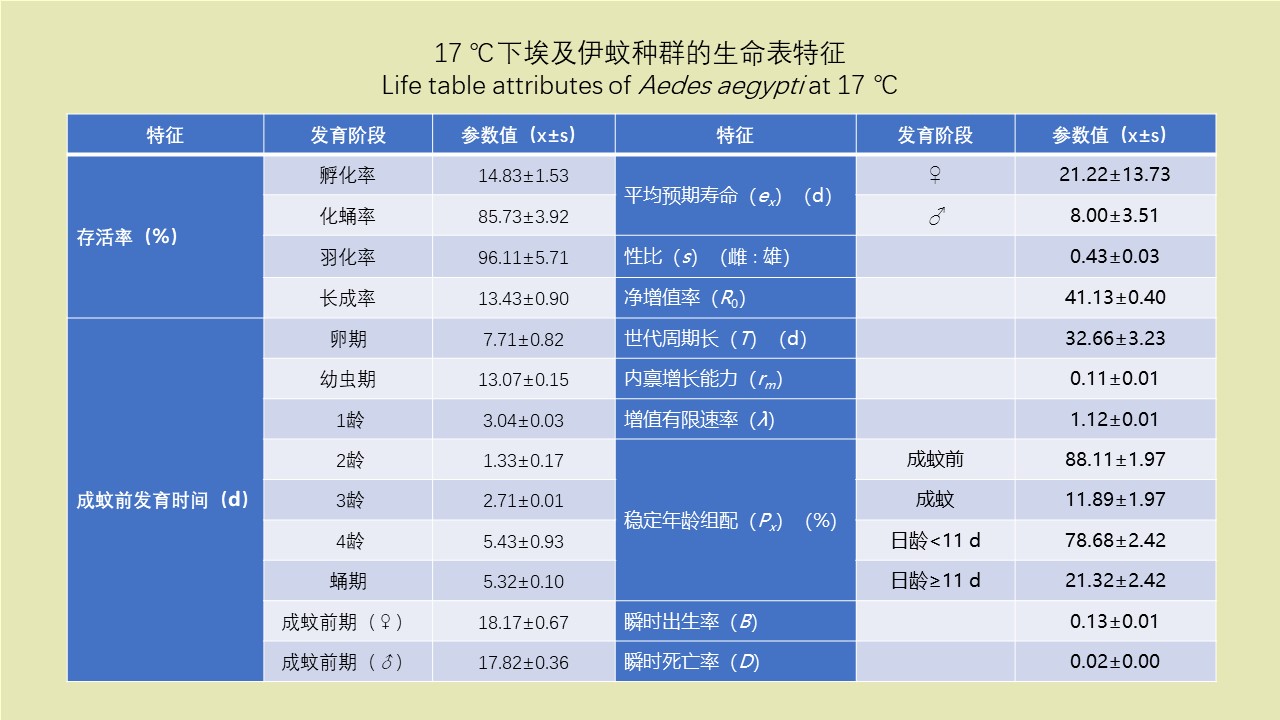
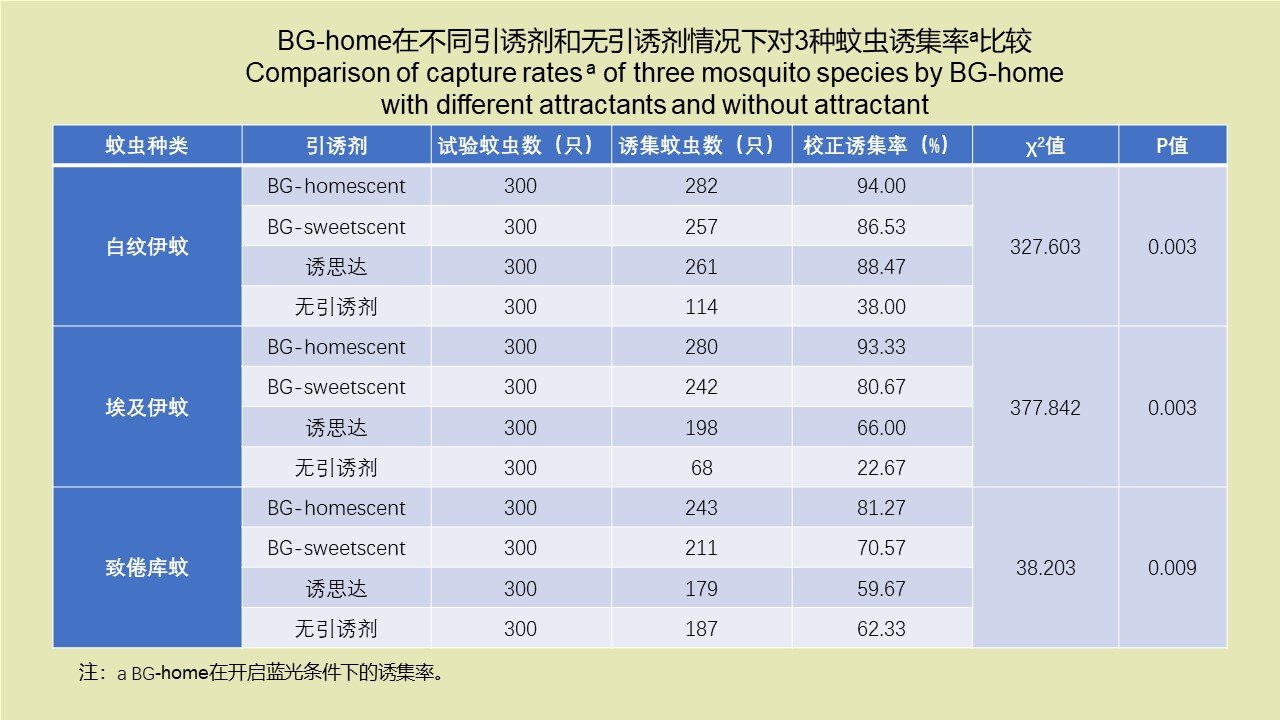
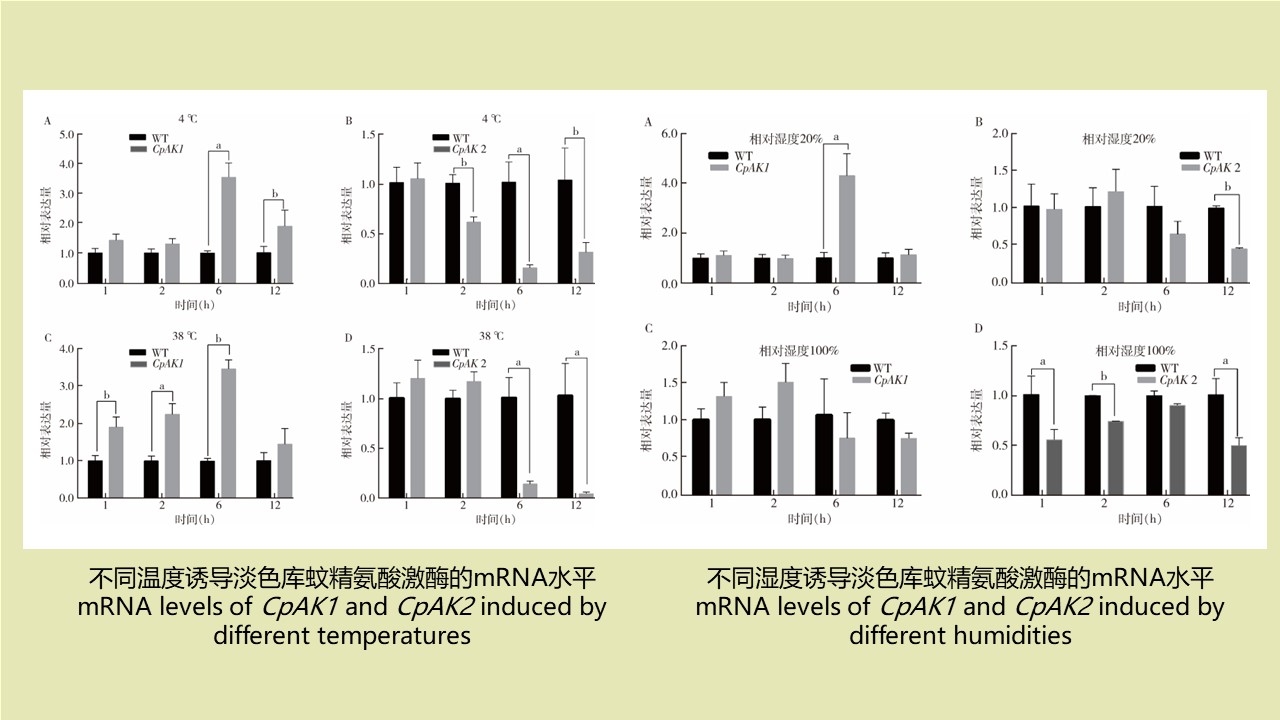
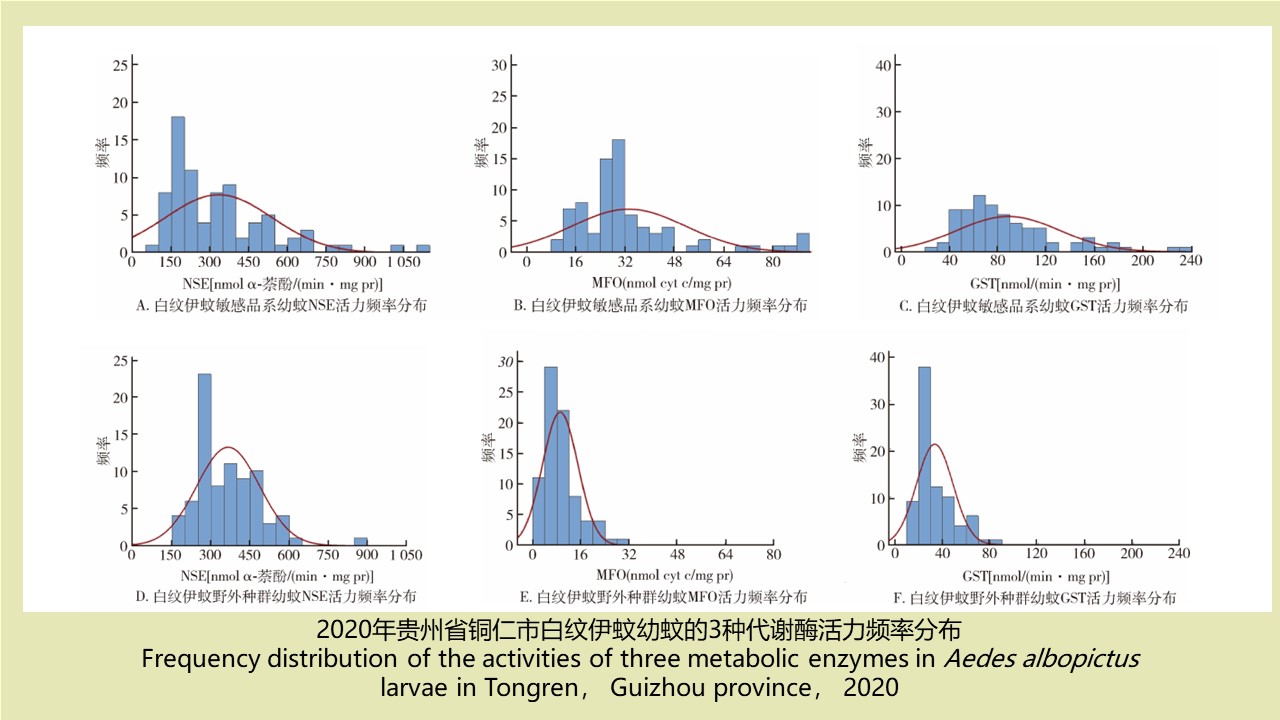
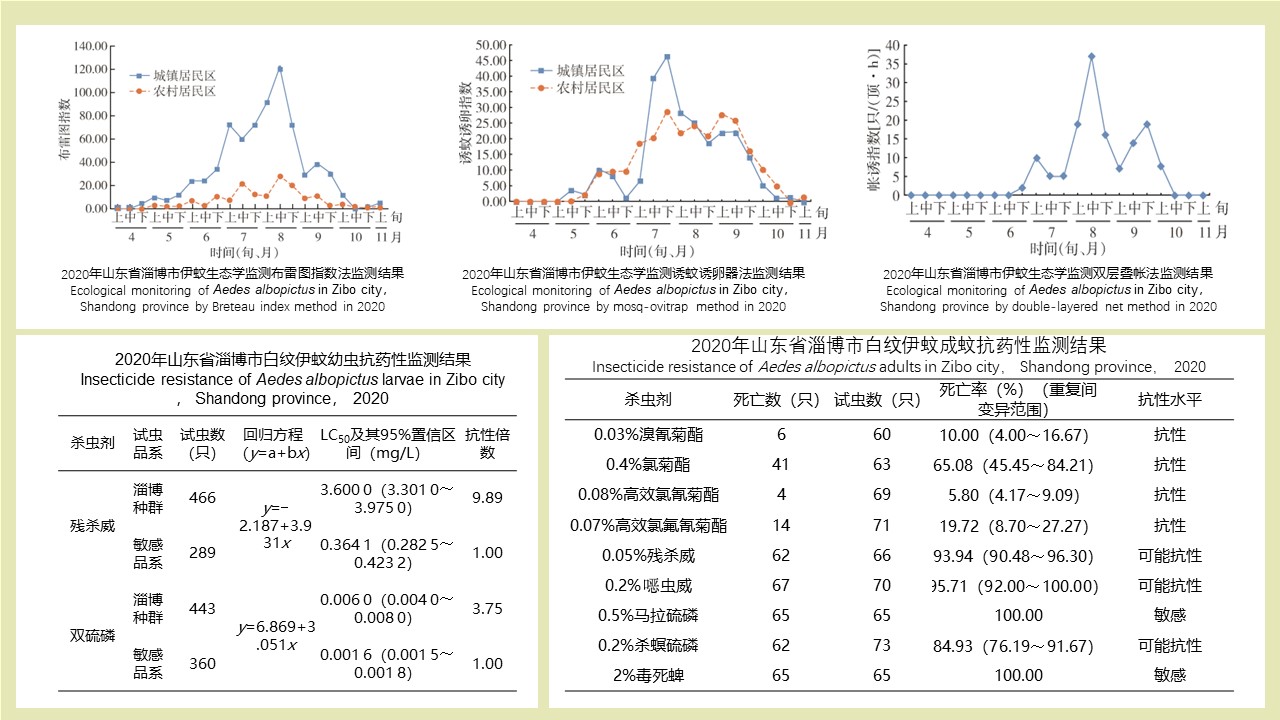
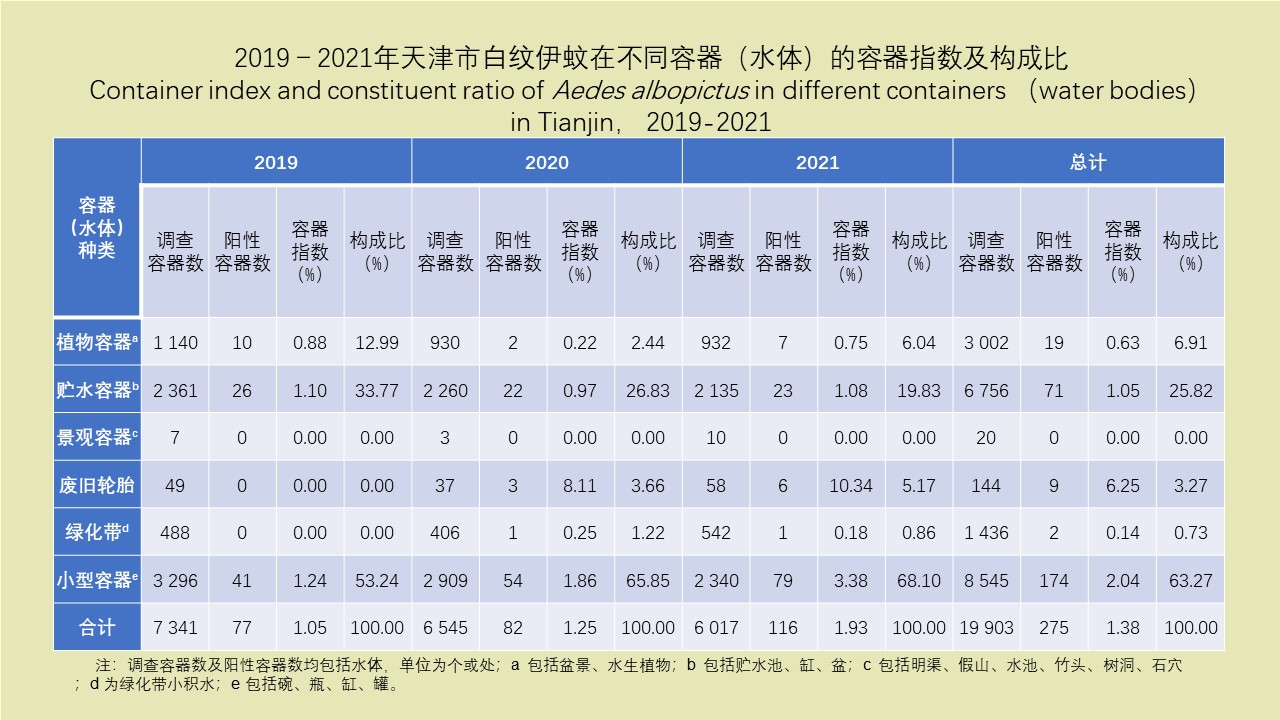
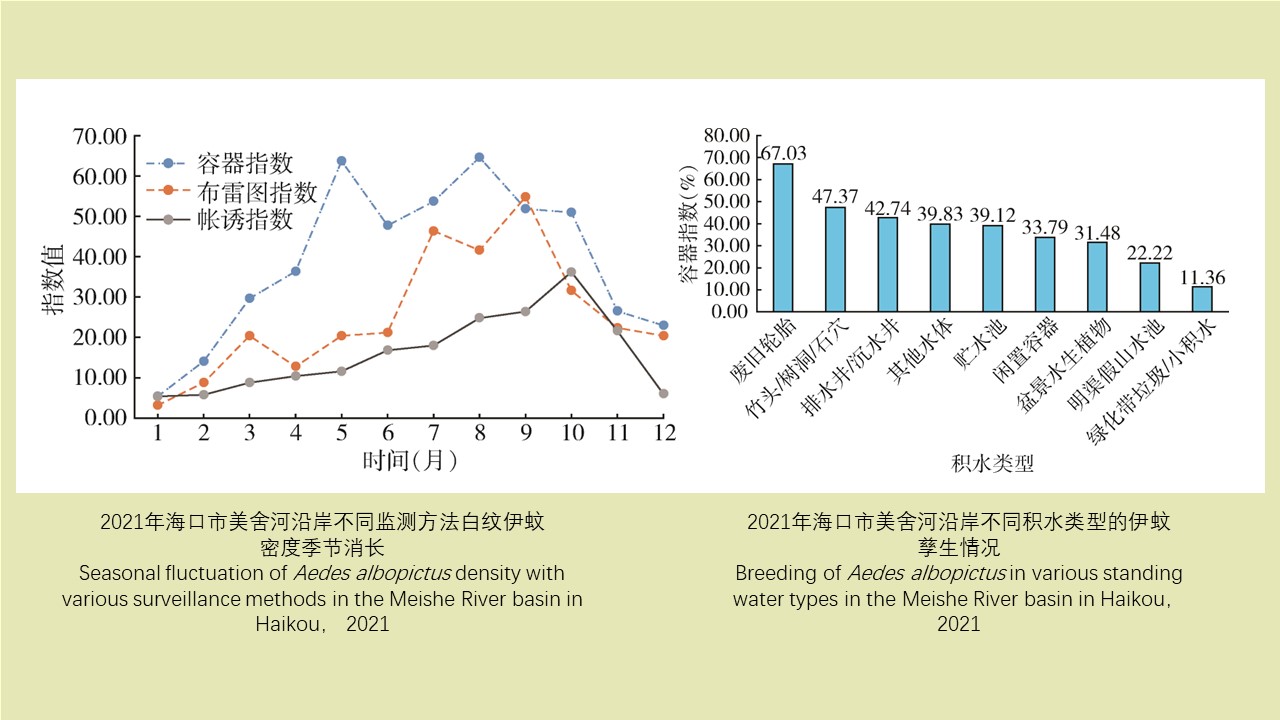
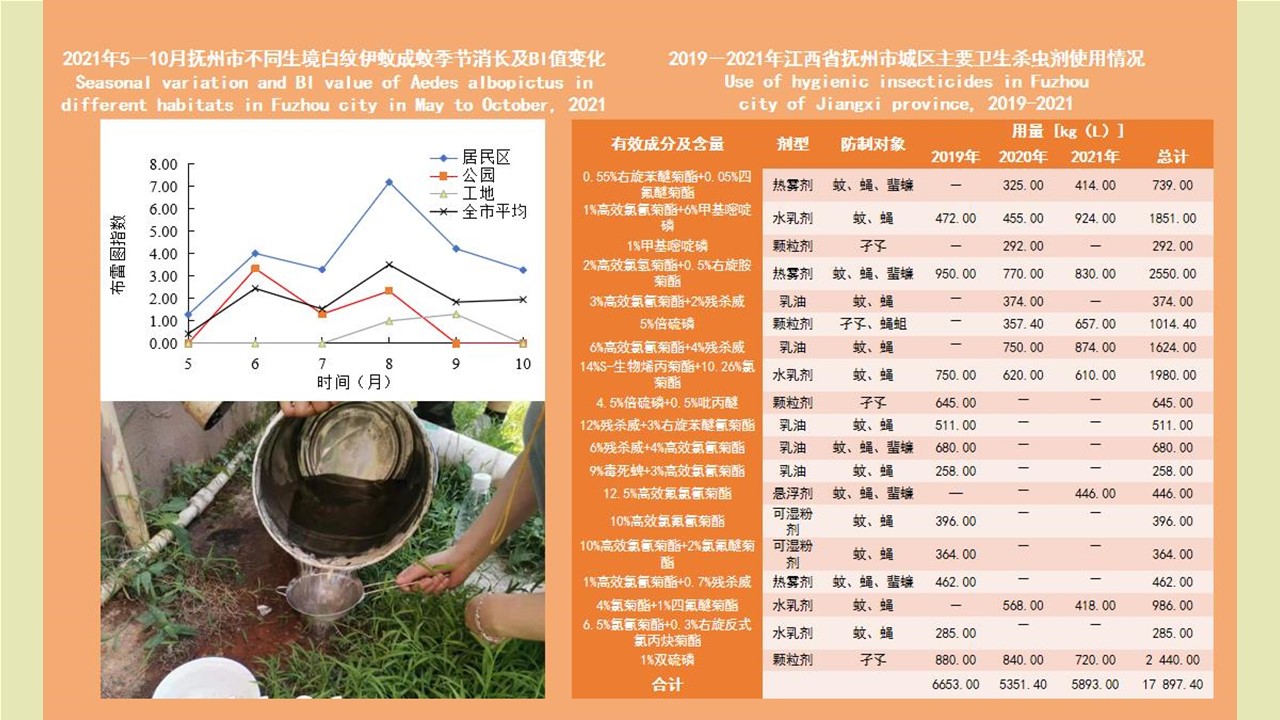
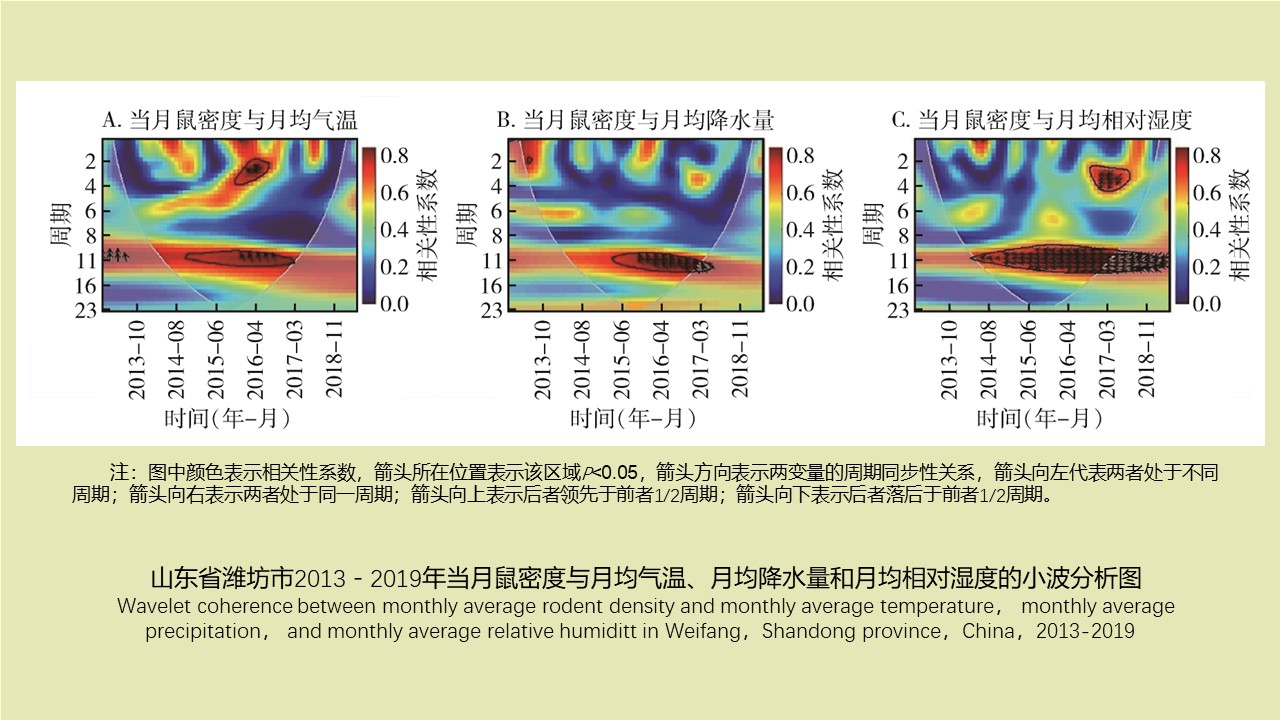
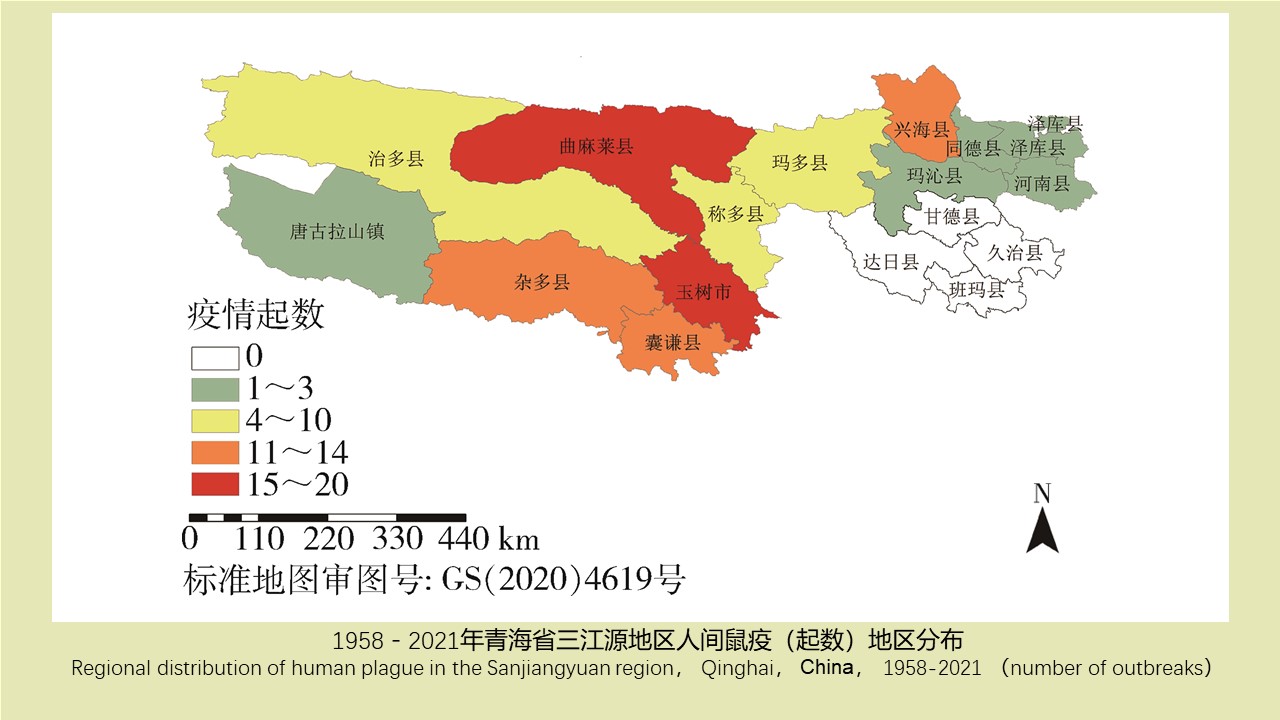
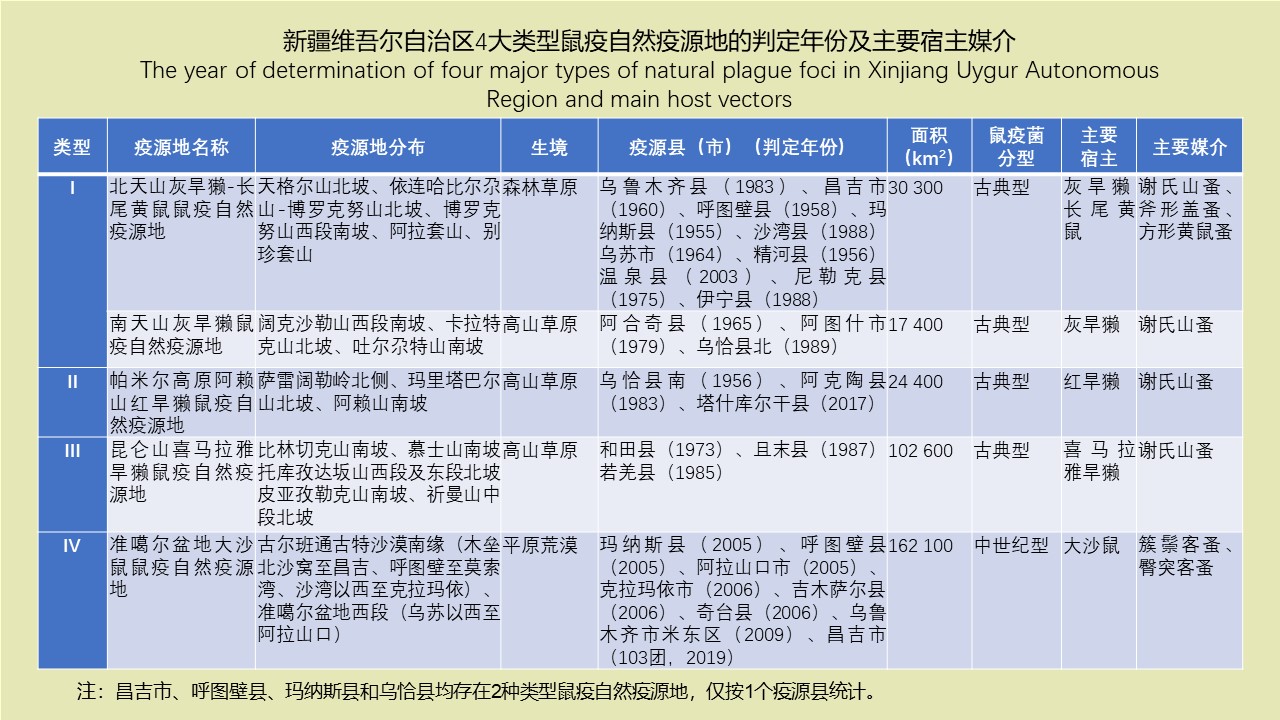
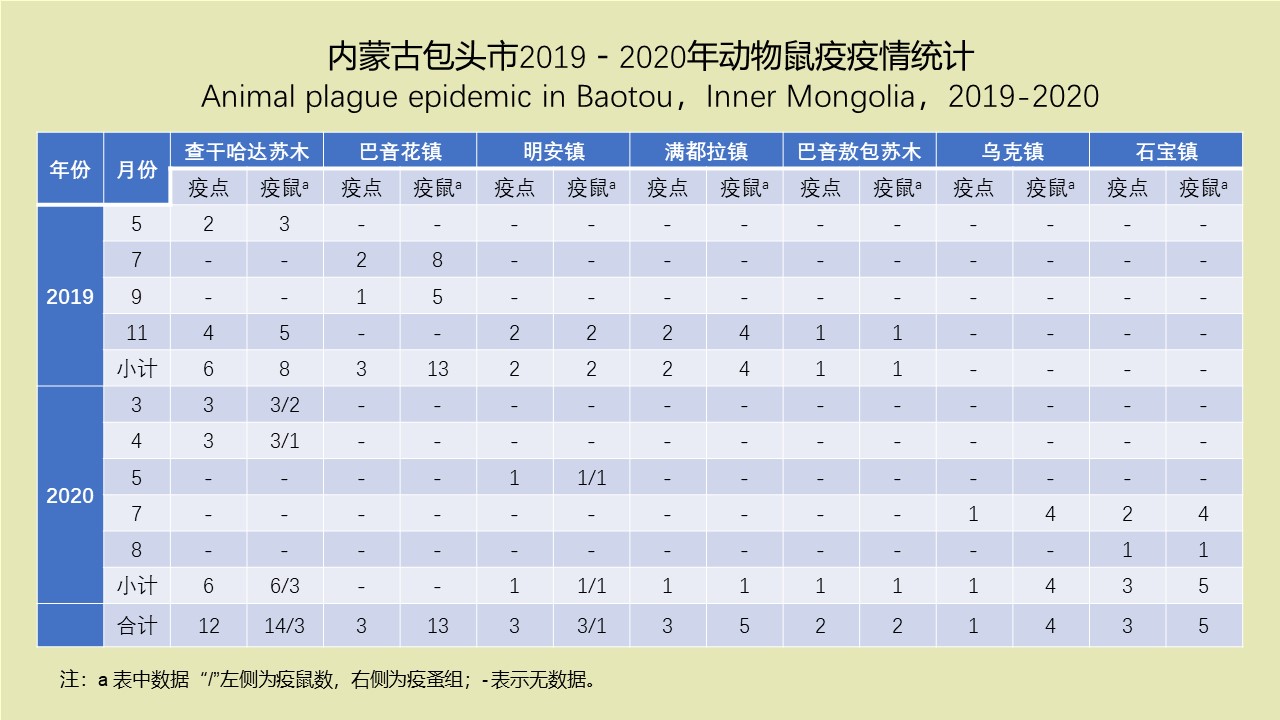
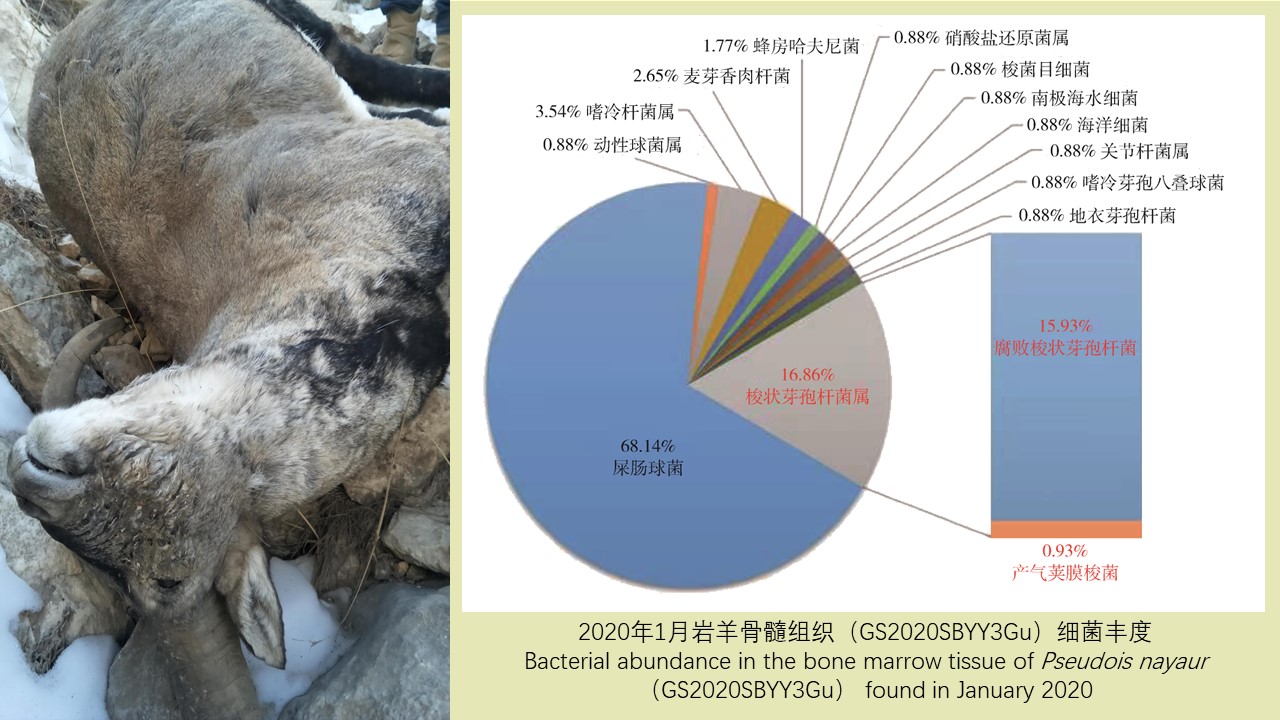
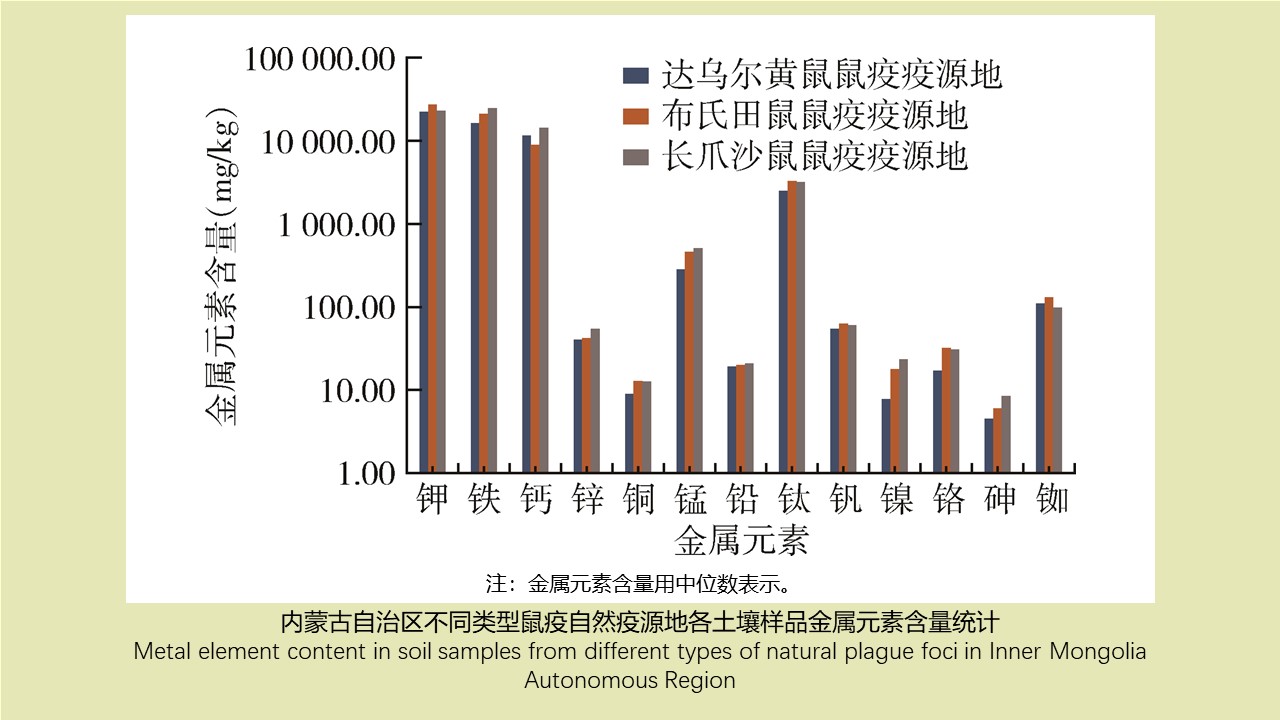
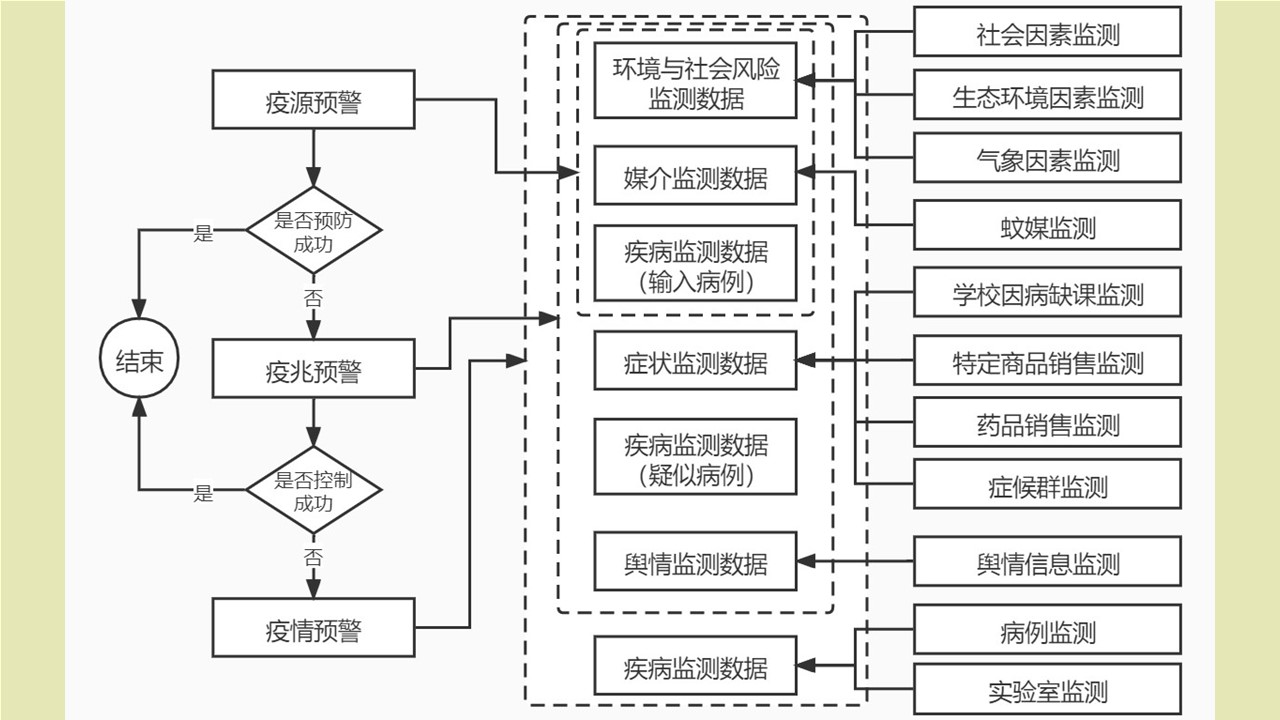
LI Zhi-tao, LIU De-xing, CHEN Jian, LI Ting-ting, WEI Xiao-ya, YUE Qiao-yun, GAN Xiang, DING Jin-yan, QIU De-yi, LIU Huan-yu
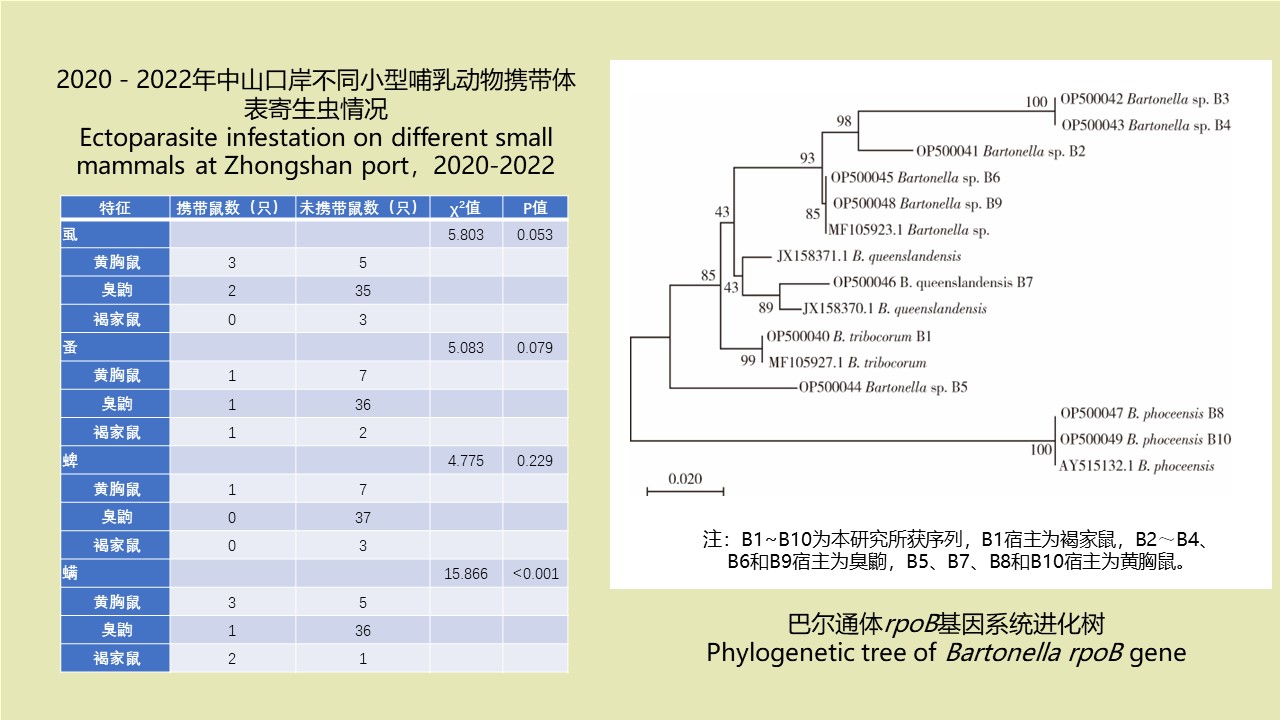
Objective To monitor the small mammal species in the four port areas of Zhongshan port (Zhongshan, Shenwan, Xiaolan, and Huangpu port areas) in China, and to investigate the parasites and natural pathogens carried by the small mammals. Methods From May 2020 to May 2022, small mammals were captured by night trapping with cages in the four port areas of Zhongshan port. Ectoparasites were collected from the small mammals, followed by nucleic acid extraction. The small mammals’ liver, spleen, lung, and kidney were harvested for nucleic acid extraction. The small mammals and ectoparasites were identified using the cytochrome c oxidase subunit Ⅰ gene, with the primers Batl5310/R6036R and LCO1490/HCO2198 for amplification, respectively. According to the standards for small mammal pathogen detection at frontier ports, the captured small mammals were examined for Yersinia pestis, hantavirus, pathogenic Leptospira, Bartonella, and Francisella tularensis. The Chi-square test was used to analyze the distribution of small mammals in the four port areas and the status of ectoparasite infestation and natural pathogen infection. Results A total of 1 630 trap-times were set in the four port areas of Zhongshan port, and 48 small mammals were captured. The average density was 2.94%. Five small mammals were caught in Zhongshan port area, 24 in Shenwan port area, 7 in Xiaolan port area, and 12 in Huangpu port area, with average densities of 1.23%, 5.88%, 1.73%, and 2.93%, respectively. A total of 34 ectoparasites were obtained, including 17 sucking lice, 12 mites, 4 fleas, and 1 tick. The small mammals’ louse, mite, flea, and tick infestation rates were 10.42%, 12.50%, 6.25%, and 2.08%, respectively. There were no significant difference in the four kinds of ectoparasite infestation rates of small mammals among the four ports (all P>0.05). Ten small mammals of three species were positive for Bartonella, with an overall positive rate of 20.83%; the positive rate was 50.00% in Huangpu port area, 16.67% in Shenwan port area, and zero in Zhongshan and Xiaolan port areas; 4, 1 and 5 mice were detected positive for Bartonella from 8 Rattus tanezumi, 3 R. norvegicus, and 37 Suncus murinus, respectively. Four Bartonella sequences were identified as B. tribocorum, B. queenslandensis, and B. phoceensis. The species of six sequences could not be determined. The strength of correlation (r) between small mammal species and Bartonella species was 0.765. All the captured small mammals were negative for Y. pestis, hantavirus, F. tularensis, and pathogenic Leptospira. Conclusion The density of small mammals at Zhongshan port is relatively high. The small mammals in all the port areas have ectoparasite infestation. The small mammals in two port areas are positive for Bartonella, with high infection rates. Sanitation management and small mammal-borne disease control should be strengthened.