 PDF(4723 KB)
PDF(4723 KB)


不同气候情景下红带锥蝽在中国潜在适生区预估
周若冰, 高源, 常楠, 马德龙, 李超, 吴海霞, 王君, 刘起勇
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1) : 125-132.
 PDF(4723 KB)
PDF(4723 KB)
 PDF(4723 KB)
PDF(4723 KB)
不同气候情景下红带锥蝽在中国潜在适生区预估
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Potential distribution of Triatoma rubrofasciata under different climatic scenarios in China
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}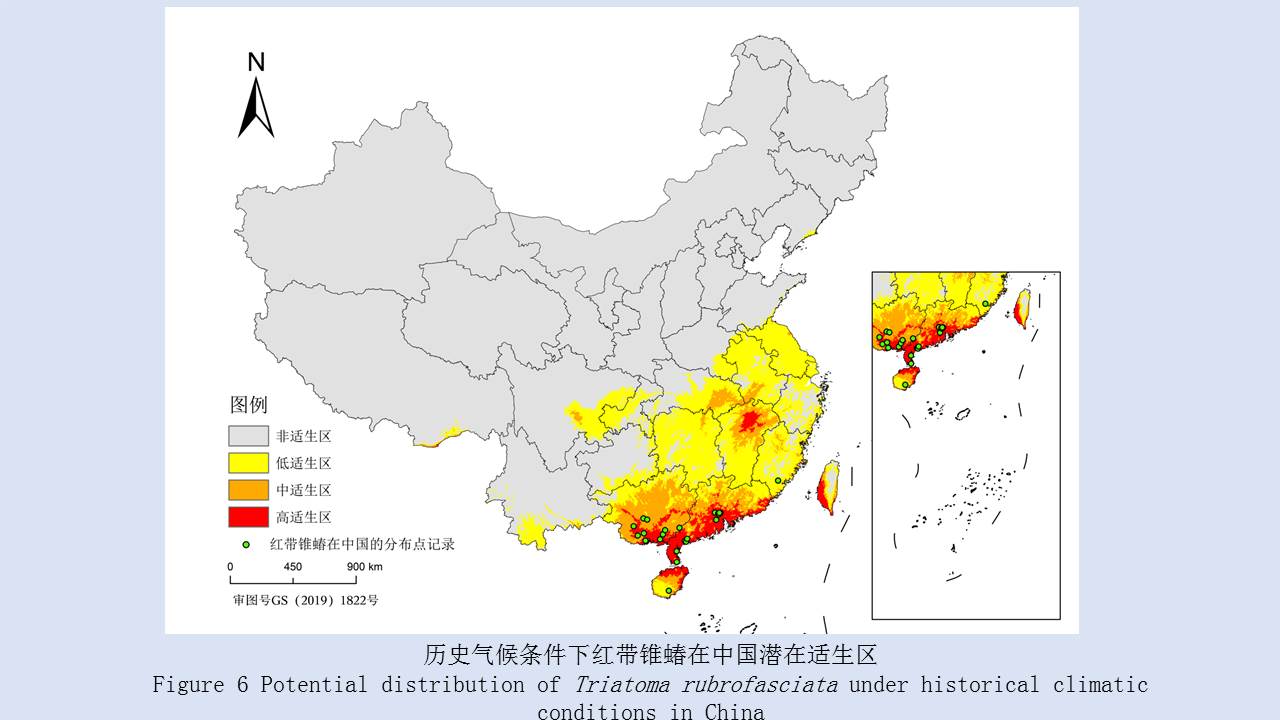
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |