 PDF(596 KB)
PDF(596 KB)


南宁市2022年白纹伊蚊击倒抗性基因型分布研究
李雪, 凌峰, 韦舒琳, 屈志强, 刁书琴, 黄燕翠, 罗密芳
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (4) : 480-484.
 PDF(596 KB)
PDF(596 KB)
 PDF(596 KB)
PDF(596 KB)
南宁市2022年白纹伊蚊击倒抗性基因型分布研究
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Distribution of knockdown resistance genotypes in Aedes albopictus in Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China, 2022
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}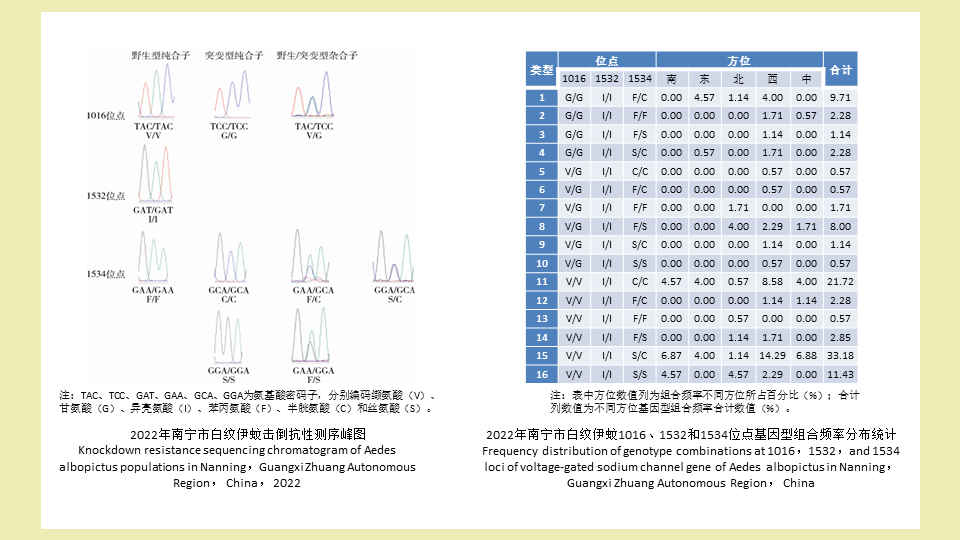
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |