 PDF(1824 KB)
PDF(1824 KB)


浙江省义乌市2021年3种不同生境中山羊寄生蜱类调查
朱心红, 吴因平, 李天奇, 王金娜, 侯娟
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4) : 493-498.
 PDF(1824 KB)
PDF(1824 KB)
 PDF(1824 KB)
PDF(1824 KB)
浙江省义乌市2021年3种不同生境中山羊寄生蜱类调查
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}An investigation of on-host ticks in goats in three different habitats in Yiwu city of Zhejiang province, China, 2021
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}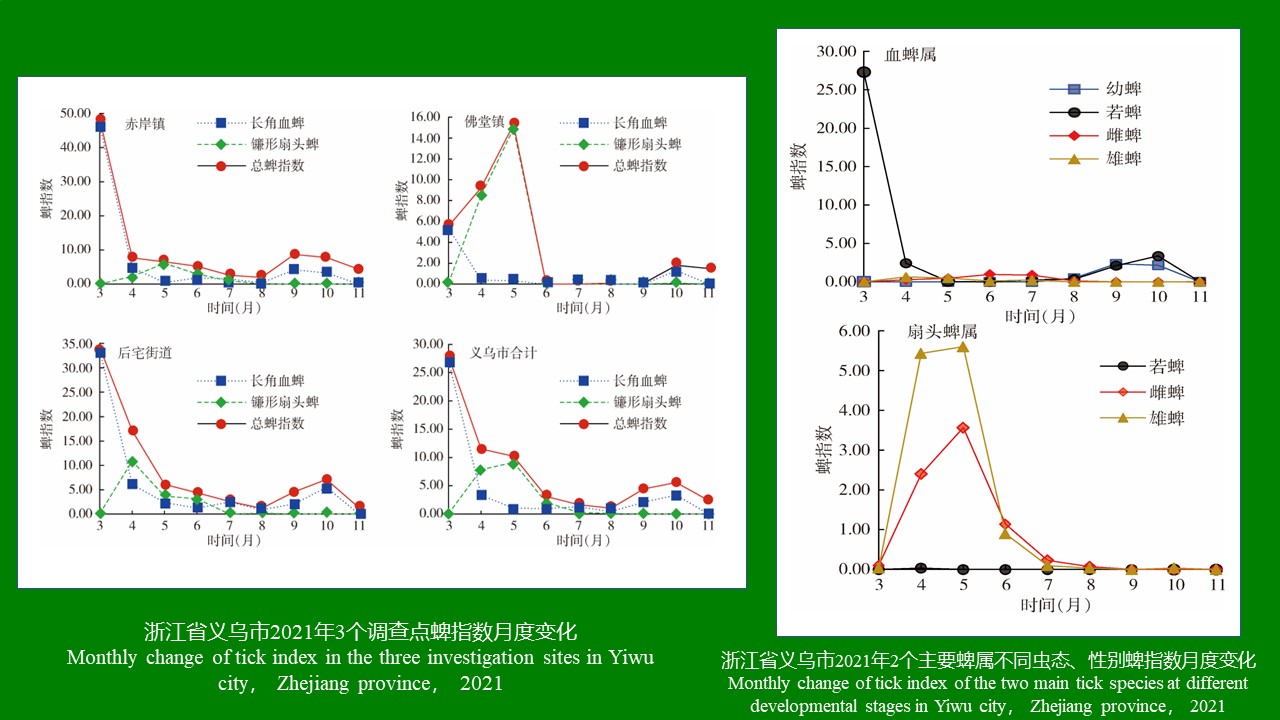
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |