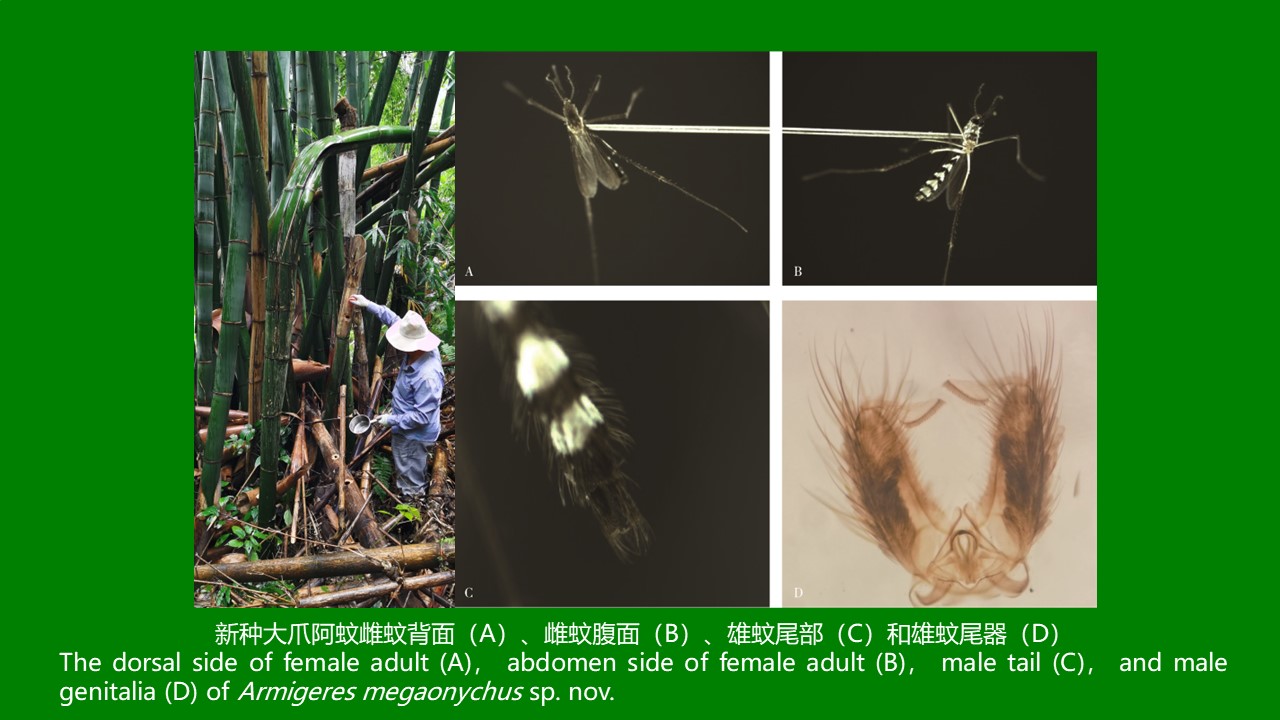
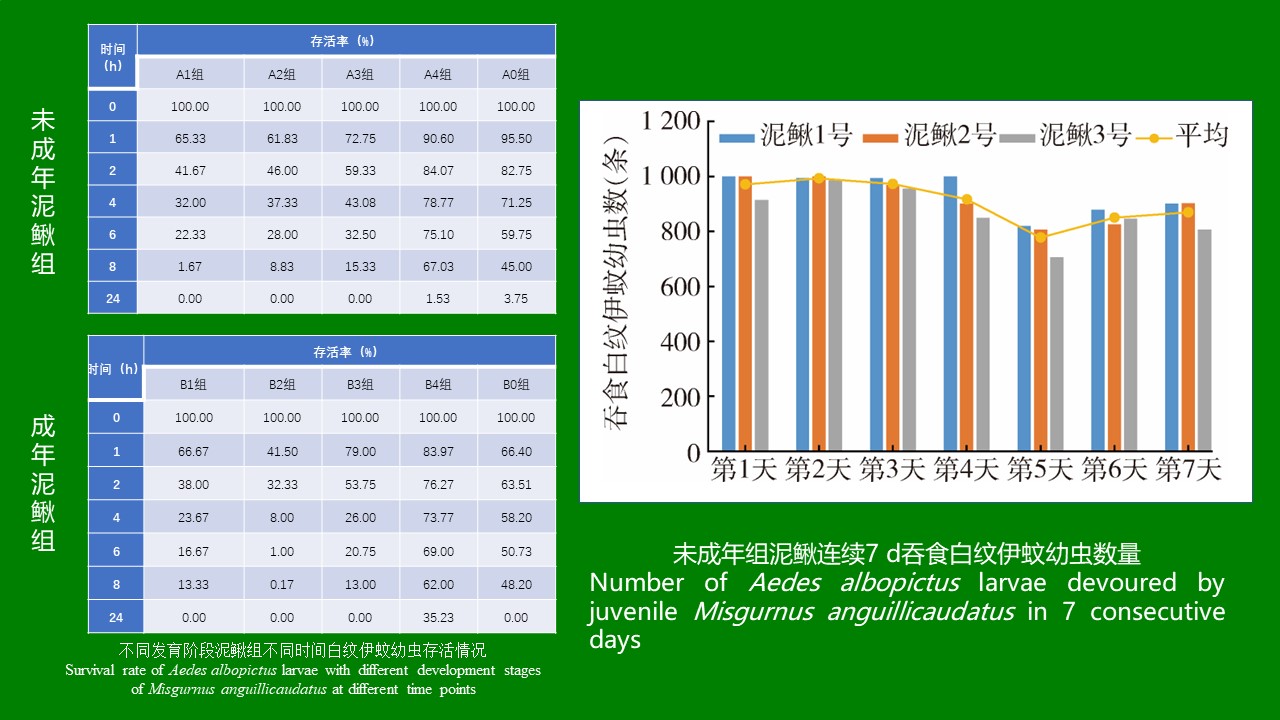
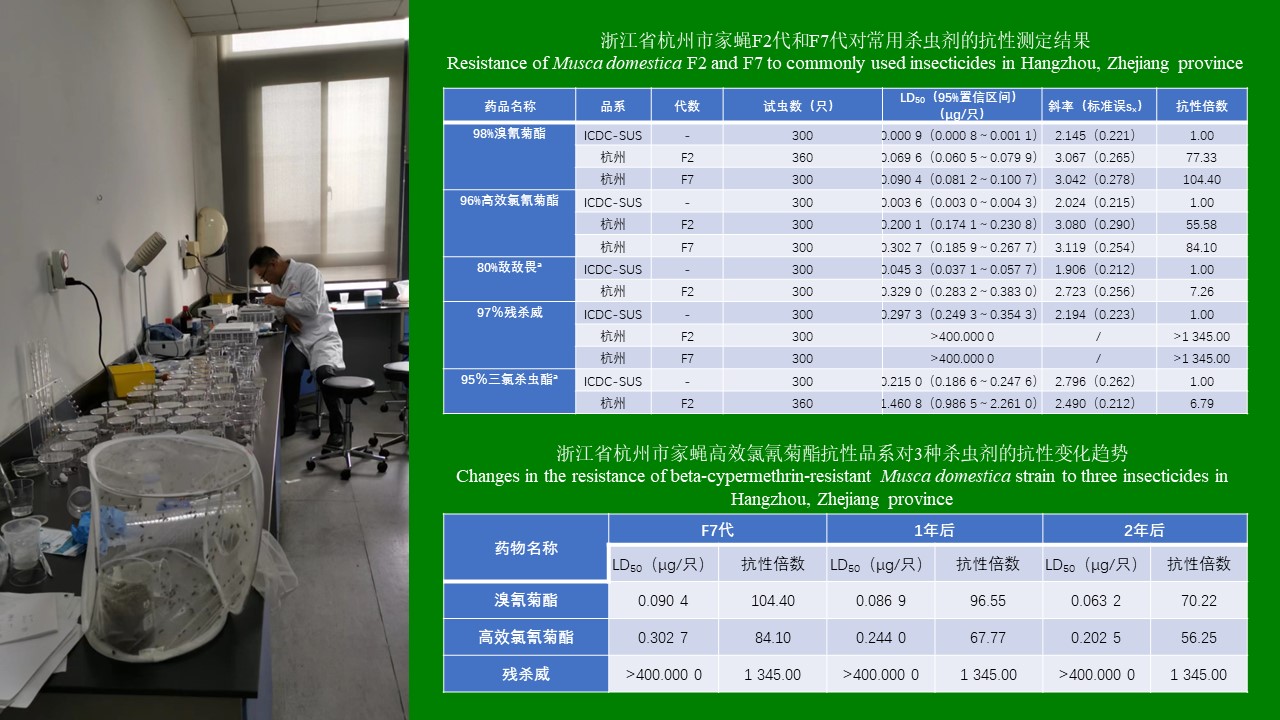
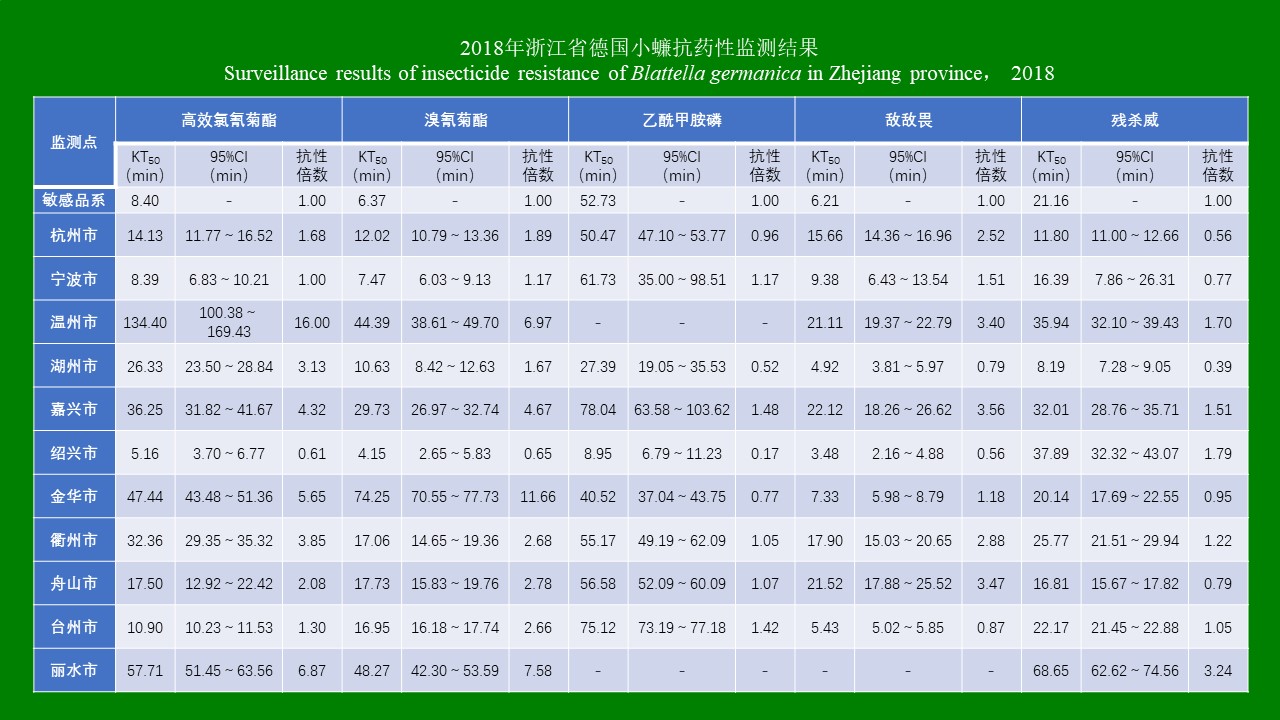
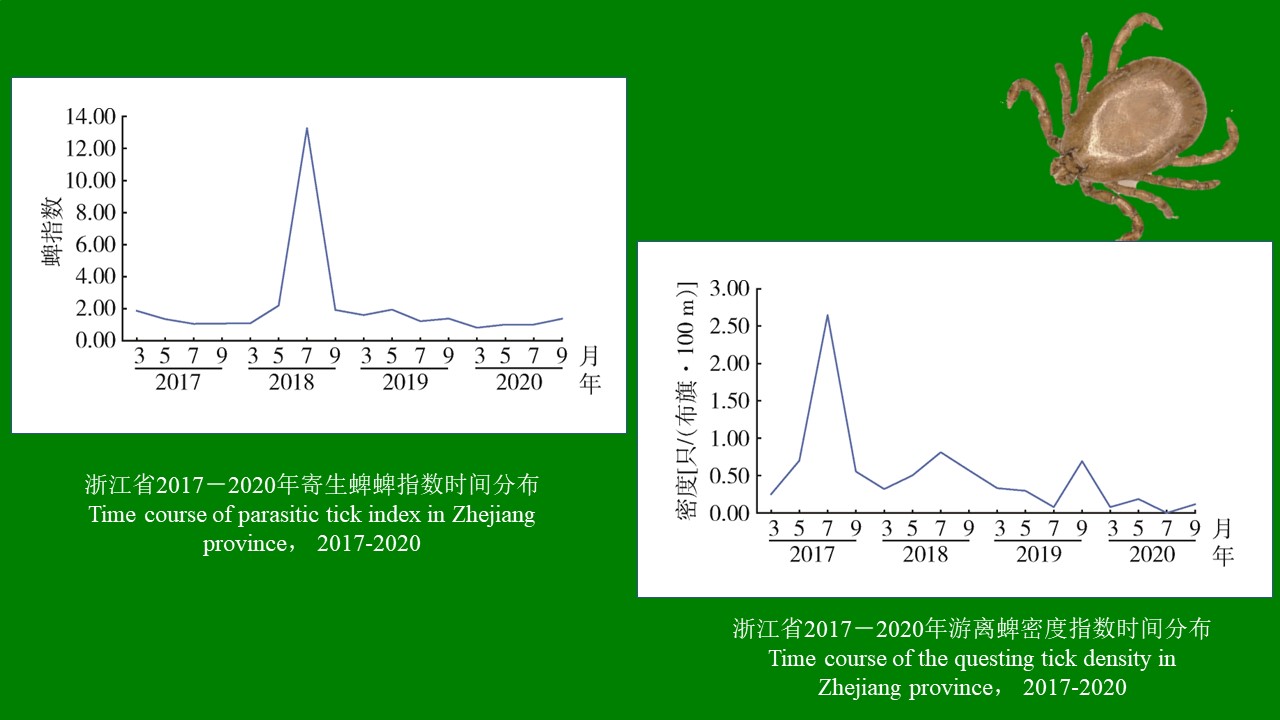
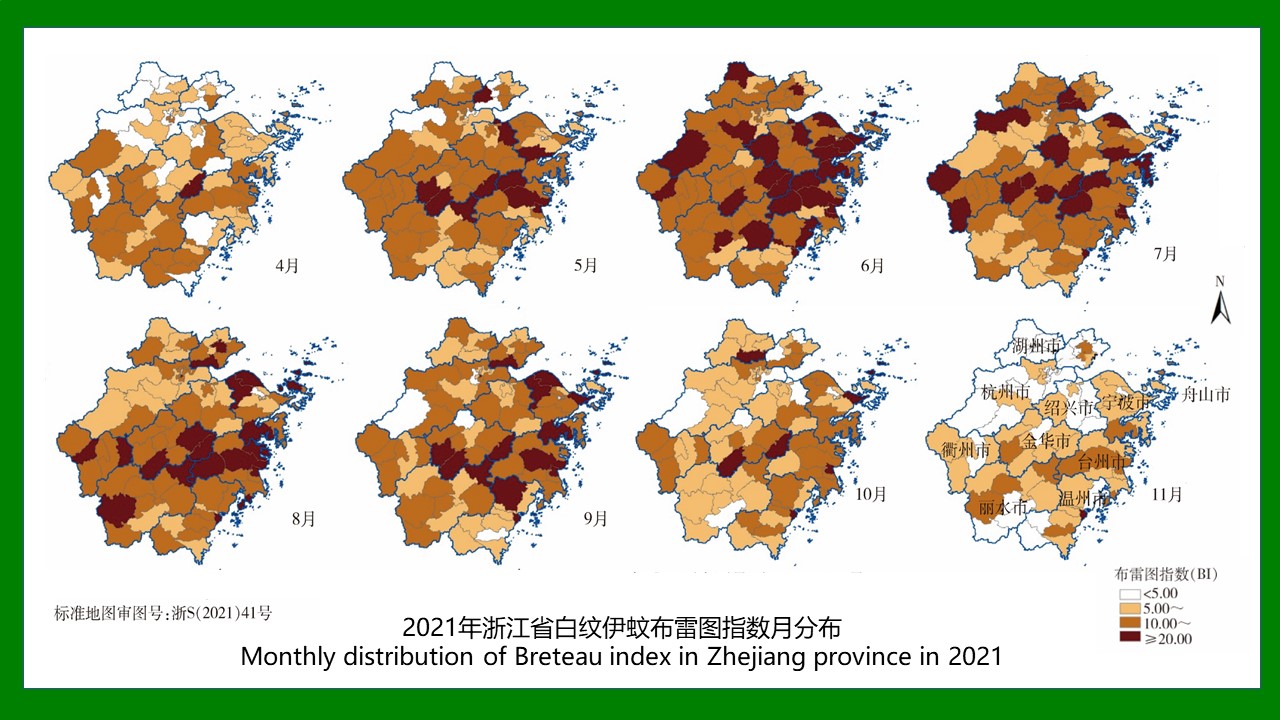
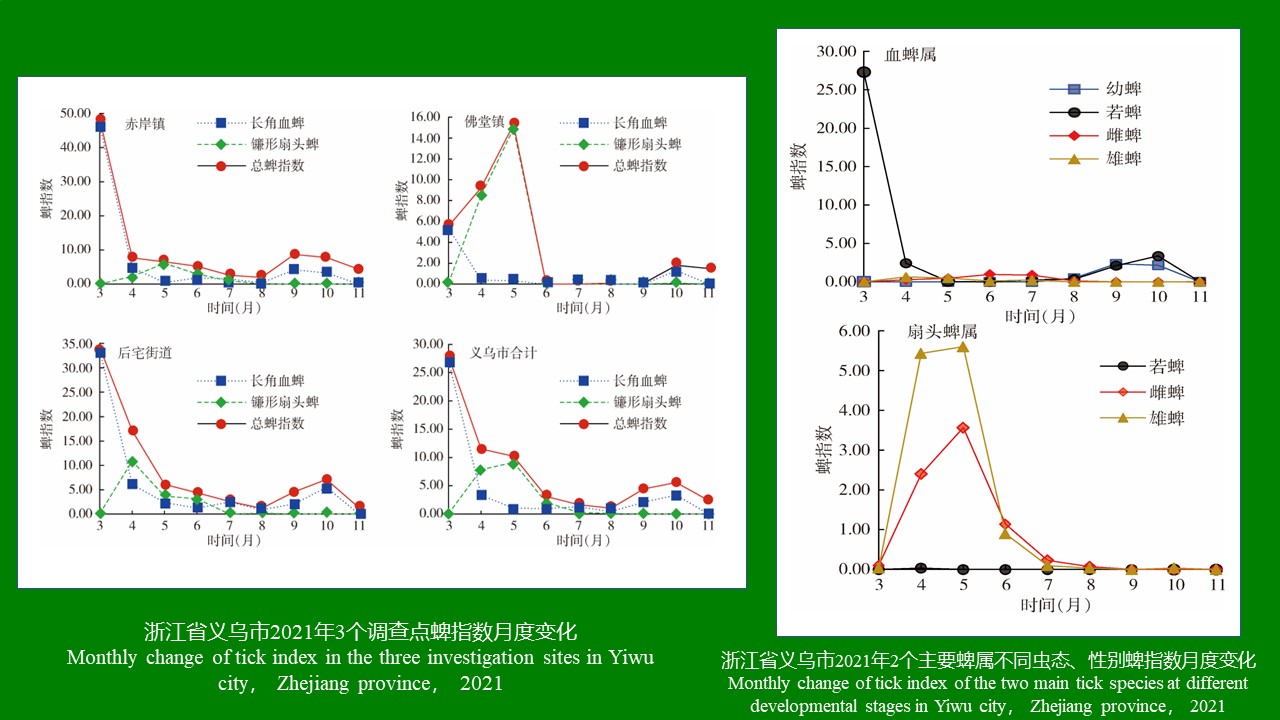
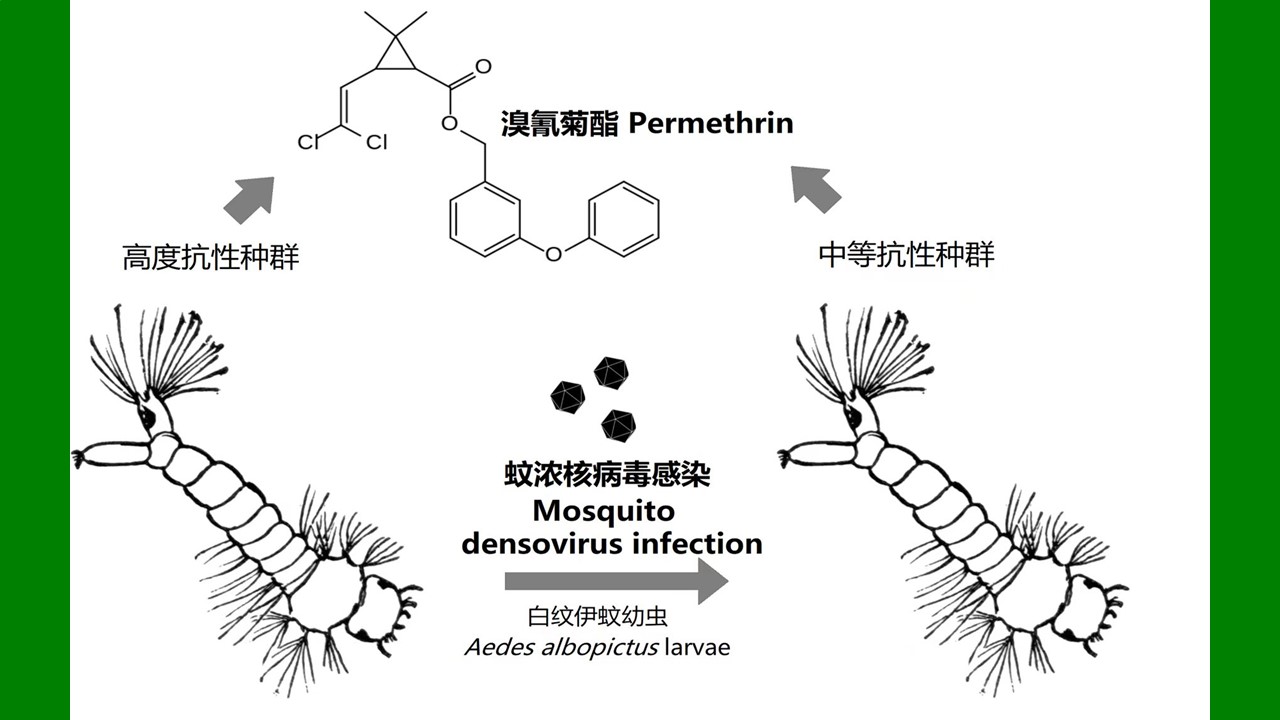
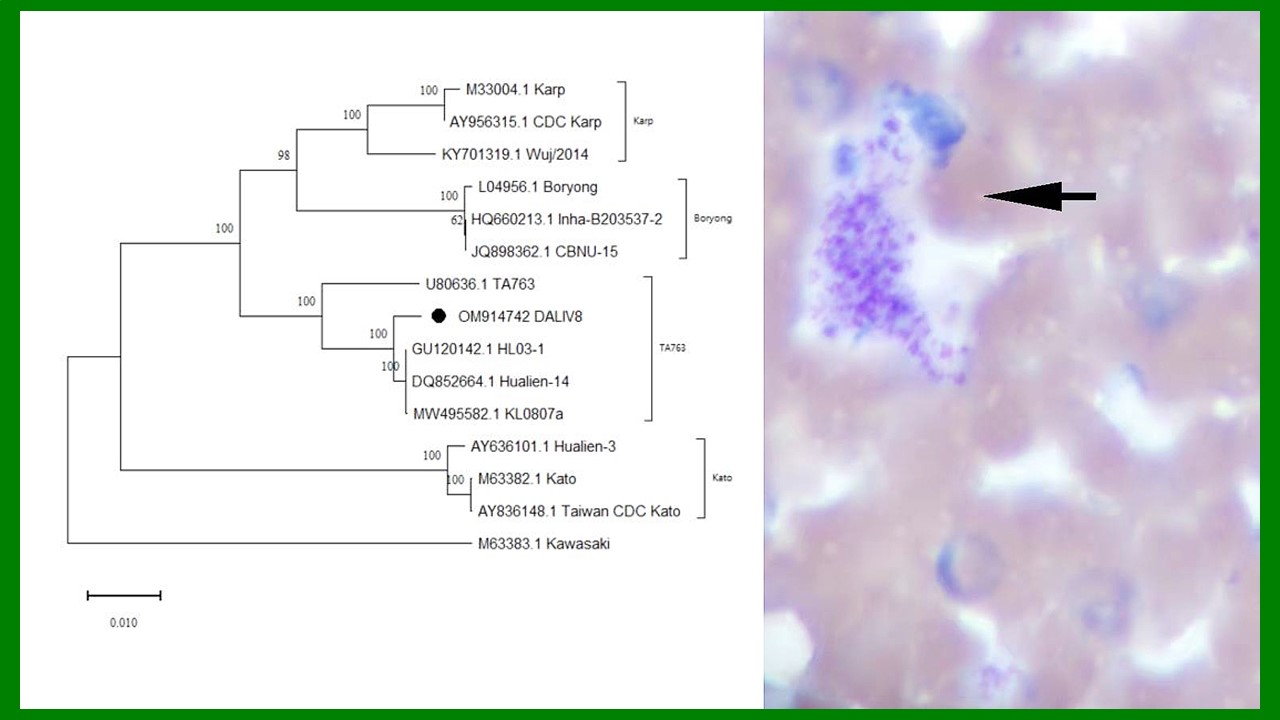
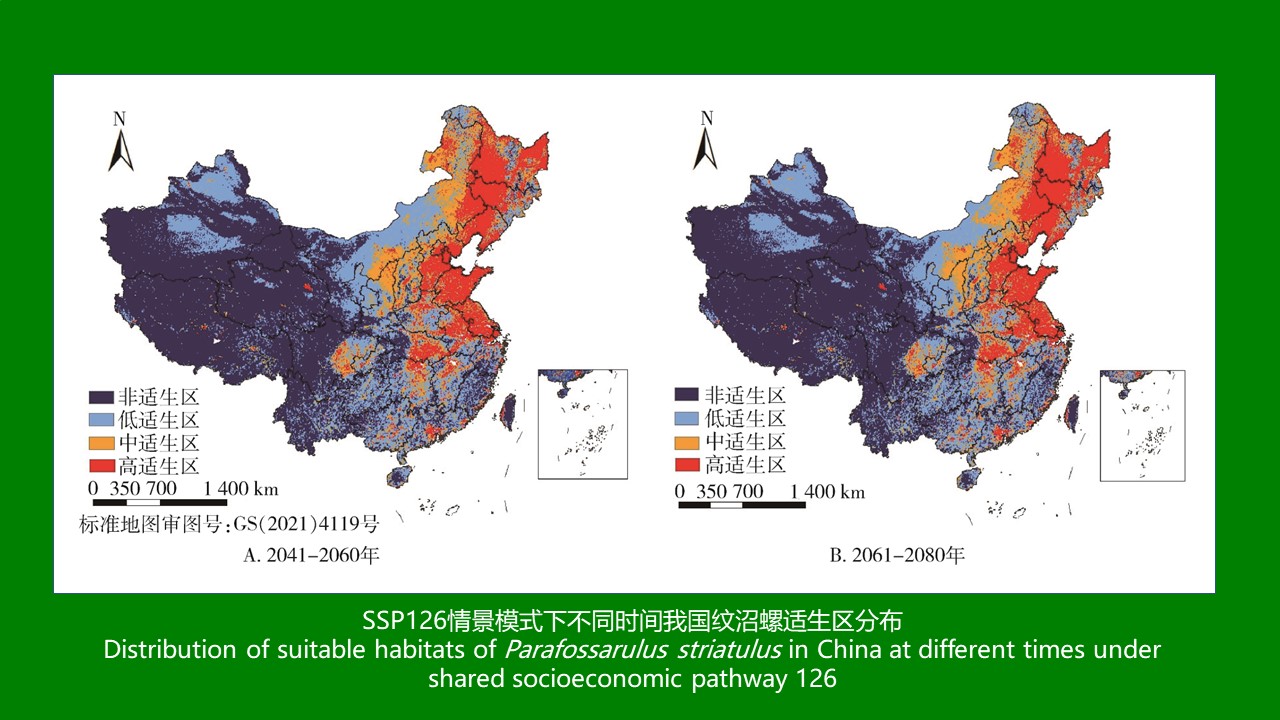
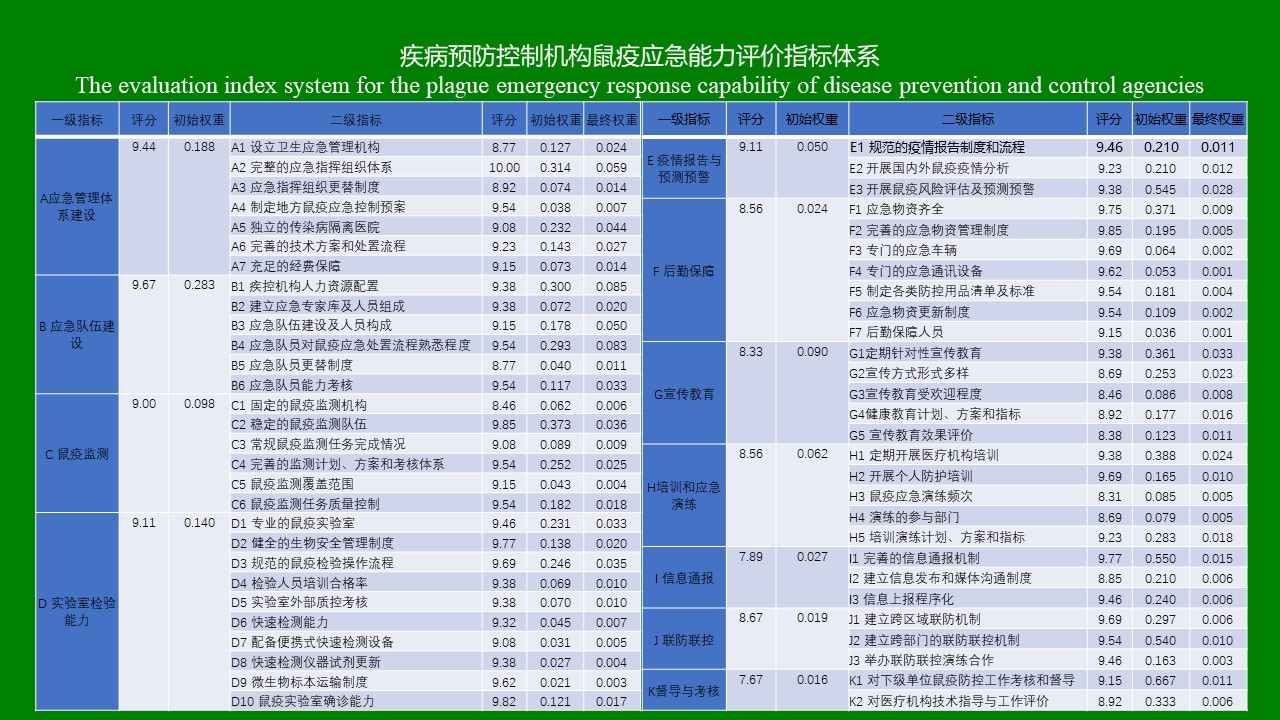
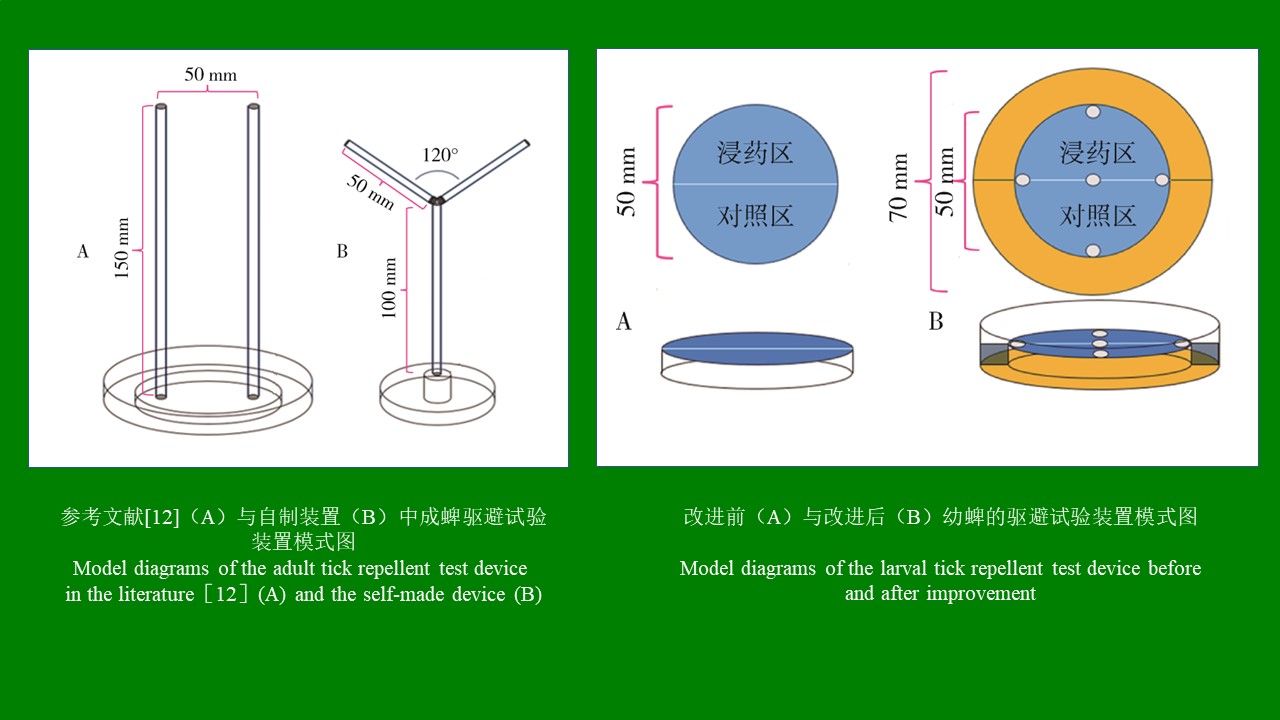
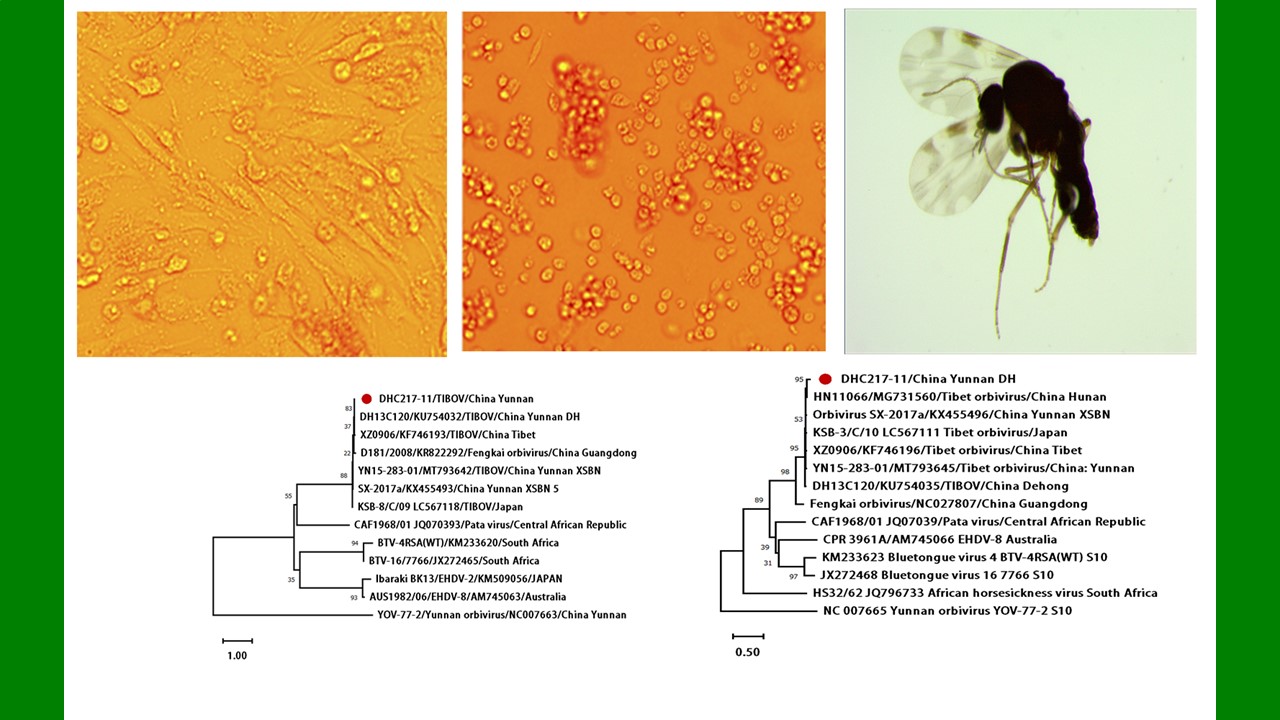
ZHANG Yan, WANG Chong, CHEN Xu-peng, CHEN Bin, CHEN Hang, LU Mo-yuan, WU Qi-xin, WANG Bai-ru, SONG Bing-dong, ZHANG Shou-gang
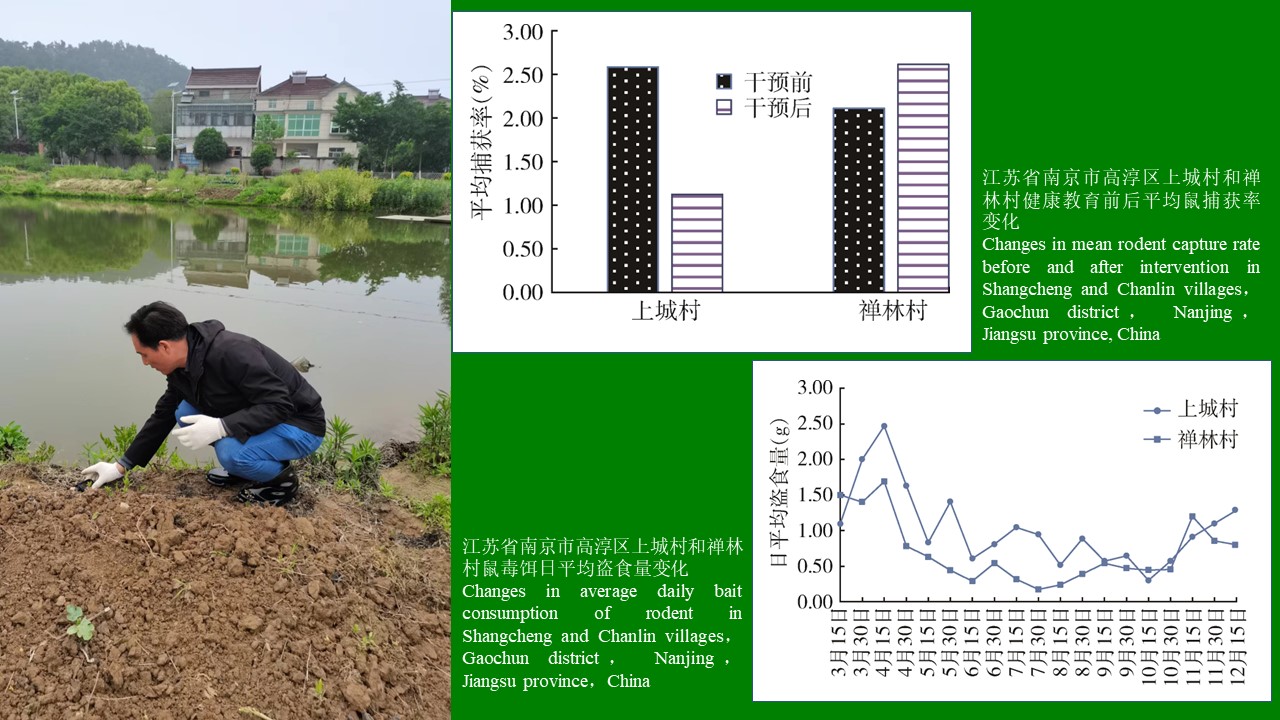
Objective To investigate the effect of health education in the chemical control of rodents, and to provide a scientific basis for formulating effective rodent control measures in Nanjing, Jiangsu province, China. Methods Shangcheng and Chanlin villages in Gaochun district, Nanjing, China were selected as intervention group (bait stations combined with health education for rodent control) and control group (bait stations alone for rodent control), respectively. The changes in farmers' awareness about rodents, bait consumption, and rodent densities in the two villages from March to December 2021 were analyzed to compare the effects of health education intervention on chemical control of rodents. Results Among 31 participants in Shangcheng village, the numbers of farmers with an awareness of general knowledge about rodents, rodent-borne diseases, control measures, and behaviors before and after health education were 22 versus 29 (χ2=5.415,P=0.043), 17 versus 25 (χ2=4.724, P=0.030), and 14 versus 23 (χ2=5.429, P=0.020), respectively, all showing statistically significant increases after health education except for knowledge about control measures. Before health education, the rodent capture rates (three times) in Shangcheng village were 3.00%, 2.22%, and 2.52%, respectively, while the capture rates in Chanlin village were 1.72%, 2.16%, and 2.45%, respectively, with no statistically significant difference between the two villages (χ2=0.344, P=0.557). The capture rates in Shangcheng village (0.41%, 2.12%, and 0.85%, respectively) after health education, and those in Chanlin village (2.09%, 1.82%, and 3.93%, respectively) at the same time showed a statistically significant difference (χ2=4.409,P=0.036). The capture rate of Shangcheng village was statistically decreased by 56.37% after health education (χ2=4.139, P=0.048), while no statistically significant change was observed in that of Chanlin village at the same time (χ2=0.384, P=0.599). Rodents' average daily bait consumption peaked in mid-April and mid-November, and generally, it was higher in Shangcheng village than in Chanlin village. Conclusion Chemical control combined with health education is more effective for rodent control than chemical control alone in rural areas.