounting for 5.54% and 0.91%, respectively. The resistance ratios of B. germanica to deltamethrin, beta-cyfluthrin, lambda-cyhalothrin, tetramethrin, permethrin, azamethiphos, alpha-cypermethrin, and acephate were 9.86, 5.08, 3.61, 2.34, 1.76, 1.52, 1.27, and 1.18 between 2018 and 2020, respectively. Conclusion B. germanica is the dominant species of cockroaches in Ezhou of Hubei province, with peak density in July, and catering environment and farmers’ market have the highest infestation rate. B. germanica has moderate resistance to deltamethrin and beta-cyfluthrin and low resistance to lambda-cyfluthrin, tetramethrin, permethrin, azamethiphos, alpha-cypermethrin, and acephate.