YANG Xin-yan, LI Hui-hui, LIN Yi, ZHONG Wen-bing, CAI Fang, LIN Chun-yan
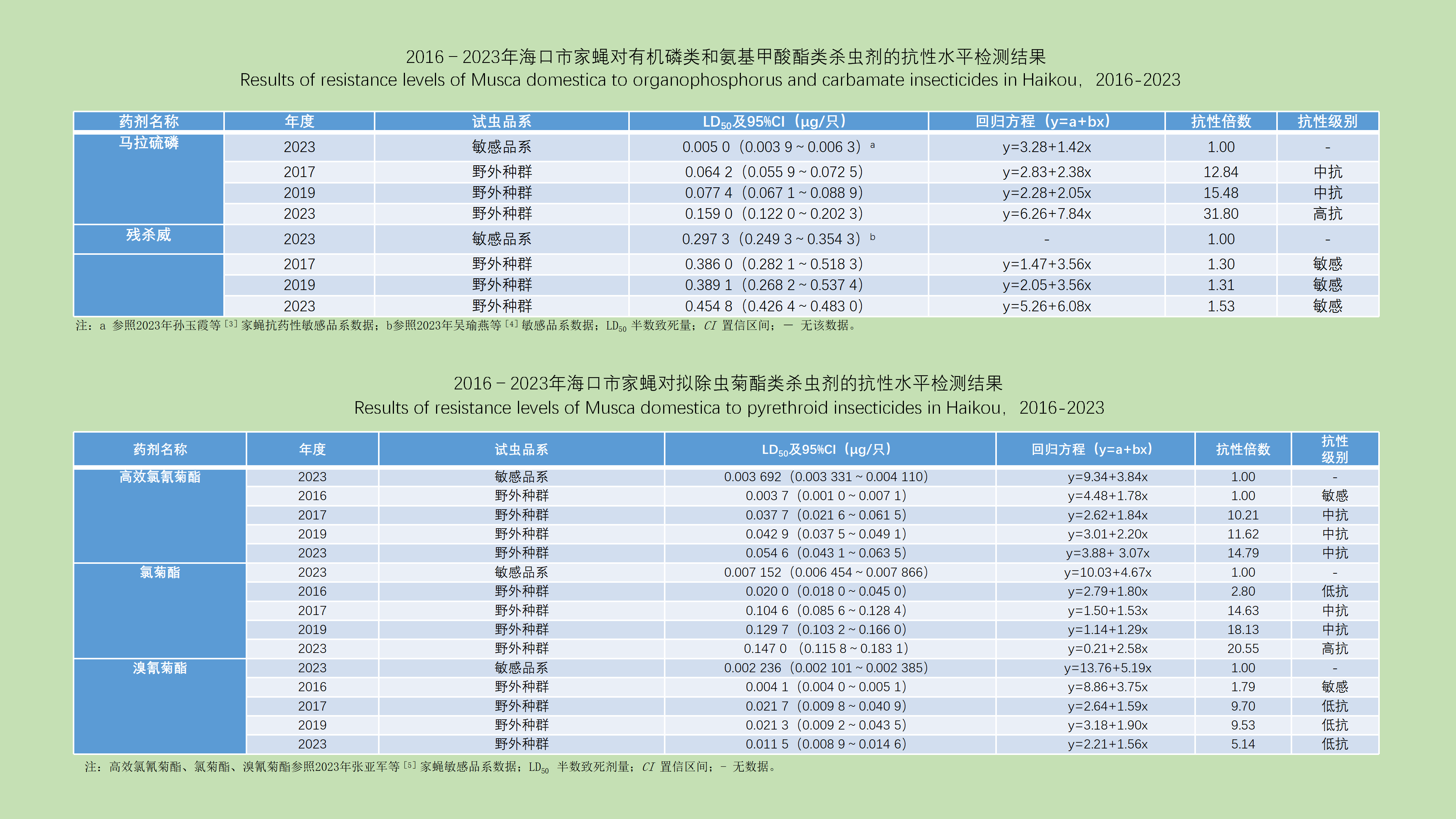
Objectives To investigate the resistance tendency of Musca domestica to several commonly used hygienic insecticides in Haikou, Hainan Province, China, so as to provide a basis for the scientific use and standardized guidance of hygienic insecticides use. Methods M. domestica were collected in four habitats of farmers' market, external environment of restaurants, park and public green belt, and urban residential area in Haikou. The topical application method was used to determine the resistance levels of M. domestica to five commonly used hygienic insecticides in pyrethroids, organophosphates, and carbamates. A Probit regresion analysis was performed using SPSS 26.0 software to calculate the median lethal dose (LD50), regression equation, 95% confidence interval, and resistance ratio. Results In 2017, 2019, and 2023, the LD50 values of malathion for field M. domestica populations were 0.064 2, 0.077 4, and 0.159 0 μg/inds, and the resistance ratios were 12.84, 15.48, and 31.80, respectively, showing an increasing trend in the resistance level year by year; the LD50 values of propoxur were 0.386 0, 0.389 1, and 0.454 8 μg/inds, and the resistance ratios were 1.30, 1.31, and 1.53, respectively, showing that the resistance level continued to remain sensitive. In 2016, 2017, 2019, and 2023, the LD50 values of beta-cypermethrin for M. domestica were 0.003 7, 0.037 7, 0.042 9, and 0.054 6 μg/inds, and the resistance ratios were 1.00, 10.21, 11.62, and 14.79, respectively; the LD50 values of permethrin were 0.020 0, 0.104 6, 0.129 7, and 0.147 0 μg/inds, and the resistance ratios were 2.80, 14.63, 18.13, and 20.55, respectively. The resistance levels to beta-cypermethrin and permethrin showed an increasing trend year by year; the LD50 values of deltamethrin were 0.004 1, 0.021 7, 0.021 3, and 0.011 5 μg/inds, and the resistance ratios were 1.79, 9.70, 9.53, and 5.14, respectively, showing a trend of first rising and then falling. Conclusions From 2016 to 2023, M. domestica in Haikou developed different resistance tendency to four hygienic insecticides including malathion, beta-cypermethrim, permethrin and deltamethrin, except propoxur to which the resistance level remained sensitive. Appropriate hygienic insecticides should be selected according to the resistance of M. domestica in the control process.