 PDF(2684 KB)
PDF(2684 KB)


四川省广元市中华按蚊杀虫剂靶标基因的多态性及抗性突变频率研究
赵琼瑶, 邱星辉, 杨研, 罗兴, 宋晓明, 贾永朝
中国媒介生物学及控制杂志 ›› 2021, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (5) : 541-545.
 PDF(2684 KB)
PDF(2684 KB)
 PDF(2684 KB)
PDF(2684 KB)
四川省广元市中华按蚊杀虫剂靶标基因的多态性及抗性突变频率研究
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Polymorphism and resistance mutation frequency of the target genes of insecticides in Anopheles sinensis in Guangyuan of Sichuan province, China
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}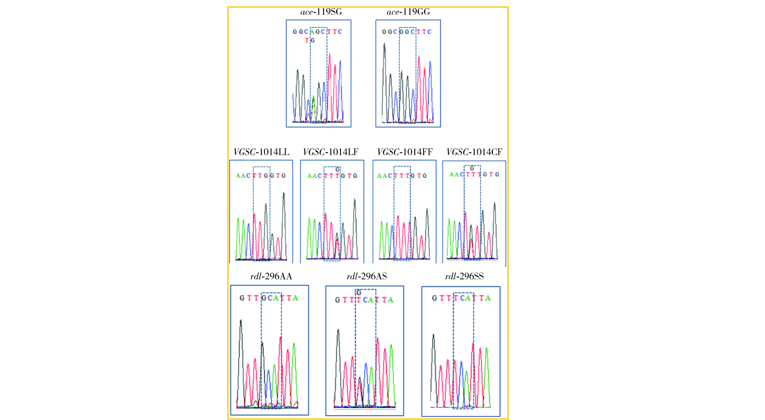
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |