 PDF(1949 KB)
PDF(1949 KB)


温州口岸截获蜱体内微生物群落结构、抗生素抗性基因及毒力因子的宏基因组分析
许雪莲, 韩阿祥, 叶诗晴, 关万春, 楼永良
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2021, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6) : 763-771.
 PDF(1949 KB)
PDF(1949 KB)
 PDF(1949 KB)
PDF(1949 KB)
温州口岸截获蜱体内微生物群落结构、抗生素抗性基因及毒力因子的宏基因组分析
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Metagenomic analysis of microbial community structure, antibiotic resistance genes, and virulence factors of ticks captured at Wenzhou port, Zhejiang province, China
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}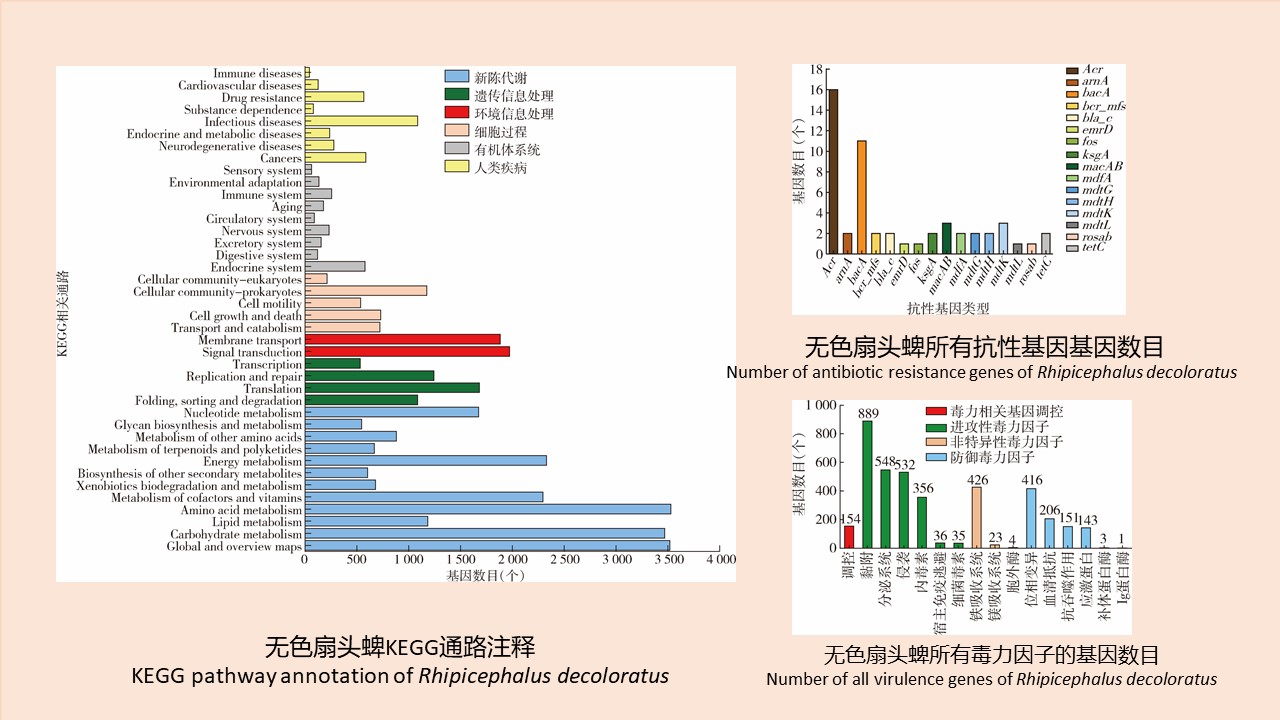
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |