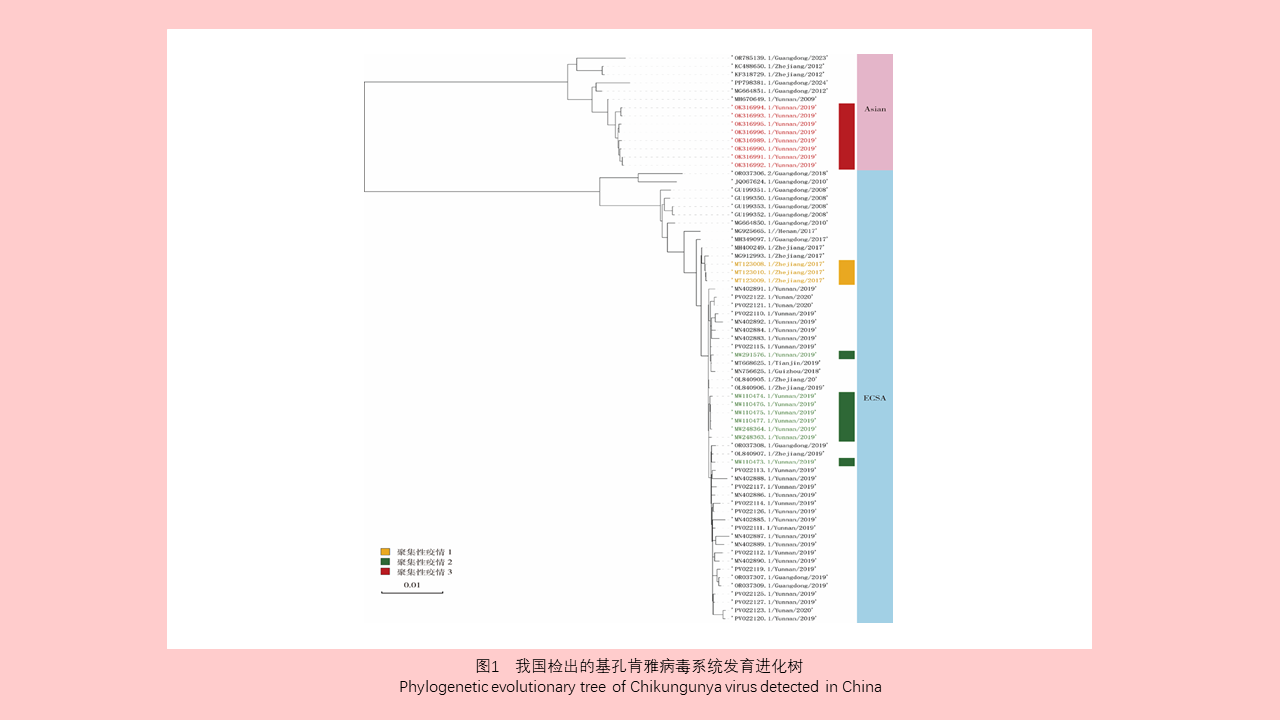
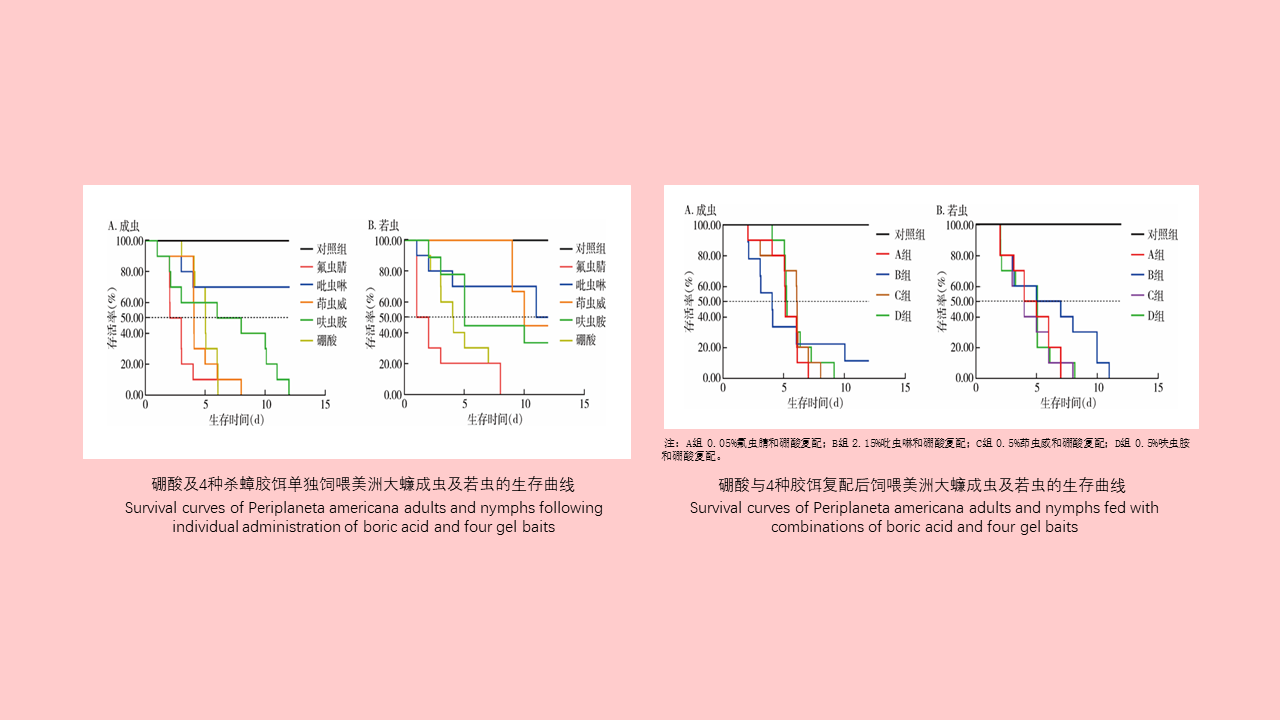
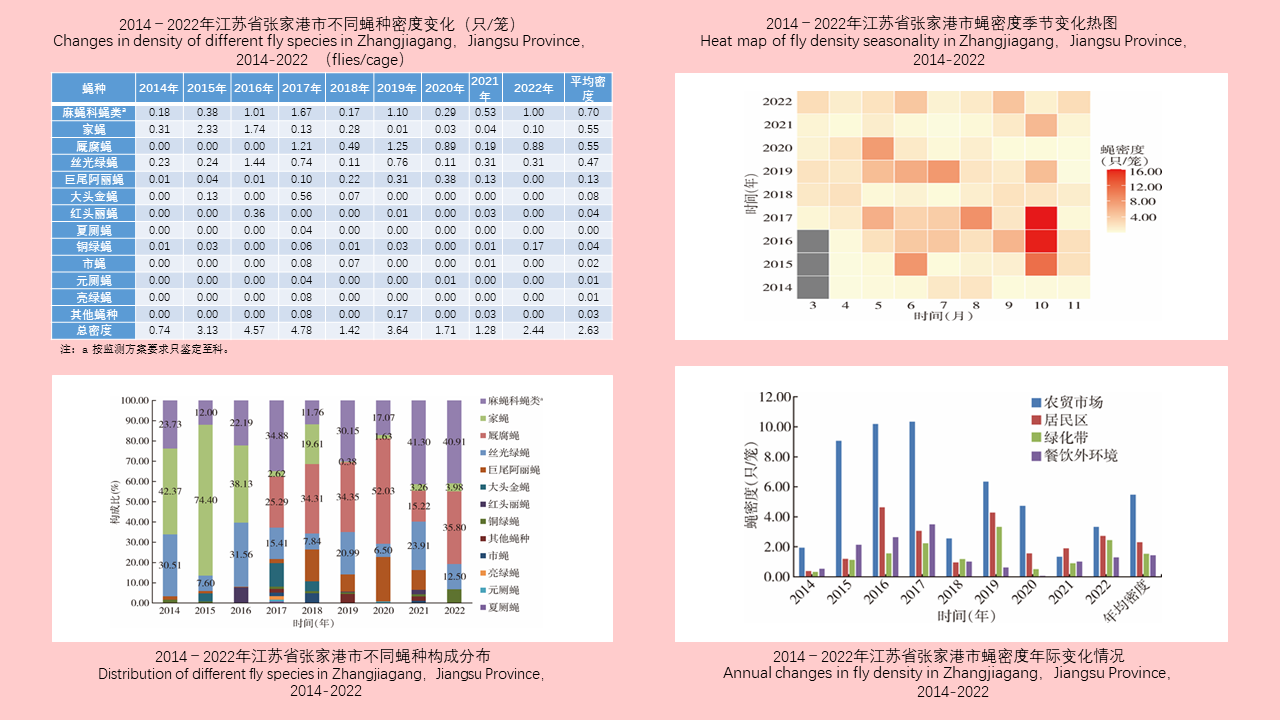
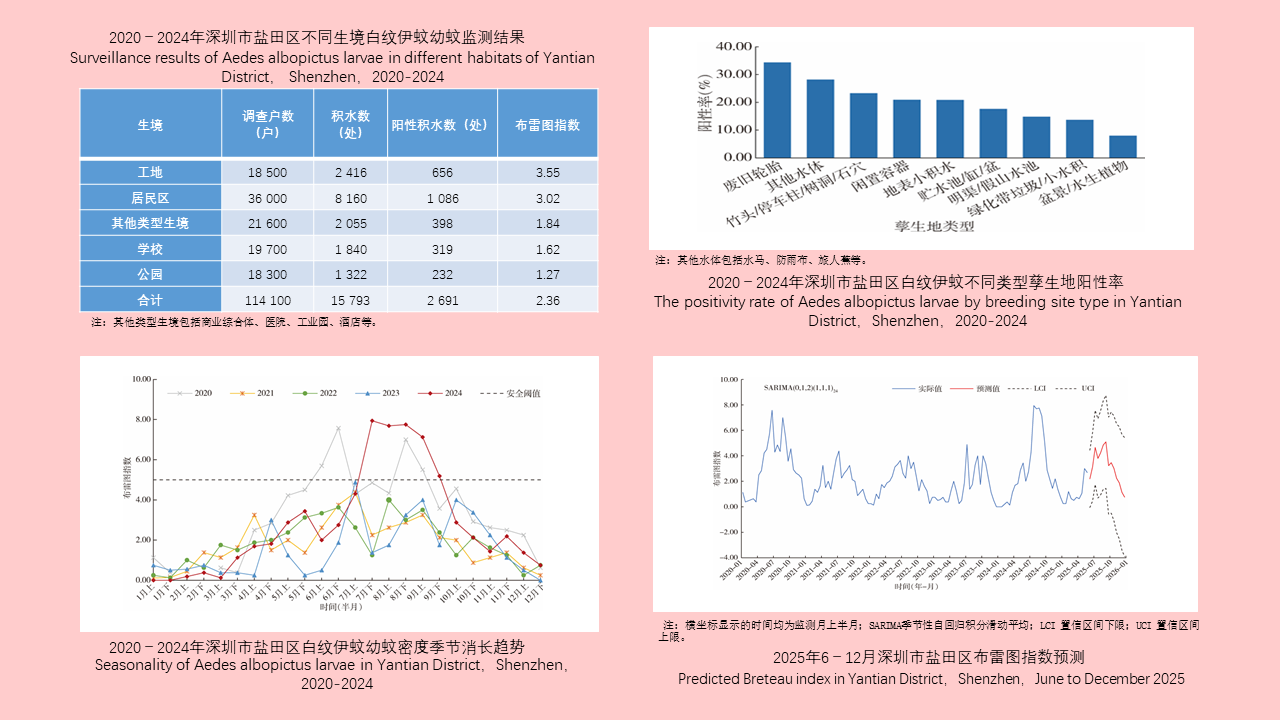
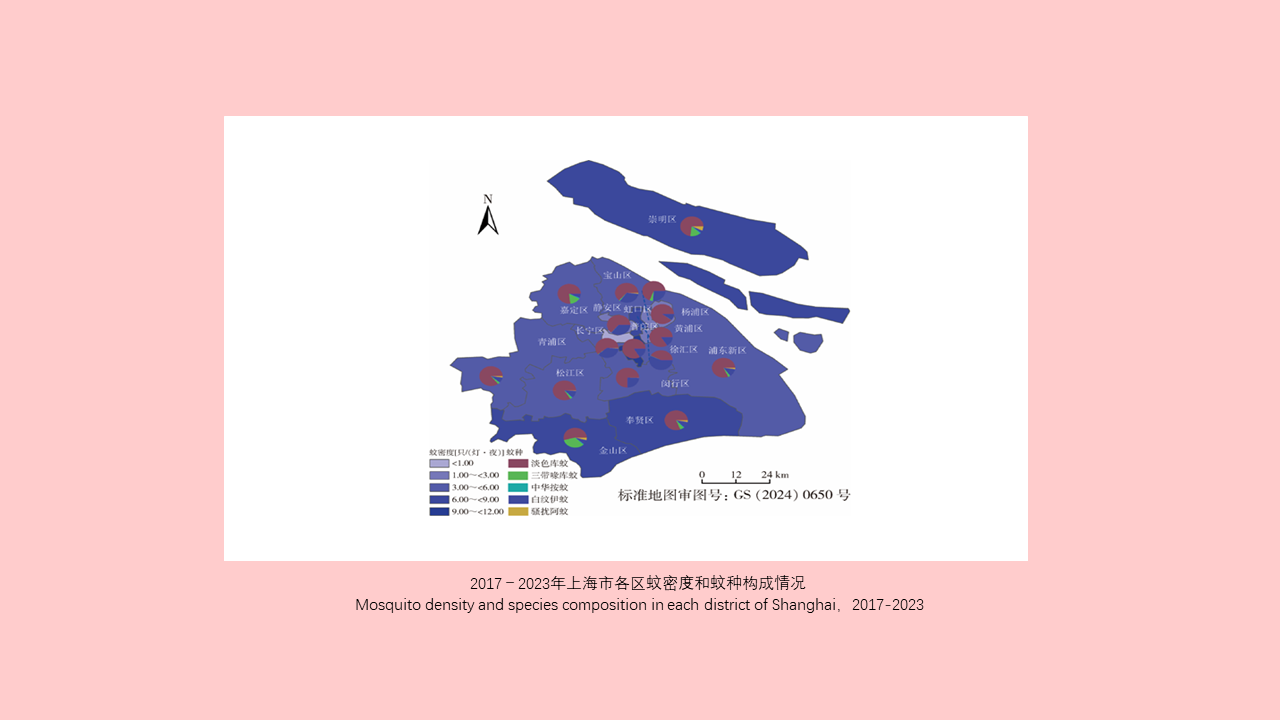
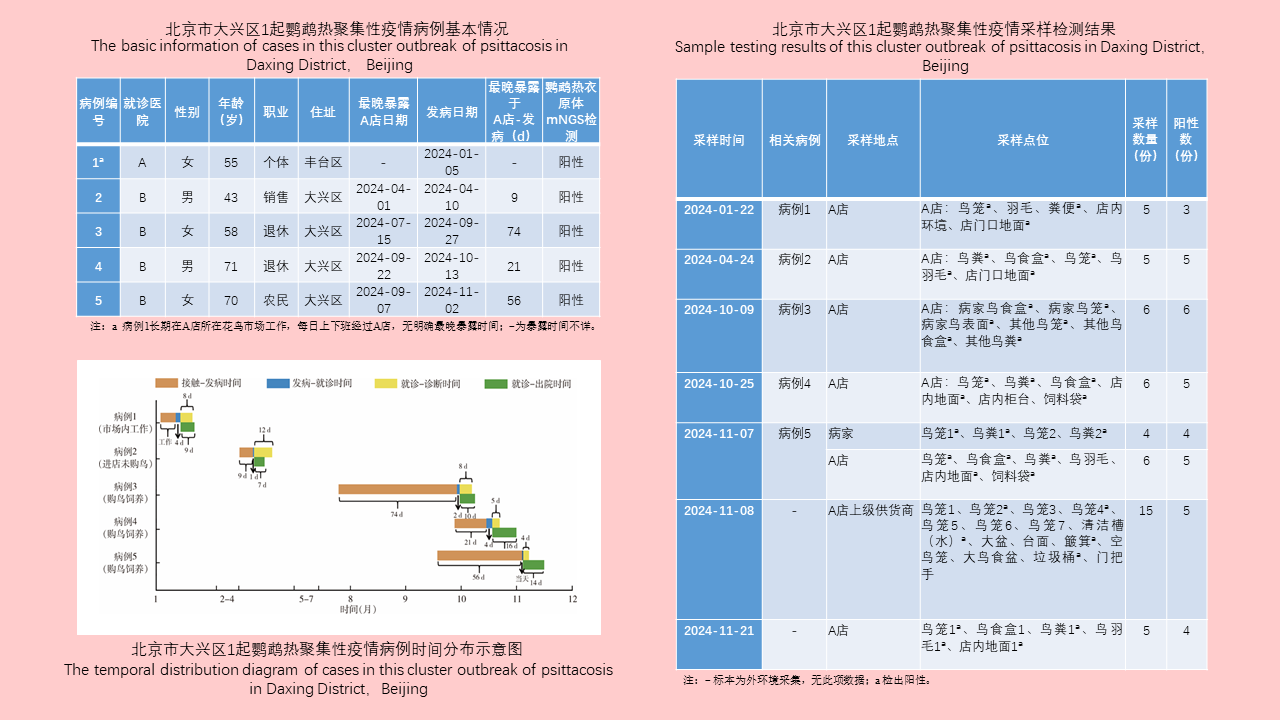
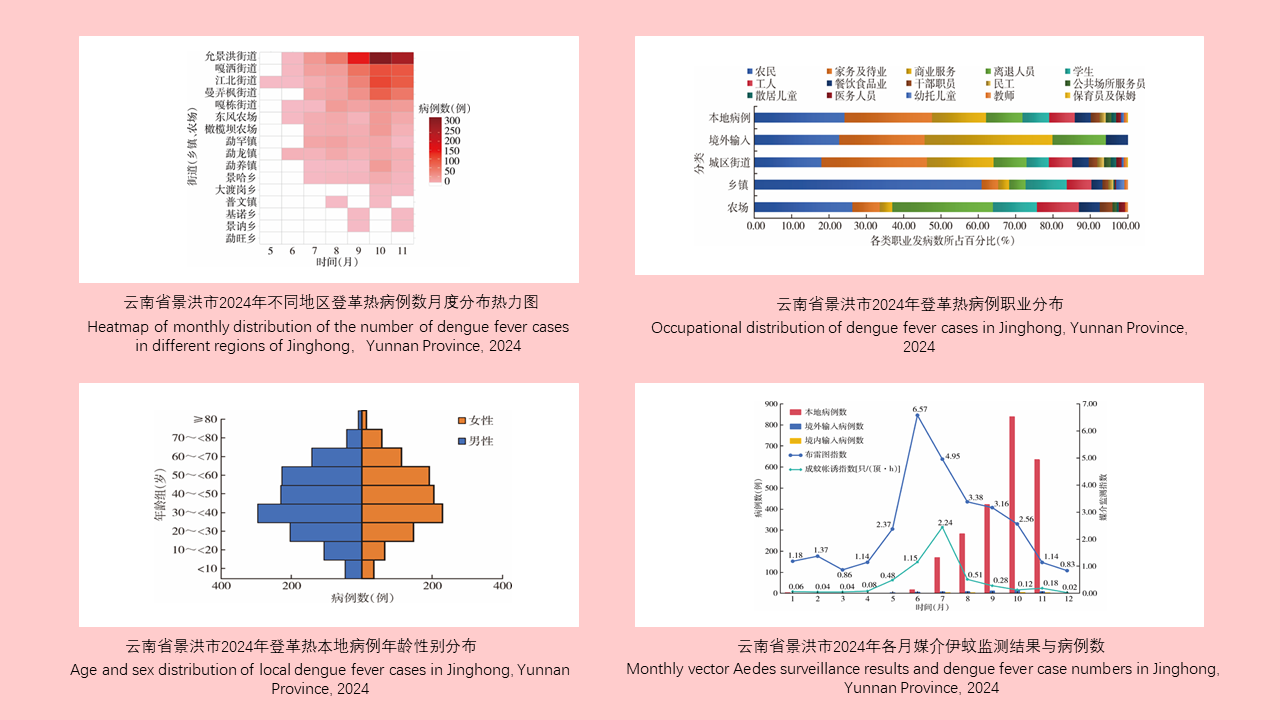
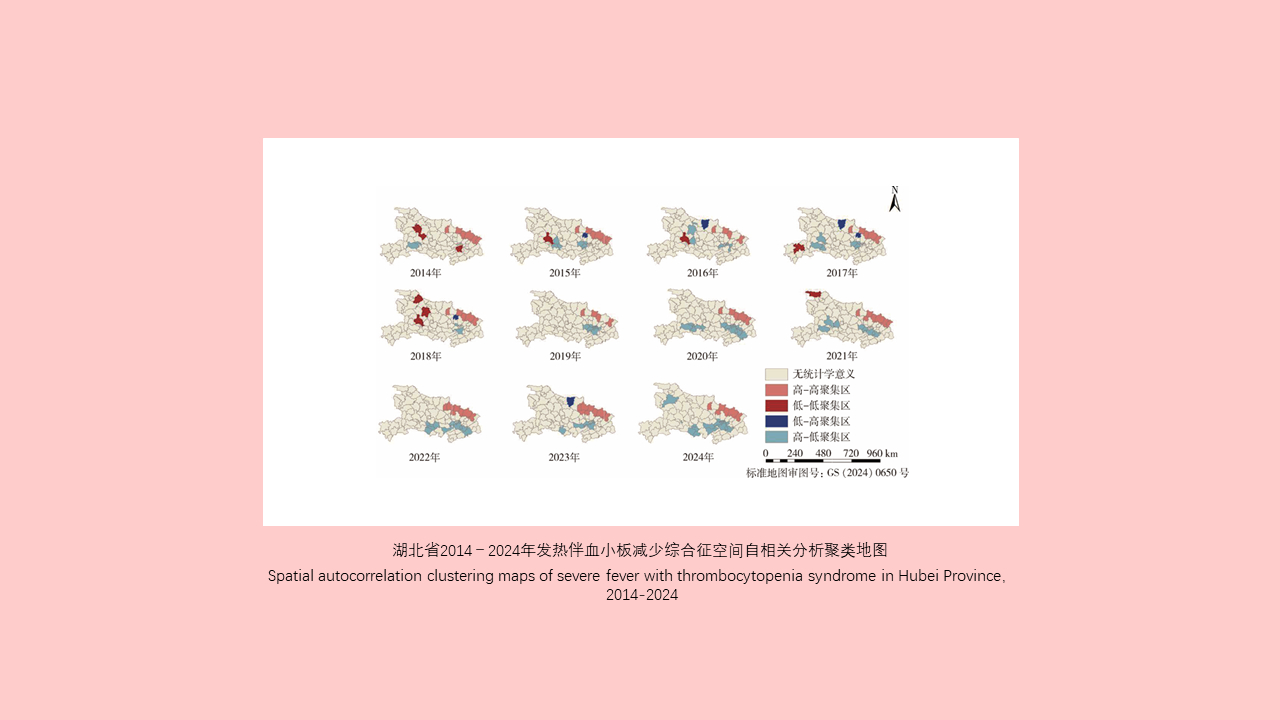
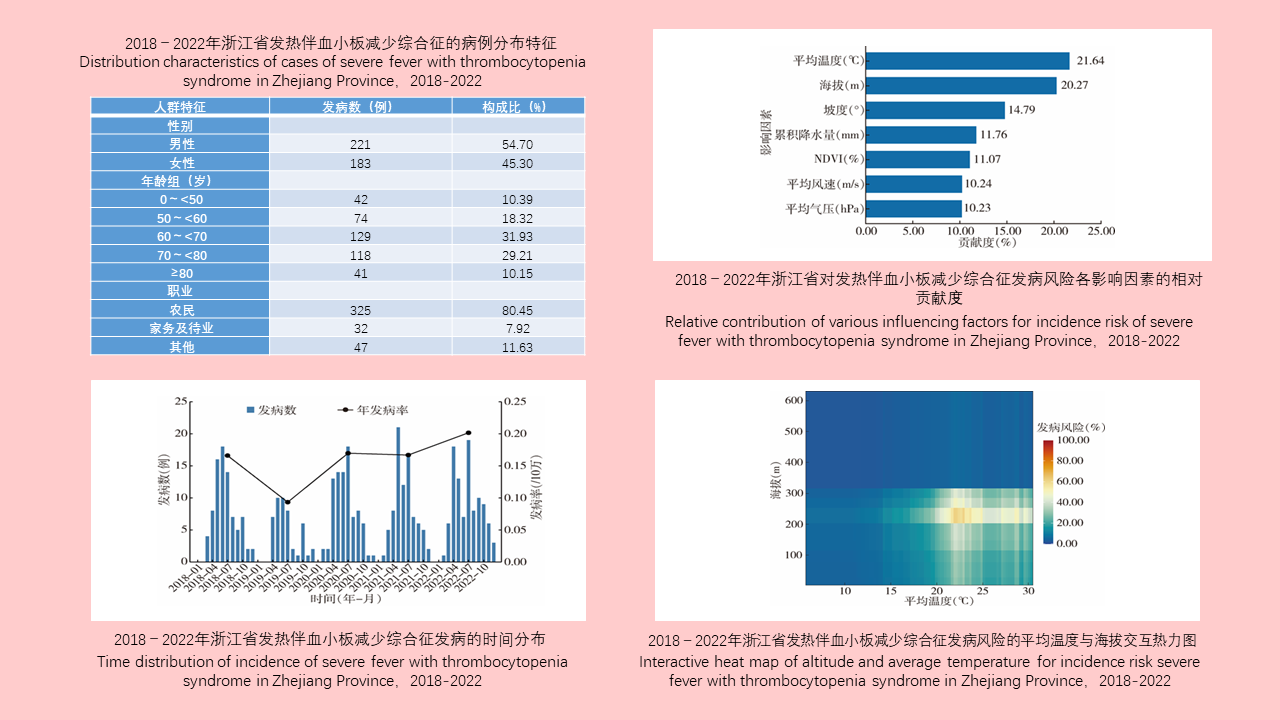
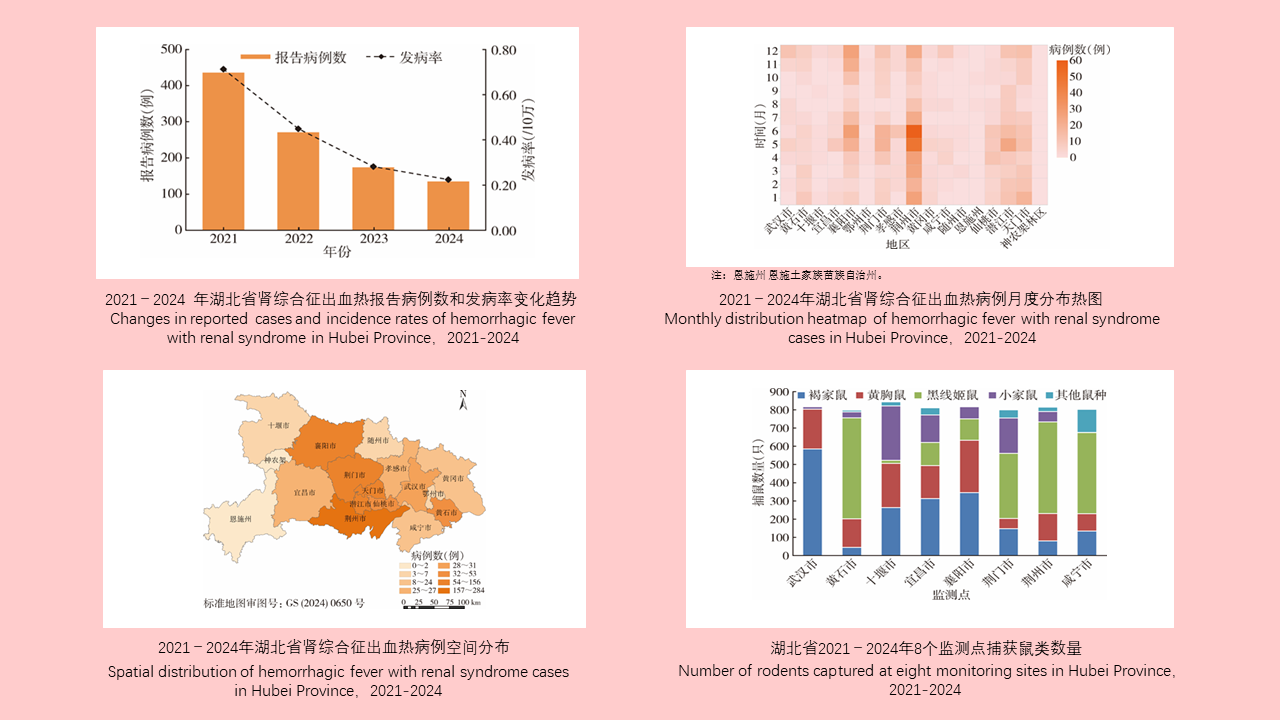
Lei BAO, Yuan-yuan LI, Hai-yan LI, Han-lao YU, Li-tao Tan
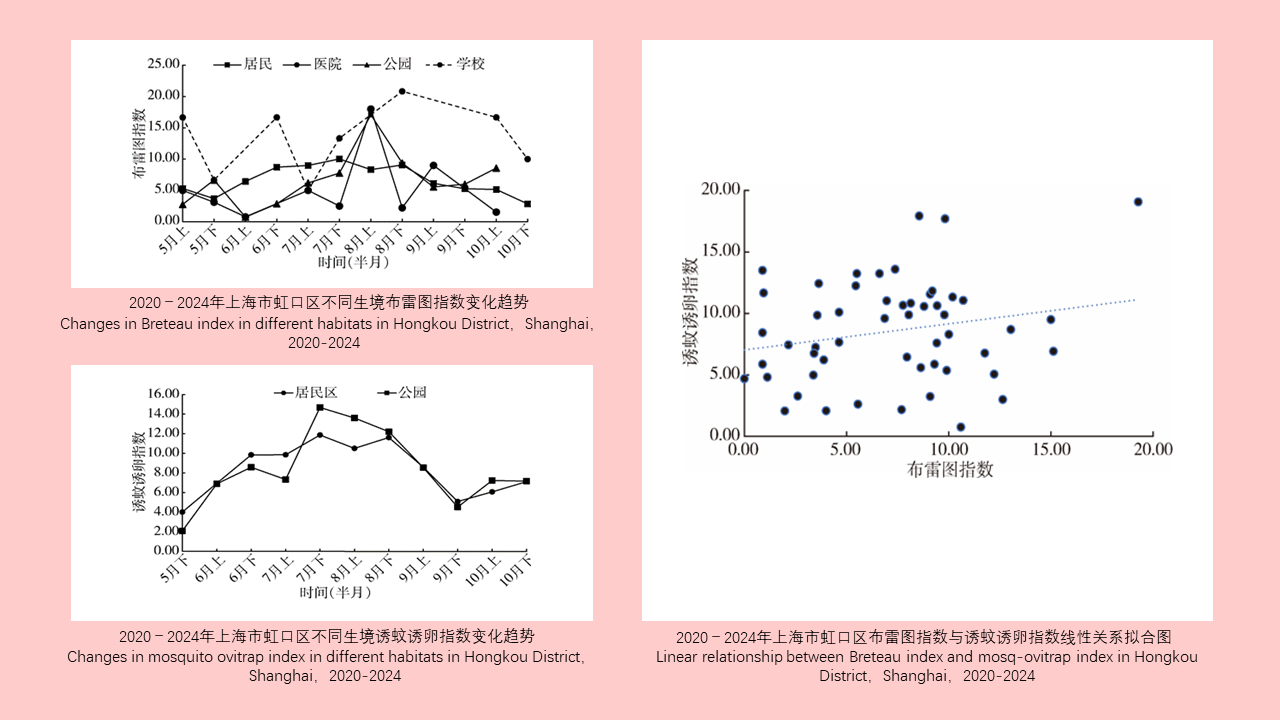
Objective: To investigate the epidemiological characteristics and influencing factors of dengue fever in Jinghong, Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture, Yunnan Province, China in 2024, so as to provide a reference for the formulation of local dengue fever prevention and control measures. Methods: Descriptive epidemiological methods were used to analyze dengue fever epidemic data of Jinhong collected through the China Disease Prevention and Control Information System as well as epidemiological case investigation reports and vector surveillance data. The Mann-Whitney U test was employed to compare the distribution of two independent samples. The Kruskal-Wallis H test was used to compare the medians of multiple independent samples. The Chi-square test was used to compare categorical data. Spearman's rank correlation test was applied to analyze the correlation between non-normally distributed measurement data. Results: In 2024, Jinghong reported a total of 2 417 dengue fever cases, with an incidence rate of 360.82 per 100 000. Among these, there were 2 361 local cases, 48 cases imported from overseas, and 8 domestically transmitted cases. The peak period for case reporting was from August to November, with a total of 2 218 cases reported, accounting for 91.77% (2 218/2 417) of the total number. The number of local cases was positively correlated with the numbers of overseas-imported cases (ρ=0.919, P < 0.001) and domestically transmitted cases (ρ=0.778, P=0.003). Five sub-districts in the main urban area reported the highest number of cases (1 923, 79.56%). A positive correlation was observed between population density and the incidence rate of local cases (ρ=0.879, P < 0.001). The male-to-female ratio of the cases was 1.26∶1, with a statistically significant difference of incidence between the sexes (χ2=9.533, P=0.002). The sex ratio was 1.24∶1 for local cases and 3.00∶1 for overseas-imported cases, showing a statistically significant difference of the sex ratio of cases between different sources (χ2=7.388, P=0.007). The age of the cases was concentrated in 20 to < 60 years, with a median age [M(P25, P75)] of 41 (29.0, 54.0) years. The top three occupations of the cases were farmers (513 cases, 21.22%), homemakers and the unemployed (494 cases, 20.44%), and commercial service workers (310 cases, 12.83%). Occupational distribution differed between urban areas (sub-districts), towns, and farms. There were 174 cluster outbreaks involving 741 people, with a statistically significant difference in the number of cluster outbreaks between sub-districts (towns and farms) (H=26.833, P=0.003). The median time [M (P25, P75)] from onset to diagnosis was 2 (1.3, 2.4) days for local cases and 3 (1.2, 3.9) days for imported cases, with a statistically significant difference (Z=-2.526, P=0.012). In 2024, the average Breteau index in mosquito surveillance was 3.57, and the average net trapping index was 0.88 mosquitoes/(net∙h). A total of 1 341 female Aedes mosquitoes were captured in routine adult mosquito surveillance, including 540 Ae. aegypti mosquitoes (40.27%) and 801 Ae. albopictus mosquitoes (59.73%). Conclusions: The incidence of dengue fever in Jinghong shows apparent seasonality and clustering, which is affected by factors such as imported cases, urban population density, and Aedes mosquito density. It is necessary to continue to strengthen the key components of epidemic containment, improve the joint prevention and control mechanism, fully promote the implementation of community-based prevention and control strategies, and institutionalize regular epidemic management.