 PDF(822 KB)
PDF(822 KB)


第24届冬奥会张家口赛区2018-2021年野鼠寄生蚤调查分析
陈永明, 康东梅, 兰晓宇, 闫东, 刘冠纯, 史献明, 杜国义, 周松, 杨顺林, 候芝林, 郑楠, 杨爱, 张晓磊, 张进一, 孙飞, 马勇, 郭超, 戴宏, 王晓燕
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3) : 414-417.
 PDF(822 KB)
PDF(822 KB)
 PDF(822 KB)
PDF(822 KB)
第24届冬奥会张家口赛区2018-2021年野鼠寄生蚤调查分析
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Investigation of parasitic fleas on wild rodents in Zhangjiakou competition zone of the 24th Olympic Winter Games, 2018-2021
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}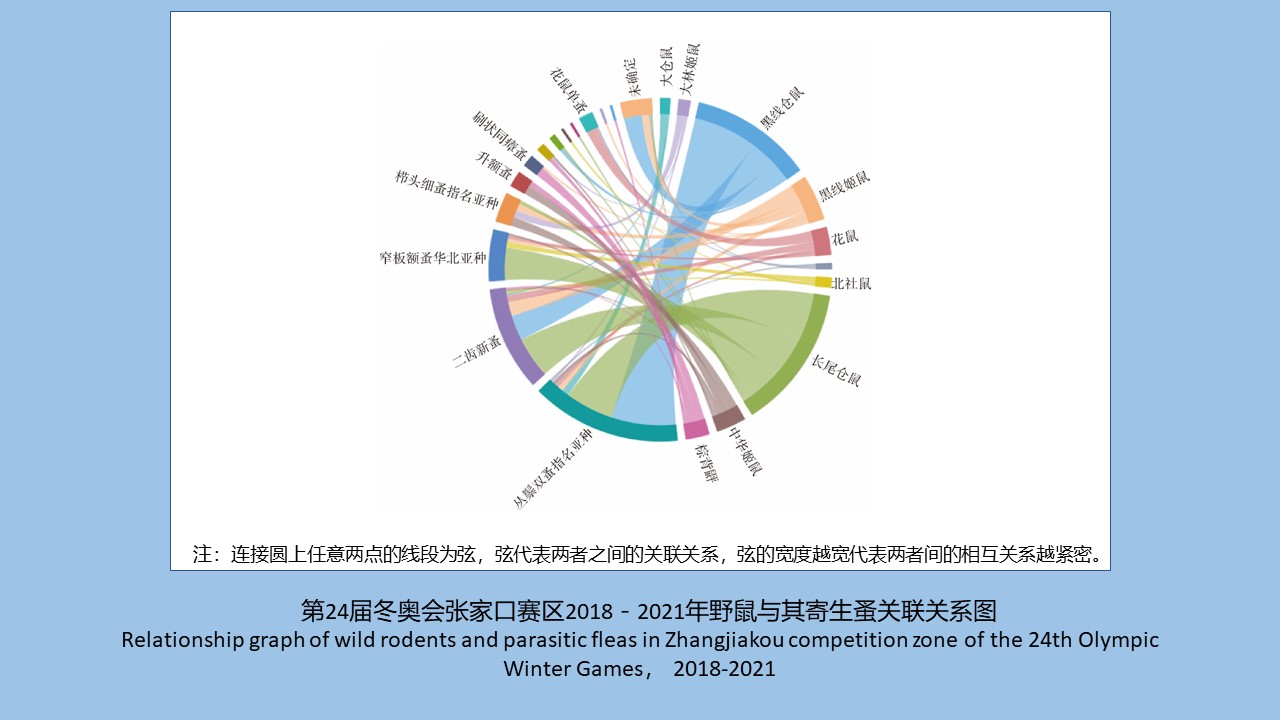
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |