 PDF(1296 KB)
PDF(1296 KB)


 PDF(1296 KB)
PDF(1296 KB)
 PDF(1296 KB)
PDF(1296 KB)
上海市蜱种类、分布及其携带病原
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Ticks species, distribution and pathogens in Shanghai, China
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}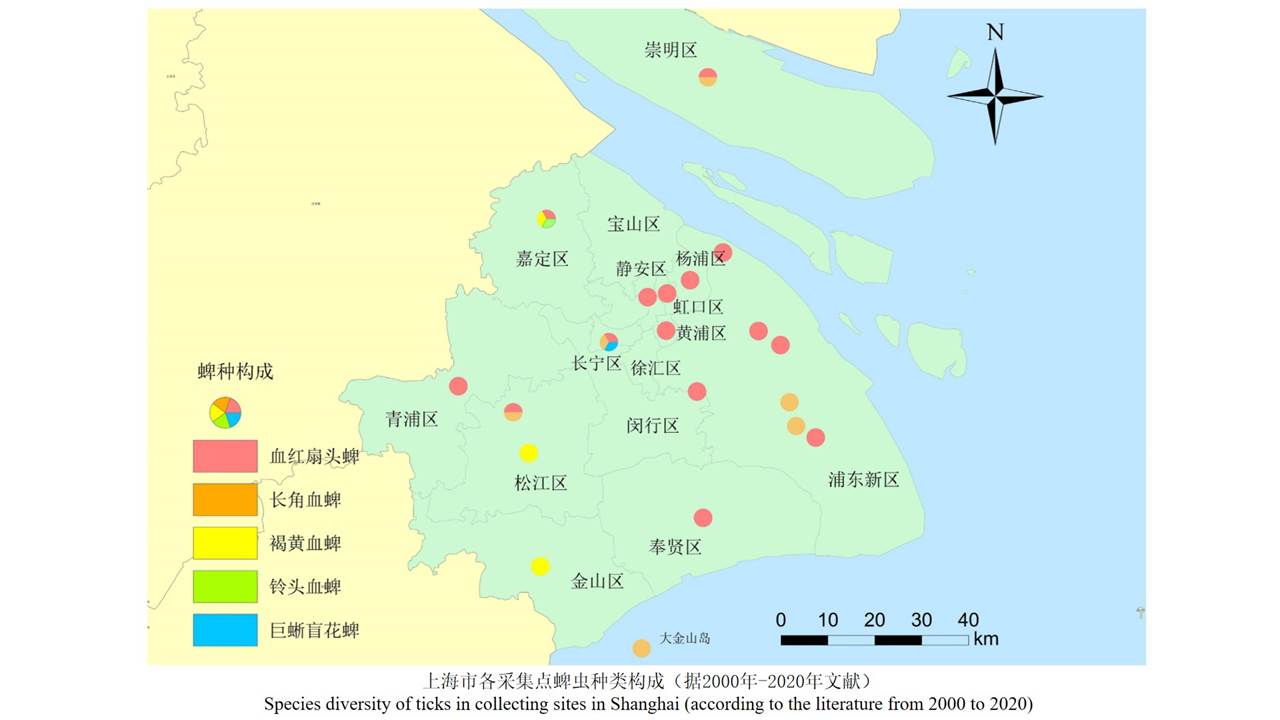
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |