 PDF(602 KB)
PDF(602 KB)


 PDF(602 KB)
PDF(602 KB)
 PDF(602 KB)
PDF(602 KB)
广东省农区鼠类物联网智能监测系统的应用研究
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Study on application of IoT intelligent monitoring system for agricultural rodent pests in Guangdong province, China
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}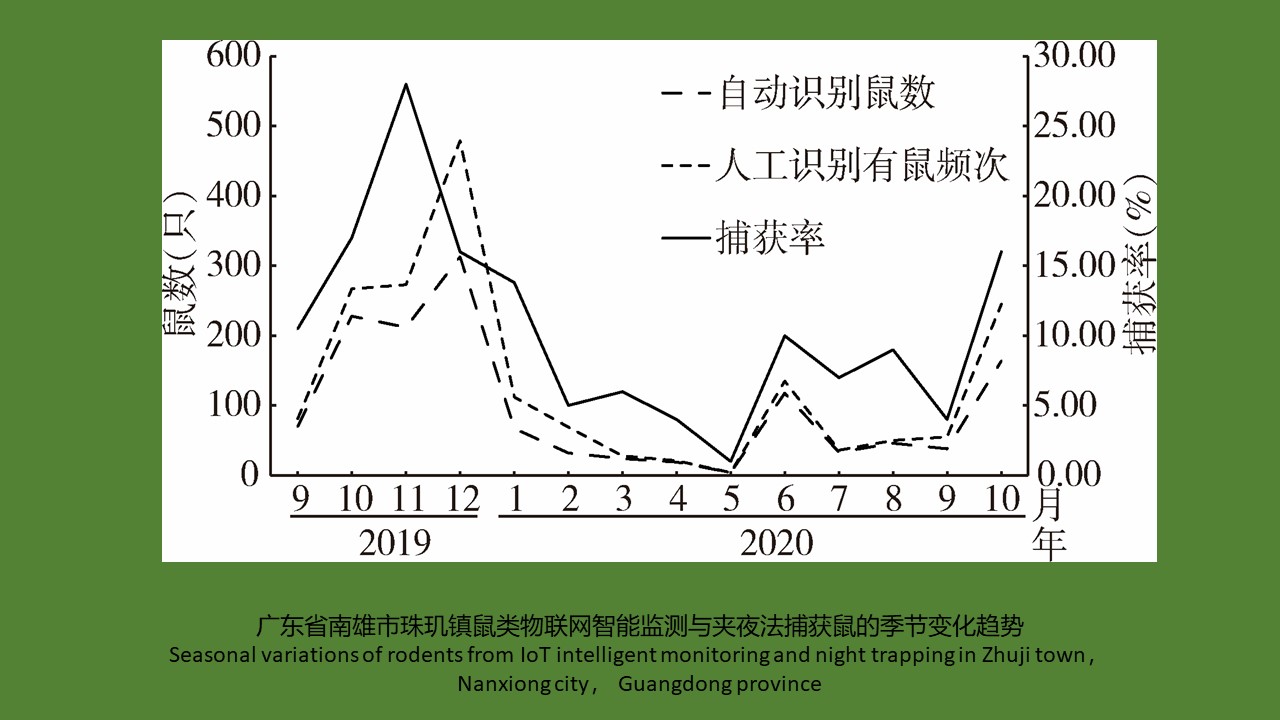
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |