 PDF(562 KB)
PDF(562 KB)


 PDF(562 KB)
PDF(562 KB)
 PDF(562 KB)
PDF(562 KB)
内蒙古自治区2020年鼠疫监测调查与分析
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Analysis of plague surveillance in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China, 2020
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}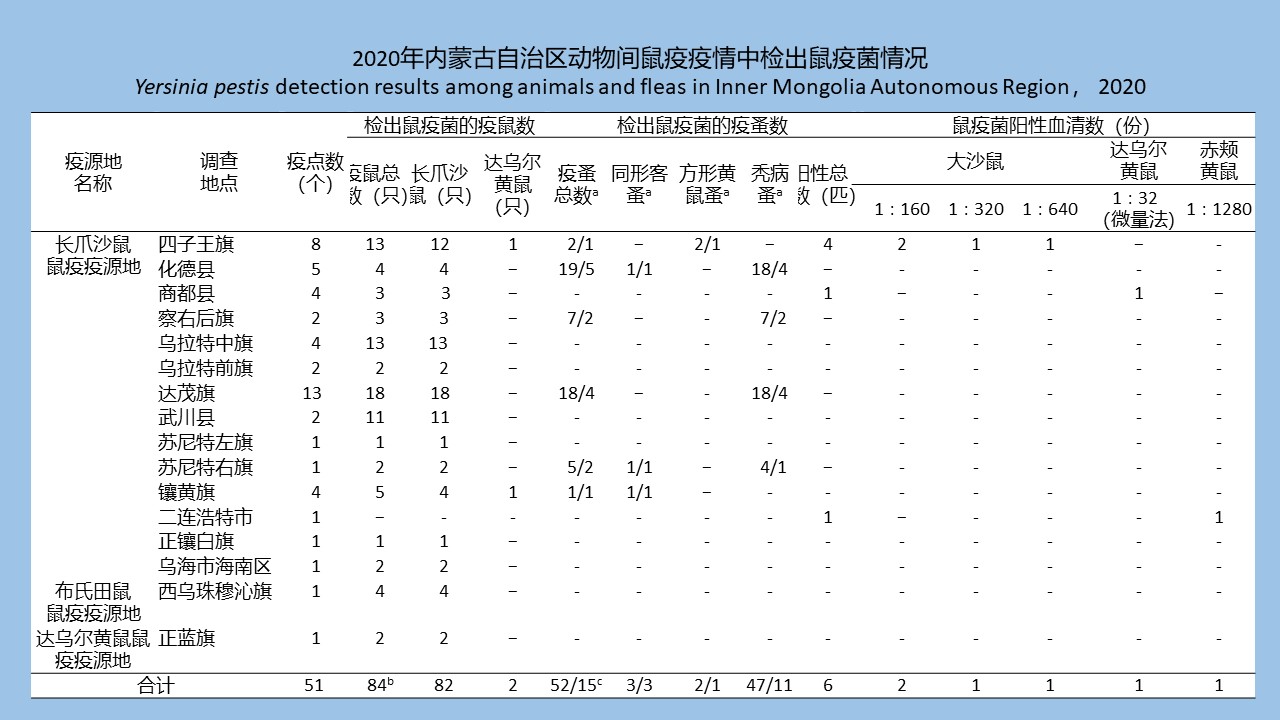
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |